Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although biologics (BIO) or Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) have improved treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), there are patients with difficult disease activity control even after using several BIO/JAKi, that is difficult-to-treat rheumatoid arthritis (D2TRA). D2TRA can be divided to two groups by mechanism: persistent inflammatory refractory RA (PIRRA) and non-inflammatory refractory RA with only persistent pain (NIRRA). We investigated these two different types of D2TRA.
Methods: Total of 147 patients switched to another BIO/JAKi because of inadequate response to previous BIO/JAKi and considered as D2TRA in our institution as of 2021. Patients with negative CRP and tender joint count > swollen joint count was defined as NIRRA, otherwise was defined as PIRRA. We investigated clinical characteristics and efficacy of following BIO/JAKi in both types of D2TRA for 52 weeks.
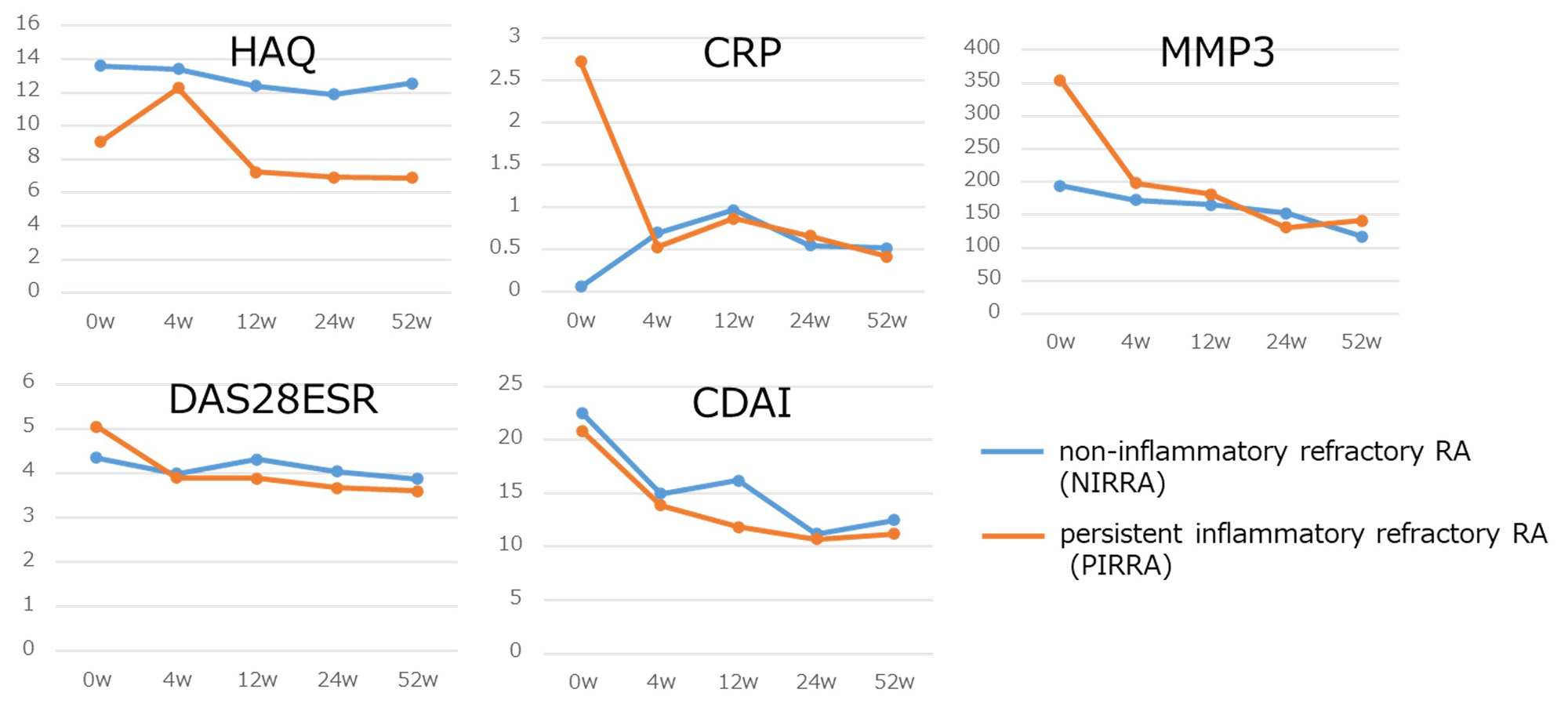
Results: Compared to NIRRA (n=33), PIRRA (n=114) showed significantly low hemoglobin (12.9 vs 12.0, p=0.02) and high DAS28ESR (4.43 vs 5.25, p=0.003) at the time of switching (baseline). There was no significant difference in MMP3 and CDAI. Retention rate at 52w also showed no difference (51.5% vs 45.6%, p=0.48). MMP3 and CDAI significantly improved during 52w in NIRRA, whereas CRP, MMP3, DAS28ESR, CDAI, and HAQ significantly improved in PIRRA. Switched BIO/JAKi consisted of IL6 inhibitors (n=7) and JAKi (n=15) in NIRRA, IL6 inhibitors (n=24) and JAKi (n=70) in PIRRA. Efficacy of switched BIO/JAKi showed no difference regardless of mechanism in both NIRRA and PIRRA.
Conclusion: MMP3 and CDAI improved after switching both in NIRRA and PIRRA. This tendency was similar whichever following BIO/JAKi was IL6 inhibitors and JAKi. Switching BIO/JAKi was effective in both types of D2TRA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Onishi K, Yamada Y, Okano T, Mamoto K, Anno S, Koike T, Nakamura H. Switching Biologics or Janus Kinase Inhibitors Is Effective in Difficult-to-treat Rheumatoid Arthritis, Regardless of Inflammation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/switching-biologics-or-janus-kinase-inhibitors-is-effective-in-difficult-to-treat-rheumatoid-arthritis-regardless-of-inflammation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/switching-biologics-or-janus-kinase-inhibitors-is-effective-in-difficult-to-treat-rheumatoid-arthritis-regardless-of-inflammation/