Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Formation of anti-drug antibodies (ADAb) to biological drugs is a clinical problem. Proactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) allows for timely detection of ADAb and may reduce the negative clinical consequences. The aim of the study was to explore the relation between ADAb and treatment outcomes and adverse events, and to assess the impact of proactive TDM.
Methods: Patients (n=615) with spondyloarthritis (n=181), rheumatoid arthritis (n=120), psoriatic arthritis (n=72), ulcerative colitis (n=114), Crohns disease (n=83) and psoriasis (n=45) on infliximab therapy were included in the Norwegian Drug Monitoring (NOR-DRUM) trials1,2 and randomised to TDM or standard infliximab therapy. Patients were followed for 30/52 weeks in the NOR-DRUM A (induction therapy) and NOR-DRUM B (maintenance therapy) trials, respectively. Neutralising ADAb were assessed with a drug-sensitive assay at each infusion. The outcomes of this study were: remission 30 weeks after initiation of infliximab, having a disease worsening during 52 weeks of maintenance therapy, having an infusion reaction and infliximab treatment discontinuation. Regression and Kaplan-Meier survival analyses were used to assess the association between ADAb and the outcomes, and the impact of proactive TDM. Remission and disease worsening were defined by disease specific composite scores1,2.
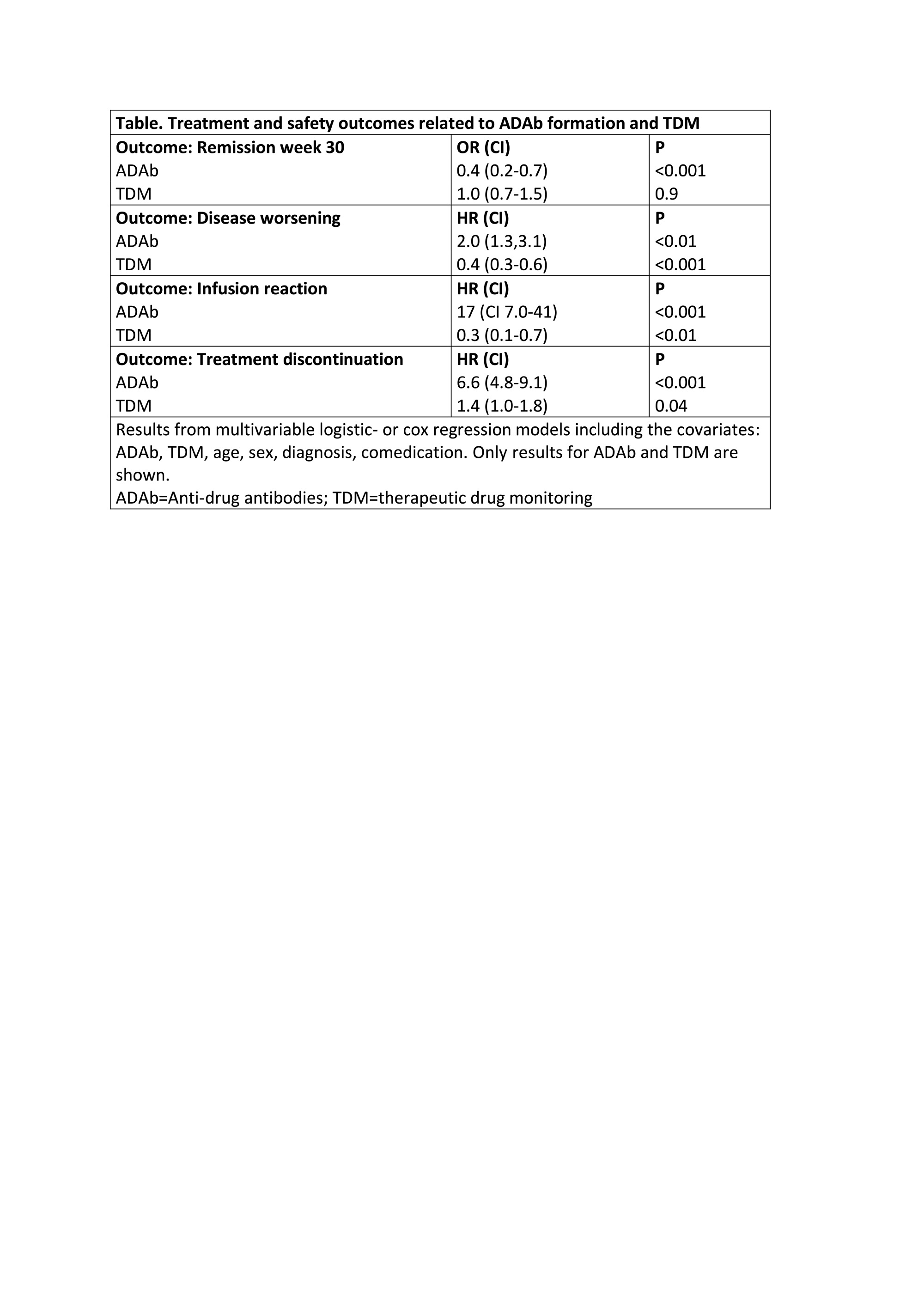
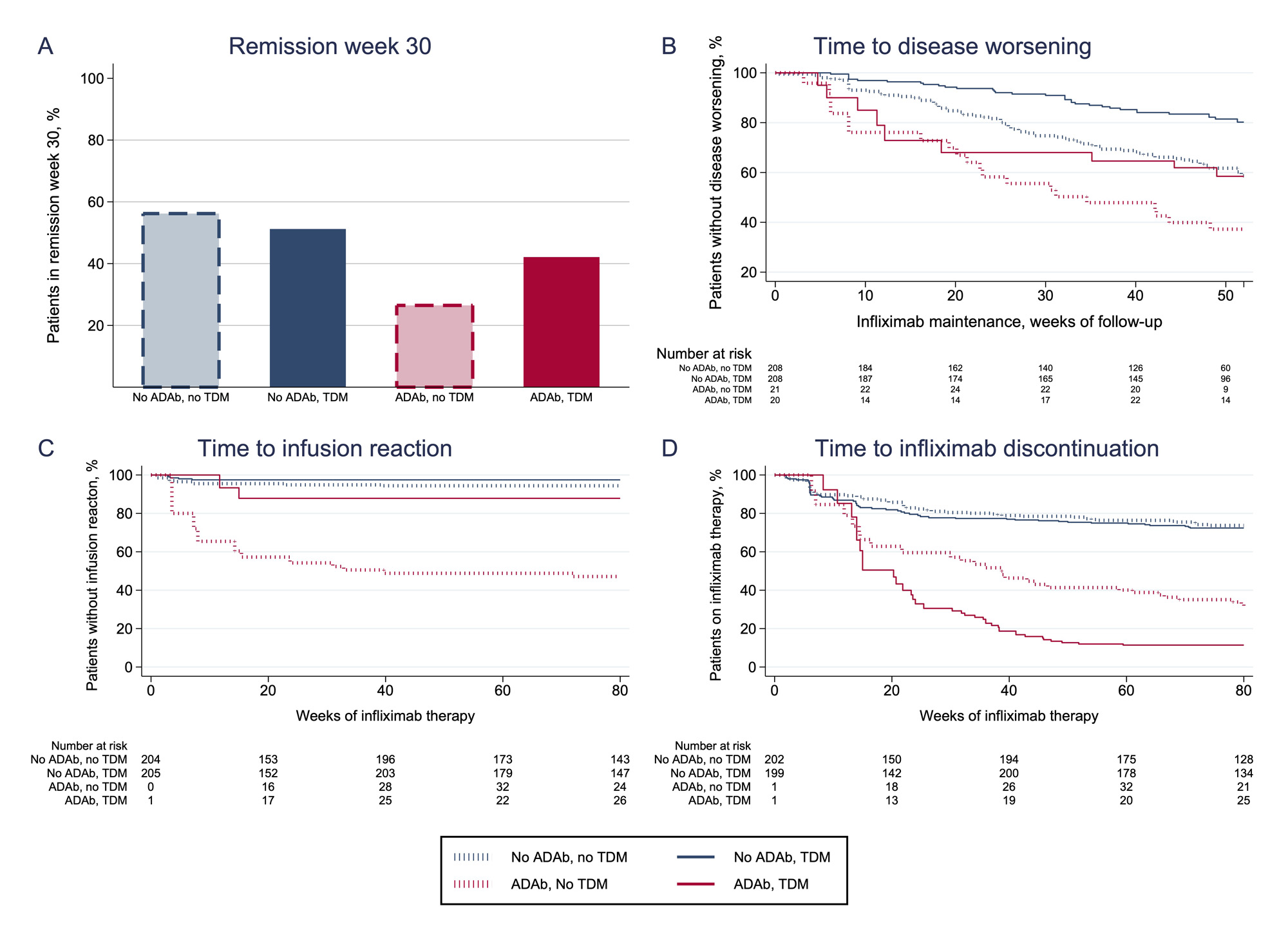
Results: ADAb were detected in 147/615 (24 %) patients. A lower proportion with ADAb achieved remission at week 30 (odds ratio (OR) 0.4, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.2-0.7, P< 0.01) (Table, Figure 1A) compared to ADAb negative. The risk of having a disease worsening was increased in ADAb positive (hazard ratio (HR) 2.0, CI 1.3-3.7, P< 0.01) (Table, Figure 1B) or an infusion reaction (HR 17, CI 7-41, P< 0.001) (Table, Figure 1C) was increased in patients with ADAb as compared to ADAb negative. The risk of infliximab treatment discontinuation was increased in ADAb positive patients (HR 6.6, CI 4.8-9.1, P< 0.001) (Table, Figure 1D). Patients developing ADAb in the TDM group had lower risk of having a disease worsening (HR 0.4, CI 0.3-0.6, P< 0.001) or an infusion reaction (HR 0.3, CI 0.1-0.7, P< 0.01) compared to patients with ADAb in the standard therapy group (Table, Figure 1B and C). Patients with ADAb discontinued infliximab treatment more often in the TDM group than in the control group (HR 1.4, CI 1.0-1.8, P=0.04) (Table, Figure 1D).
Conclusion: Formation of ADAb led to poorer clinical outcomes during infliximab treatment and increased the risk of infusion reactions. Early detection of ADAb by proactive TDM reduced the negative consequences of ADAb, both on infliximab effectiveness and safety. Our results highlight the role of proactive TDM in optimising TNFi therapy.
References
1. Syversen SW et al. JAMA 2021;326(23)
2. Syversen SW et al. JAMA 2021;325(17)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brun M, Bjørlykke K, Gehin J, Warren D, Klaasen R, Sexton J, Sandanger Ø, Kvien T, Mørk C, Jahnsen J, Bolstad N, Jørgensen K, Haavardsholm E, Goll G, Syversen S. Clinical Consequences of Infliximab Immunogenicity and the Impact of Proactive Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: Secondary Analyses of a Randomised Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-consequences-of-infliximab-immunogenicity-and-the-impact-of-proactive-therapeutic-drug-monitoring-secondary-analyses-of-a-randomised-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinical-consequences-of-infliximab-immunogenicity-and-the-impact-of-proactive-therapeutic-drug-monitoring-secondary-analyses-of-a-randomised-clinical-trial/