Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1100–1123) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
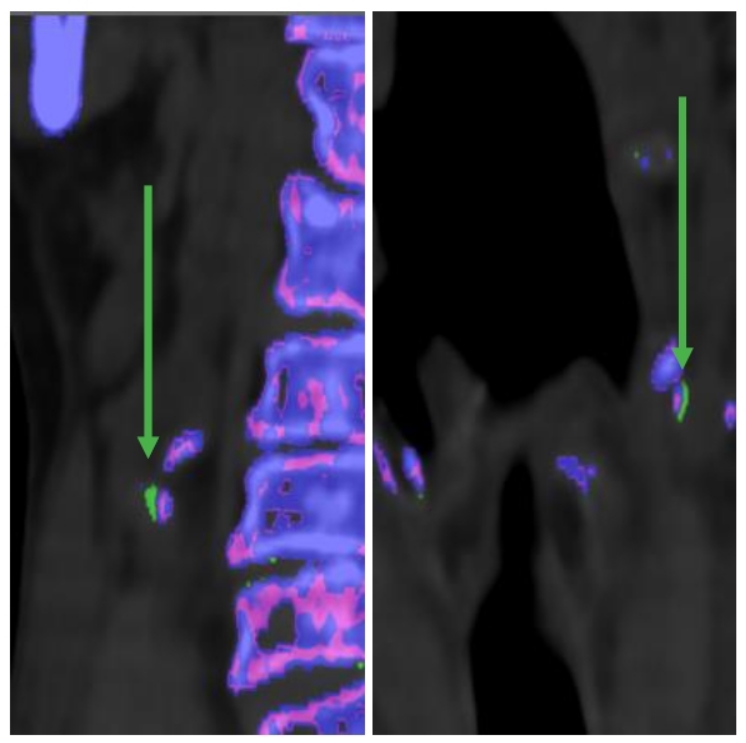
Background/Purpose: To find out if a Dual energy CT can detect monosodium urate deposition in carotid arteries and whether the presence of monosodium urate crystals has any effect on atherosclerotic disease in terms of plaque volume.
Methods: This is a retrospective study. All patients who underwent any Dual energy neck imaging (like carotid angiogram, neck soft tissues or cervical spine) from January 2015 to December 2022 were included. All patients’ charts were reviewed to determine to find gout patients with clinical and laboratory evidence. Charts were also rigorously reviewed to find potential confounding variables like hypertension, dyslipidemia, CKD and smoking as these may have effect on plaque volume. Patients with a smoking history were excluded as it has a well-established role in atherosclerotic disease. Non-smokers with either hypertension, dyslipidemia, CKD or either of two were included as most of the patients have similar comorbidities. Comprehensive data extraction was done to allow multivariable regression analysis for confounding variables. Same number of healthy controls (without a clinical history of gout or other rheumatic diseases) were included during same study period which were then age (within 5 years), sex and confounders-matched to gout patients using MedCalc. Patients with any extensive artefacts, spinal metal implants, carotid stents, carotid endarterectomy prior to scan date or prior radiotherapy to the head and neck were excluded. DECT datasets were post-processed using Syngo.ViaVB30 with gout application class at default factory settings including a DECT iodine ratio of 1.27, minimum HU at 130, resolution of 3mm, and air distance 5. Volumetric analysis of atherosclerotic plaque was performed using Syngo.ViaVB30 with Calcium scoring application in matched gout patients with carotid monosodium deposition, gout patients without carotid monosodium deposition and control/non-gout patients.
Results: Out of total 2157 patients who underwent dual energy neck imaging during study period, 85 were established gout cases with confirmed clinical and laboratory evidence. Of 85 gout cases, 2 were excluded due to presence of streak artefacts from dentures hence, n=83. Out of 83, Monosodium urate deposition was detected in carotid arteries of 10 patients (12%). None of the matched control patient demonstrated monosodium crystal deposition. Volumetric analysis of atherosclerotic plaque demonstrated larger plaque volumes in gout patients with monosodium urate deposition (n=10) than matched gout patients without monosodium urate deposition (n=10) and matched control/non-gout patients (n=10) (p value of 0.03).
Conclusion:
- Dual energy CT is an effective tool to detect monosodium urate deposition in carotid arteries.
- Carotid arteries are not a common site for monosodium urate deposition but if present, can lead to increased atherosclerosis in the involved vessel.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sarfraz M, Treanor L, Nicolaou S, Sheikh A. Role of Dual-energy Computed Tomography (DECT) in Detection of Carotid Artery Monosodium Urate Deposition in Patients with Gout [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-dual-energy-computed-tomography-dect-in-detection-of-carotid-artery-monosodium-urate-deposition-in-patients-with-gout/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/role-of-dual-energy-computed-tomography-dect-in-detection-of-carotid-artery-monosodium-urate-deposition-in-patients-with-gout/