Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Direct functionality of the hand is not commonly assessed in daily practice or clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Functional dexterity test (FDT), developed to assess a patient’s ability to use the hand for daily tasks and widely used in rehabilitation medicine, has also been suggested as a legitimate tool for RA patients [Aaron et al, J Hand Ther. 2003]. Aim: To examine the value of FDT in a cohort of RA patients and to study the correlation between the results of FDT and RA activity.
Methods: Patients with established RA were followed in the outpatient clinic of Bnai Zion Medical Center performed the FDT during their regular follow-up visits. All patients were given 100 seconds (sec) to complete the test; the performance was measured in seconds separately for the dominant and non-dominant hands. FDT results were compared among 28 patients with active RA and clinical disease activity index(CDAI) greater than 10, 20 RA patients with controlled disease activity (CDAI of less than or equal to 10), and 20 volunteers with no rheumatic disease from the hospital personnel who agreed to perform the FDT.
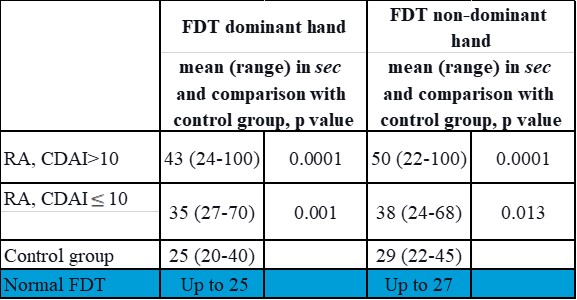
Results: A group of patients with active RA was younger than other groups, with a median age of 56 years (range 30-88 years) vs. 65 years (range 41-78 years) in the controlled RA group vs. 62 years (range 40-82 years) in the control group, p < 0.03. The mean disease duration was 11 years (range 3-26 years) in the active disease group and 11 years (range 1-47 years) in the controlled RA group, p=0.97. The gender composition of the groups was similar, with female patients comprising 70% to 82% (p=0.67). All 28 RA patients with CDAI >10 and 16 of 20 patients with CDAI< or equal to 10 were treated with biologics (p=0.02). Mean FDT for the dominant hand was 43 sec (range 24-100 sec) in the active RA group, 35 sec (range 27-70 sec) in the controlled RA group, and 25 sec (range 20-40 sec) in persons without arthritis. Corresponding FDT results for the non-dominant hand were 50 sec (range 22-100 sec), 38 sec (range 24-68 sec), and 29 sec (22-45 sec), respectively (Table 1). The difference in the FDT results between the two RA groups was non-significant for the dominant hand (p=0.28) but reached statistical significance for the non-dominant hand (p=0.02). Individuals without arthritis performed FDT either by dominant or non-dominant hand significantly better than any RA group (p values from 0.013 to 0.0001). FDT results significantly correlated with CDAI in the group of active RA only, with R=0.47/p=0.01 for the dominant hand and R=0.49/p=0.007 for the non-dominant hand vs. R=0.29/p=0.2, and R=0.4/p=0.08, respectively, in the controlled RA group. Minimally or non-functioning dominant hand, as predefined by FDT, was observed in 17 of 28 patients with active RA (61%), 11 of 20 patients (55%) with controlled disease, and 3 of 20 (15%) volunteers with no rheumatic disease.
Conclusion: FDT revealed a significant decrease in hand function in most RA patients. In patients with high or moderate RA activity, FDT correlated well with CDAI scores, while this correlation was lost in the group of patients with low disease activity or remission, where 55% of patients still demonstrated a significant loss in the dominant hand function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shouval A, Levkovitch A, Rosner I, keret s, Rokhyan I, Tchalabian B, Hof E, Slobodin G. Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients, Achieving Low Disease Activity State or Remission, Still Demonstrate Significant Hand Disability, as Assessed by Functional Dexterity Test: A Disconnection Between CDAI and Functional Hand Assessment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-achieving-low-disease-activity-state-or-remission-still-demonstrate-significant-hand-disability-as-assessed-by-functional-dexterity-test-a-disconnection-between-cdai/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-achieving-low-disease-activity-state-or-remission-still-demonstrate-significant-hand-disability-as-assessed-by-functional-dexterity-test-a-disconnection-between-cdai/