Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a prototypical collagen-vascular disease with prominent vasculopathy. Although microvascular changes are the earliest histopathologic manifestation of SSc, the vascular dysregulation and immune environment of vascular niche in SSc are largely unknown. Here, we applied Imaging Mass Cytometry (IMC) as a spatial proteomic approach to deconvolute the heterogeneity of vascular cells at single-cell level in situ and to characterize cellular alterations of the vascular niches of SSc patients.IMC is a multiplex imaging technique that detects metal isotope-labelled antibodies in tissues using localization-specific laser mediated ablation coupled with mass-spectrometry.
Methods: Skin biopsies collected from 19 SSc patients and 14 matched healthy individuals were analyzed by IMC, yielding a total of90,755 cells including 8,865 vascular cells and 4,096 immune cells. Single cells were clustered according to marker expression, referred back to the tissue, quantified and correlated with clinical disease outcomes. Direct cellular interactions and accumulation of immune cells in the local vascular niches of specific endothelial cell subsets were analyzed.
Results: Our analyses revealed microvascular rarefaction with significant reductions in blood vessels and lymphatic vessels in SSc. However, we showed that increase in the number of apoptotic and proliferating ECs in SSc was restricted to blood vessels and was not observed in lymphatic vessels. We identified seven different subpopulations of blood endothelial cells (BECs), two subpopulations of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) and three subpopulations of pericytes by unsupervised clustering. A novel population of CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BECs was more common in SSc, whereas numbers of endothelial precursor cells (EPCs) were decreased. EPCs displayed significant changes in cellular turnover in SSc patients. The microenvironment of CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BECs, but not of EPCs, was enriched for immune cells and myofibroblasts. Monocytes, CD4+ T cells, dendritic cells (DCs), classically activated macrophages (CAMs), and alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs) were found to be enriched numerically in the niche of CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BECs, but with differential proximity in the inner niche and in the outer niche determined by distance measurement. Consistent with the expression of αSMA as a marker of myofibroblasts, the density of CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BECs was associated with clinical markers of progression of fibrotic remodeling in SSc patients.
Conclusion: We unraveled the heterogeneity of vascular cells in healthy individuals and SSc patients using IMC. We identified CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BECs as a novel EC population that is increased in SSc patients, and is located in close proximity to immune cells and myofibroblasts. CD34+;αSMA+;CD31+ BEC counts were associated with clinical outcomes of progressive fibrotic remodeling, thus providing a novel cellular correlate for the crosstalk of vasculopathy and fibrotic remodeling.
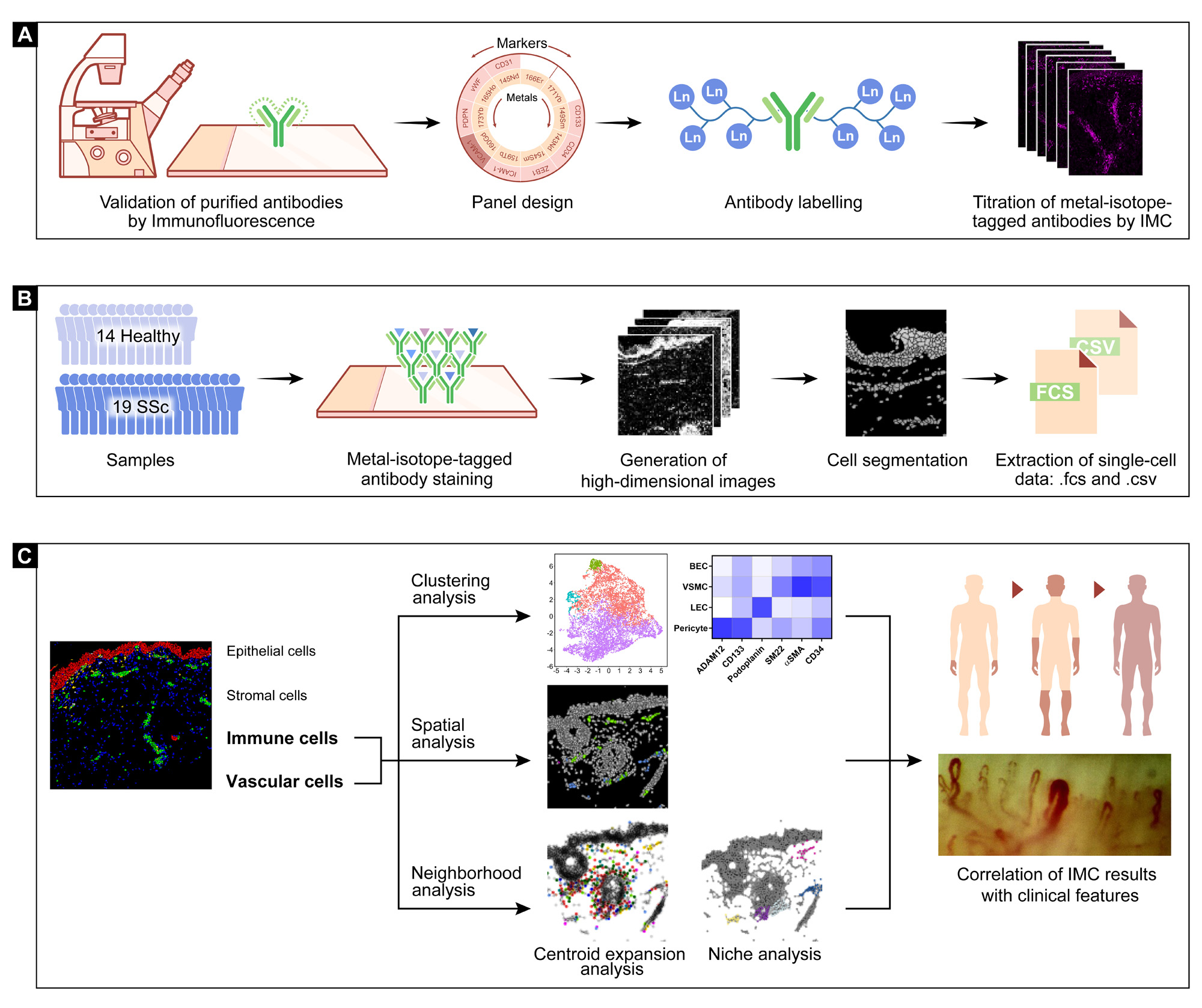
(A) All purified antibodies were first tested by standard immunofluorescence staining. Each antibody was assigned to one channel according to its signal intensity and predicted spillover. After validation by immunofluorescence, the purified antibodies were labeled with lanthanide metal epitopes and further tested at different dilutions by IMC. (B) A total of 33 skin biopsies, 14 healthy controls and 19 SSc patients were stained with a panel of 38 metal-labelled antibodies as well as Iridium 193 and 191 isotopes, and further processed with the Hyperion IMC device. After generation of high-dimensional images and cell segmentation, the single-cell data with spatial information were generated by convertion from 40-channel stacked .tiff to .csv and .fcs files. (C) Major clusters of epithelial cells, vascular cells, immune cells and stromal cells were gated according to the specific cell markers. Populations of interest were selected and clustered using an unsupervised analysis pipeline, which was validated spatially by visualization in segmented map. Centroid expansion analysis and niche analysis were applied to describe neighborhood associations, including direct cell-cell contact and composition of the vascular niche. The above results were compared between healthy subjects and SSc patients and correlated with clinical phenotypes of SSc patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liang M, Rius Rigau A, Li y, Distler J. Characterization of the Vascular Niches in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) as a Prototypical Immune-mediated Fibrotic Disease with Prominent Vasculopathy Using Imaging Mass Cytometry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-the-vascular-niches-in-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-as-a-prototypical-immune-mediated-fibrotic-disease-with-prominent-vasculopathy-using-imaging-mass-cytometry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterization-of-the-vascular-niches-in-systemic-sclerosis-ssc-as-a-prototypical-immune-mediated-fibrotic-disease-with-prominent-vasculopathy-using-imaging-mass-cytometry/