Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1345–1364) Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is one of the most common autoimmune diseases in women of childbearing age and female sex hormones are known to play a role in the pathophysiology of SLE. Multiple studies have suggested impaired ovarian reserve in patients with even mild SLE. Women with SLE may also be advised to defer pregnancy until disease remission; however, the likelihood of conception decreases with advancing age and the use of potentially gonadotoxic immunomodulatory agents. For these reasons, assisted reproductive technology (ART) is an important consideration for women with SLE who desire pregnancy. Patients with SLE utilizing ART are theoretically at increased risk of hormone-associated disease flare or thrombosis. In this study, we aim to evaluate outcomes in women with SLE who have utilized ART in our center. We also performed a systematic literature review regarding safety and efficacy of ART in women with SLE.
Methods: A retrospective chart review was performed at a large tertiary care center. Patients with a diagnosis of SLE whose records included mention of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) or ART between 2010-2023 were reviewed. All included patients had a diagnosis of SLE based on the modified 1997 ACR criteria. In addition, a literature search was performed using electronic databases including PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. Studies that reported data for patients with SLE who utilized ART were included. Case reports were excluded. Data collected for both the case series and literature review included type of ART utilized and number of cycles performed, demographic data, obstetric history, autoantibody positivity, etiology of infertility, delivery mode, maternal outcomes including SLE disease activity, and fetal outcomes.
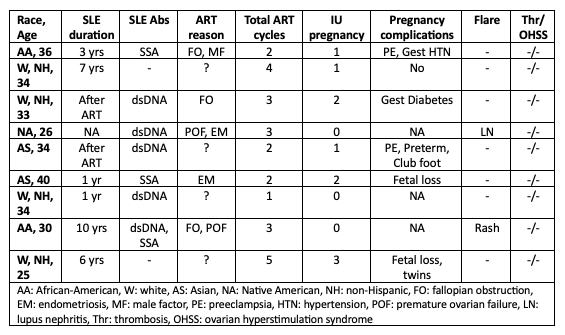
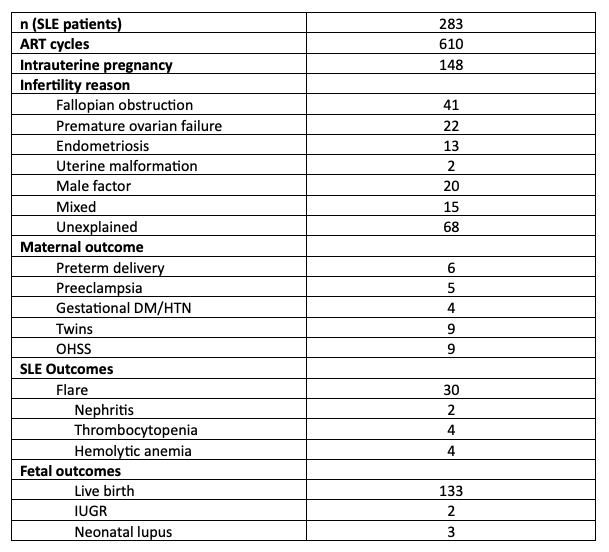
Results: Nine patients were included in the case series and 6 studies in the literature review. Amongst patients included in the case series, ART was performed in 7 patients with SLE and SLE developed after the use of ART in 2 patients. Table 1 summarizes the main clinical features of patients. A total of 25 ART stimulation attempts resulted in 10 intrauterine (IU) pregnancies (40%). Of these, 8 resulted in live births. Two patients had SLE flare while receiving hormonal therapy. Our literature review revealed 256 relevant articles. The full text of 25 articles was reviewed resulting in 6 eligible studies. Between these studies and our case series, 283 SLE patients were reviewed. A total of 610 ART cycles were analyzed. These ART cycles resulted in 148 IU pregnancies and clinical pregnancy rate was 24.3%. Live birth occurred in 133 cases (89.9%). Table 2 summarizes clinical features and major outcomes in the literature.
Conclusion: The rate of SLE flare in patients utilizing ART appears to be like that of SLE patients not receiving hormonal therapy. The success rate of ART in women with SLE is similar to that of the general population. This case series and review of the current literature supports the use of ART in patients with SLE who desire pregnancy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coe E, Petrinec E, Pamuk O. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Assisted Reproductive Technology: A Case Series and Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-assisted-reproductive-technology-a-case-series-and-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-assisted-reproductive-technology-a-case-series-and-systematic-literature-review/