Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Treatments I: Novel RA Treatments & Mechanisms of Action
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: RA is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with autoantibodies. Despite the use of targeted therapies, up to half of patients fail to achieve remission or low disease activity (LDA). Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs), key autoantibodies that predict progression of joint destruction in RA, are largely an immunoglobulin G (IgG) isotype. Nipocalimab is a high affinity, fully human, IgG1 monoclonal antibody that is designed to selectively block the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), preventing recirculation and thereby lowering IgG levels, potentially including ACPAs and other pathogenic antibodies. In this phase 2a proof-of-concept study (IRIS-RA; NCT04991753), we report the efficacy and safety of nipocalimab in patients with moderate to severe, active RA.
Methods: Eligible adult patients with moderate to severe RA (≥6 swollen/tender joints), positive for ACPA or rheumatoid factor, and ≥1 advanced therapies, were randomized 3:2 to receive intravenous 15 mg/kg nipocalimab or placebo every 2 weeks for 10 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change from baseline in the Disease Activity Score 28 using C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) at Week 12. Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients who achieved ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, and ACR90 responses, DAS28-CRP remission, and change from baseline in Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index (HAQ-DI) at Week 12.
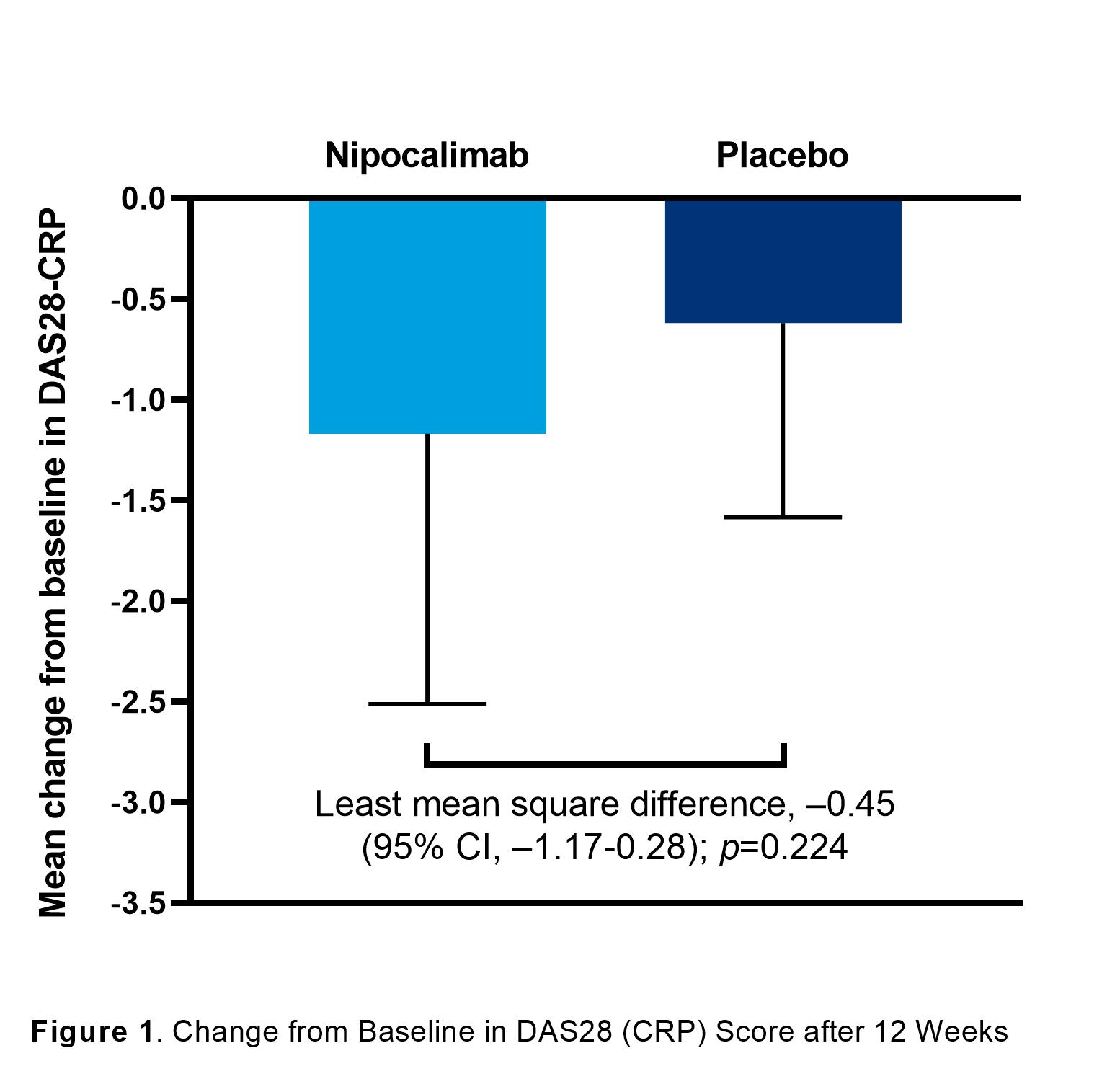
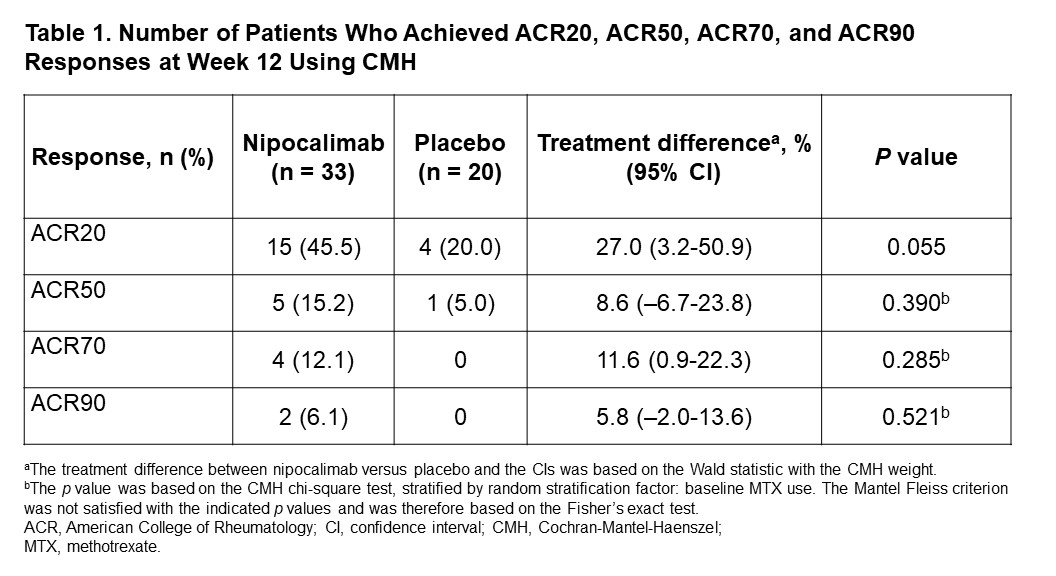
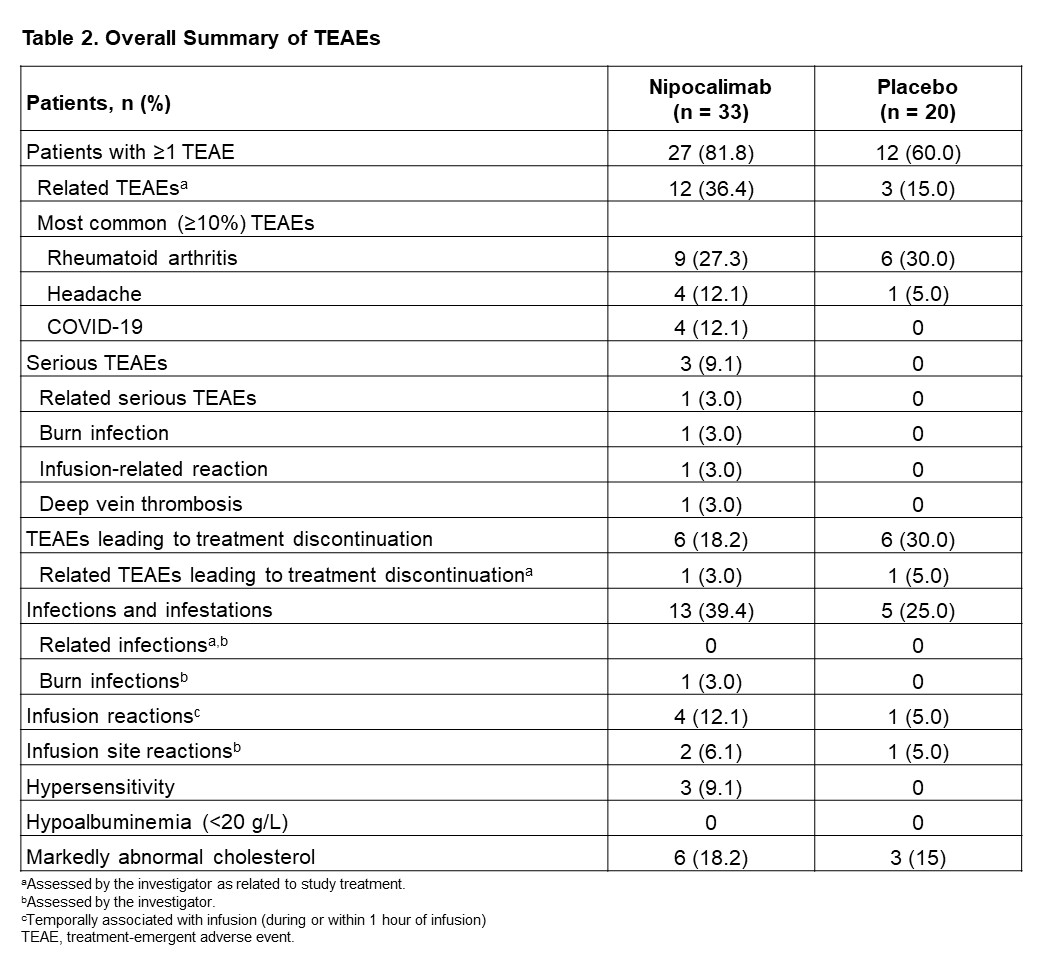
Results: In total, 53 patients were enrolled (nipocalimab, n=33; placebo, n=20). Most patients were female (67.9%) and white (90.6%) with a median age of 59 (range, 26-74) years. Demographic and baseline disease characteristics were comparable between groups except higher CRP in placebo. At Week 12, patients treated with nipocalimab showed a numerically greater mean (standard deviation [SD]) change in DAS28-CRP score compared to the placebo group (–1.17 [1.34] vs –0.62 [0.96]; mean difference [95% confidence interval], –0.45 [–1.17-0.28]; p=0.224); Figure 1). A numerically higher proportion of patients achieved ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, and ACR90 responses compared to placebo (Table 1). In the nipocalimab group, 7 (21.2%) patients achieved DAS28-CRP remission compared to 2 (10.0%) patients in the placebo group (treatment difference, 9.9% [–9.5-29.3%]; p=0.456). Similarly, patients in the nipocalimab group had a numerically greater mean (SD) improvement in HAQ-DI score (–0.27 [0.55] vs –0.11 [0.36], respectively). Median post-dose serum nipocalimab concentrations ranged from 411.0-426.0 µg/mL across Weeks 0, 2, and 8. The proportion of patients with treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were 81.8% vs 60.0% in the nipocalimab vs placebo groups (Table 2). In the nipocalimab group, 3 serious TEAEs were reported, including burn infection, infusion-related reaction, and deep-vein thrombosis. There were no TEAEs that led to death.
Conclusion: Treatment with nipocalimab resulted in consistent and numerically higher improvements across ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, and ACR90 responses, as well as DAS28-CRP, DAS28-CRP remission, and HAQ-DI, with acceptable safety profile. Nipocalimab showed activity in patients with moderate to severe RA and warrants further investigation to understand the predictors of nipocalimab response.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Schett G, Ibrahim F, Zhou B, Leu J, Liva S, Wang Q, Cella R, Karyekar C, Fei K. Efficacy and Safety of Nipocalimab in Patients with Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): The Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blinded, Placebo-controlled Phase 2a IRIS-RA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-nipocalimab-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-the-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-phase-2a-iris-ra-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-nipocalimab-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-the-multicenter-randomized-double-blinded-placebo-controlled-phase-2a-iris-ra-study/