Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: 14-3-3η protein may be elevated in the blood of inflammatory arthritis patients. It is a commercially available novel biomarker used to aid in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), in addition to rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP), especially in seronegative patients. 14-3-3η is not routinely checked in all patients with arthritis. We aim to see the positivity rate of the 14-3-3η in real-world patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to other arthritis.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted via review of electronic medical records after approval by the institutional review board. All patients with a result for the lab test of 14-3-3η in the last five years (March 2018 – February 2023) were included. The data, including demographics, arthritis diagnosis, and relevant lab components, were compared.
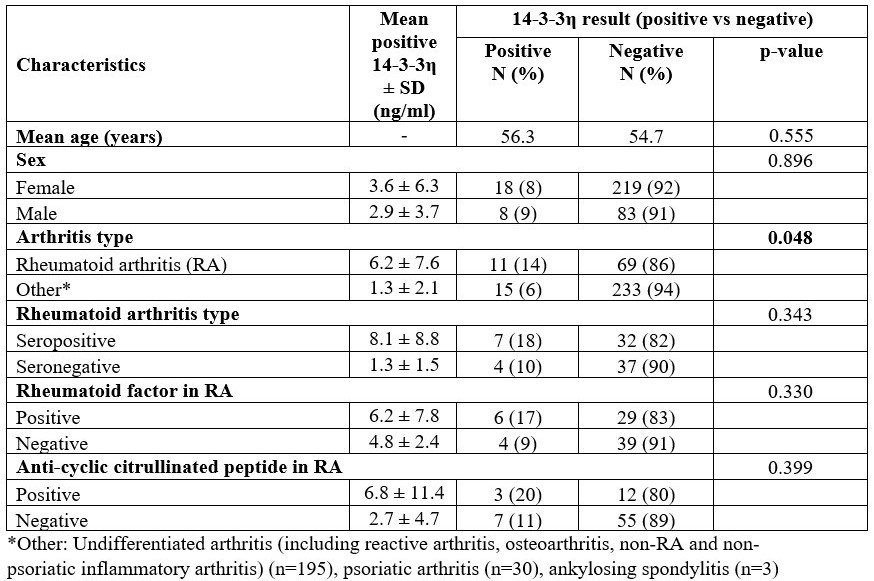
Results: Three hundred and twenty-eight patients were tested for 14-3-3η, with 26 (8%) positive results. The mean age was 55 ± 15 years, with 72% female and 84% white. The characteristics of the patients with positive and negative 14-3-3η results are summarized in Table 1. Eighty patients (24%) with positive results were diagnosed with RA, with 39 patients being seropositive. The positivity rate of 14-3-3η was significantly higher in RA patients than other arthritis (14% vs. 6%, p=0.048). Other diagnoses with positive values included undifferentiated arthritis (n=14) and reactive arthritis (n=1). No patients with psoriatic arthritis had positive values. The mean value for 14-3-3η in RA patients was 6.2 ± 7.6 compared to 1.3 ± 2.1 in non-RA patients (p=0.06; reference range 0.2 ng/ml – >20 ng/ml). In the patients with RA, RF was positive in 44%, anti-CCP positive in 19%, and both were positive in 14%, and antinuclear antibody was positive in 25%. The positivity rate of 14-3-3η was numerically higher in seropositive RA compared to those with seronegative RA (18% vs. 10%, p=0.343). The mean value for 14-3-3η in seropositive RA was 8.1 ± 8.8 compared to 1.3 ± 1.5 in seronegative (p=0.09). Logistic regression showed no association between 14-3-3η positivity with age, sex, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, RF, or anti-CCP in patients with RA.
Conclusion: 14-3-3η protein is positive more often in patients with RA than in other causes of arthritis but is not exclusive to RA. Although 14-3-3η has been thought to increase the sensitivity of diagnosis of seronegative patients, the positivity rate was only 10% in our study. Further studies are needed to better understand its importance in seronegative patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Subedi R, Jimenez Artiles M, Al Najada A, Misbah A, Wang Q, Kusnik A, Tang Z, Zabiullah S, Ocon A. Real-world Positivity of 14-3-3η Protein in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-positivity-of-14-3-3%ce%b7-protein-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-positivity-of-14-3-3%ce%b7-protein-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/