Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1554–1578) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Behcet’s syndrome (BS) is an autoimmune disease characterized by recurrent mucocutaneous ulcerations, vascular and nervous system involvement. While there have been a lot of researches proving that immune cells play a vital role in rheumatic disease, opinions on the effect of different immune cell subsets on BS is inconsistent. Therefore, we performed this real-world study to investigate the changes in the levels of several immune cell subsets in BS, and the correlation between the levels of different immune cell subsets and clinical features in patients with BS.
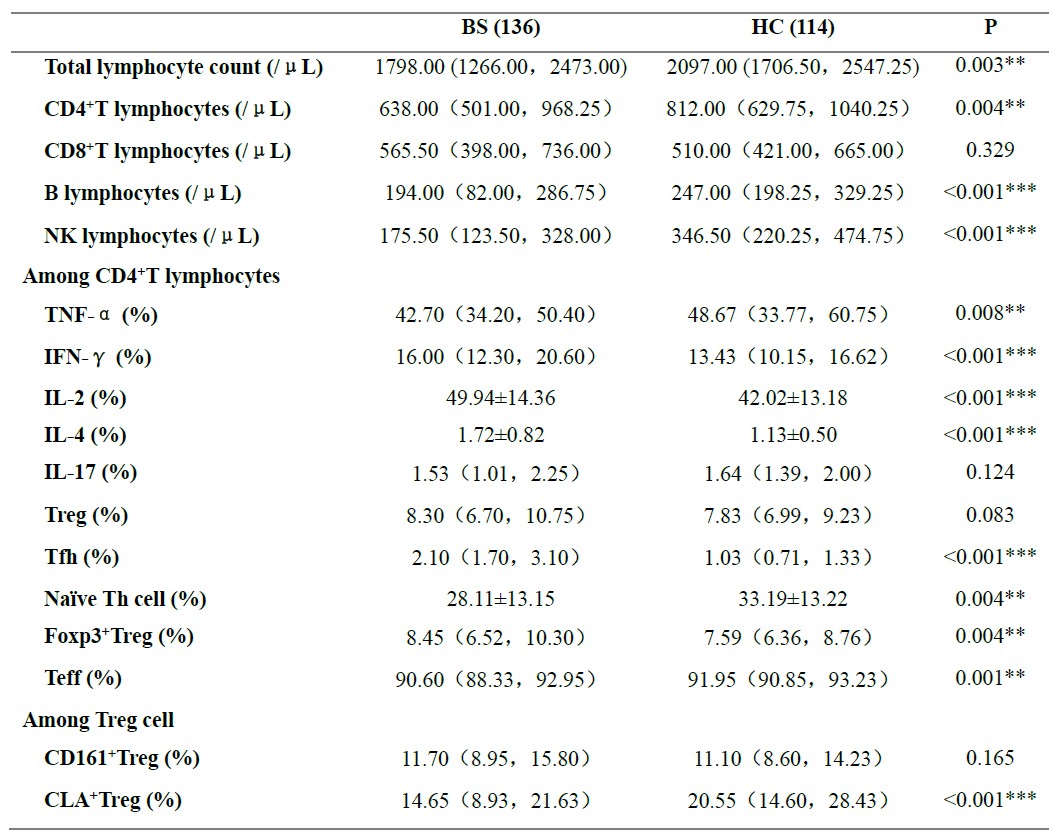
Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center study conducted in Beijing. We enrolled a total of 136 patients diagnosed with BS in rheumatology and immunology department of Peking University People’s Hospital from 2018 to 2021 and 114 healthy controls (HCs) in this study. All patients met the International Criteria for Behcet’s Disease (ICBD). The levels of peripheral immune cells, including CD4+ T lymphocytes, CD8+ T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, NK lymphocytes, several subsets of CD4+ T lymphocytes and several subsets of Treg cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Wilcoxon rank test, student’s t-test and Logistic regression analysis were used and a P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
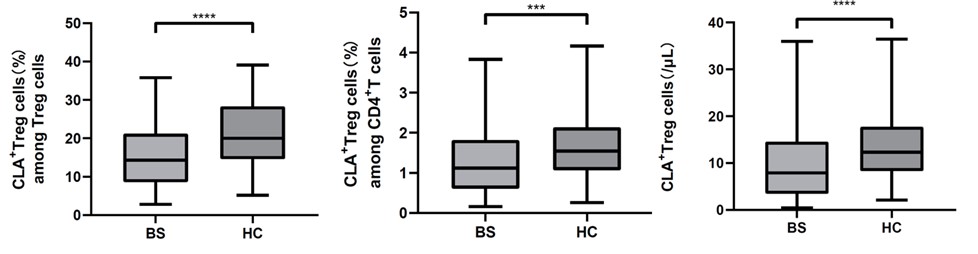
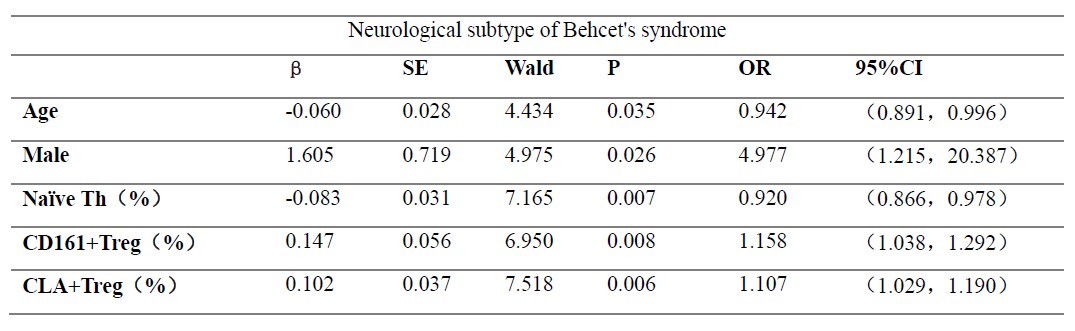
Results: Compared with HCs, the absolutely numbers of CD4+ T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes and NK lymphocytes were decreased in BS patients. Among CD4+ T lymphocytes, the proportion of IFN-g, IL-2 and IL-4 producing lymphocytes, follicular helper T cells and Foxp3+ Tregs were significantly elevated, while TNF-a producing lymphocytes, Naïve Th cells and T effectors were significantly decreased in BS patients. (P< 0.05) There was a significant decrease in the absolute number (7.91[ 3.69, 14.92] vs 12.56[ 8.39, 18.15], P< 0.001), proportion of CLA+ Tregs among CD4+ T lymphocytes (1.18[ 0.61, 1.91] vs 1.61[ 1.78, 2.15], P=0.001) and CD4+ regulatory T cells (14.65[ 8.93, 21.63] vs 20.55[ 14.60, 28.43], P< 0.001) in BS patients. We observed that BS patients with arterial aneurysm had lower proportion of CLA+ Treg among Tregs (10.67±5.92 vs 16.90±9.80, P=0.019) compared with those without arterial aneurysm and patients had nervous system involvement had higher proportion of CLA+ Treg among Tregs (20.95[ 16.63,26.85] vs 13.00[ 8.00,20.60], P=0.001) than patients without that manifestation. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that decreased level proportion of CLA+ Treg among Tregs was a protective factor of nervous system involvement in BS patients ( b=0.102, SE=0.037, Wald=7.518, P=0.006, OR=1.107, 95%IC: [ 1.029, 1.190]). The proportion of CLA+ Treg among Tregs in 11 BS patients of 14 was elevated after treatment of corticosteroids and immune suppressor.
Conclusion: BS patients have a decreased level of CLA+ Treg than HCs. Decreased CLA+ Treg may be a protective factor of nervous system involvement in BS patients. BS patients’ level of CLA+ Treg can be elevated after treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li J, Sun F, Zhou W, Liu T. Decreased Level of Peripheral CLA+ Treg Is a Protective Factor of Nervous System Involvement in Behcet’s Syndrome: A Real-World Study in China [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-level-of-peripheral-cla-treg-is-a-protective-factor-of-nervous-system-involvement-in-behcets-syndrome-a-real-world-study-in-china/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/decreased-level-of-peripheral-cla-treg-is-a-protective-factor-of-nervous-system-involvement-in-behcets-syndrome-a-real-world-study-in-china/