Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The clinical effectiveness of 6-month IV BEL use in SLE has previously been described in a post hoc pooled analysis from six OBSErve cohort studies.1 Here we present expanded post hoc analysis of eight pooled OBSErve studies investigating the long-term effectiveness of BEL on reducing oral CS (OCS) use and achieving low disease activity (LDA) and remission, which are important treatment targets for SLE to minimize irreversible organ damage.2,3
Methods: This was a post hoc pooled analysis (GSK Study 219649) of data from eight OBSErve studies in Argentina, Canada, Germany, USA, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Spain, and Switzerland. Clinician-reported data were captured for adults with SLE at IV BEL initiation (index) and at 6–24 months after index. All studies captured 6 months of data after index, with Argentina and USA data extending up to 24 months after index. Enrollment was 6 months post index for all studies except Argentina and n=284/501 USA patients (pts) who enrolled 12 months after index. The primary objective was to describe the proportion of pts achieving a daily OCS dose ≤10 mg, ≤7.5 mg, ≤5 mg, or 0 mg at 6, 12, 18, or 24 months after index. Secondary objectives included: the proportion of pts who maintained their 6-month post index daily OCS dose threshold over time; and the proportion of pts achieving LDA (modified Lupus Low Disease Activity State; SLEDAI score ≤4 with no worsening of clinical manifestations and OCS dose ≤7.5 mg/day4) or remission (modified Definition Of Remission In SLE; SLEDAI score=0 and OCS dose ≤5 mg/day5) at 24 months after index.
Results: Data from 959 pts were included. Most pts were from the USA (52.2%), Germany (10.6%), and Argentina (8.4%). At enrollment, the mean age was 41.5 years, 89.5% were female, 64.6% were White (N=878 only); 55.2% had SLE for ≥5 years before enrollment.
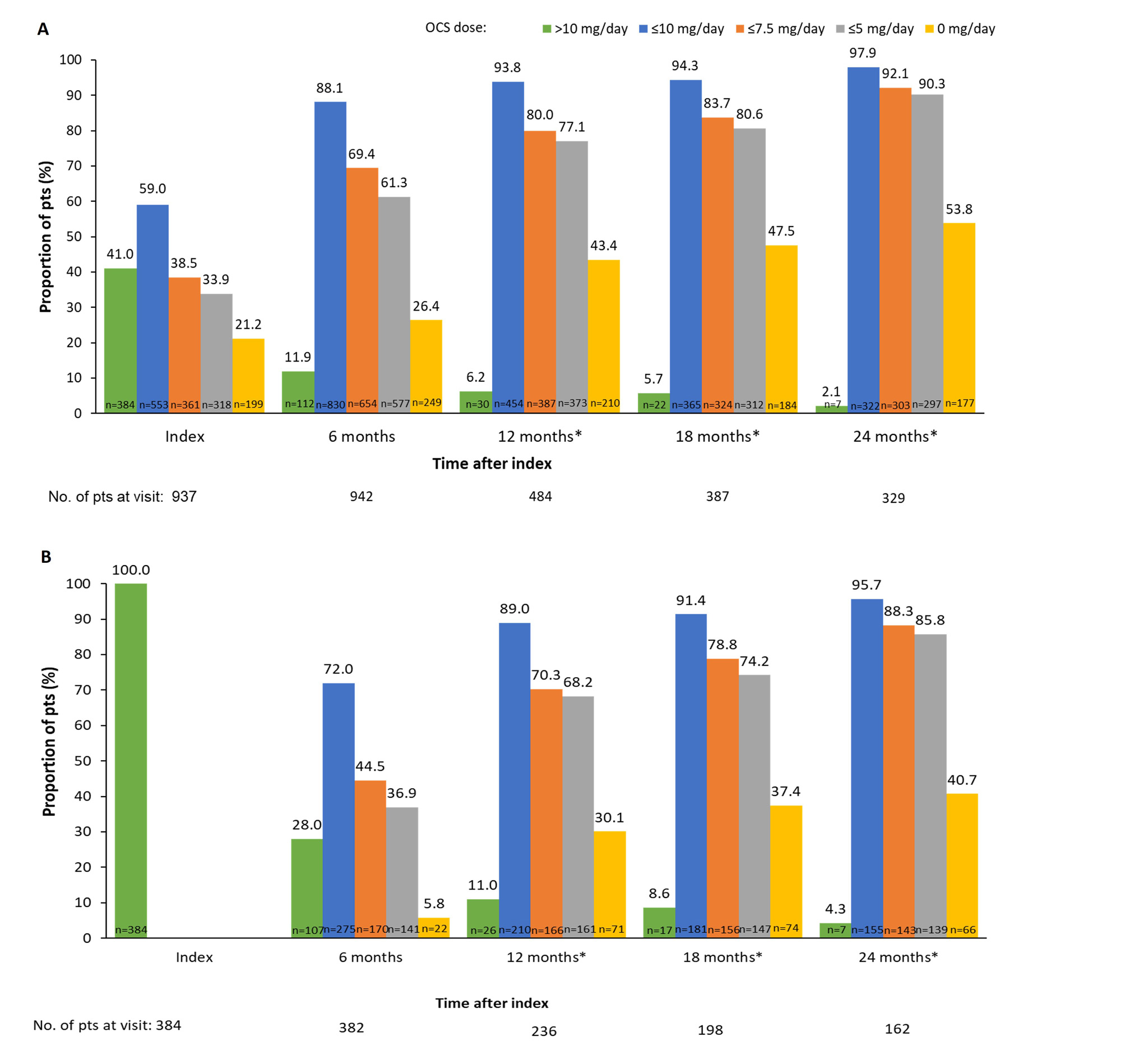
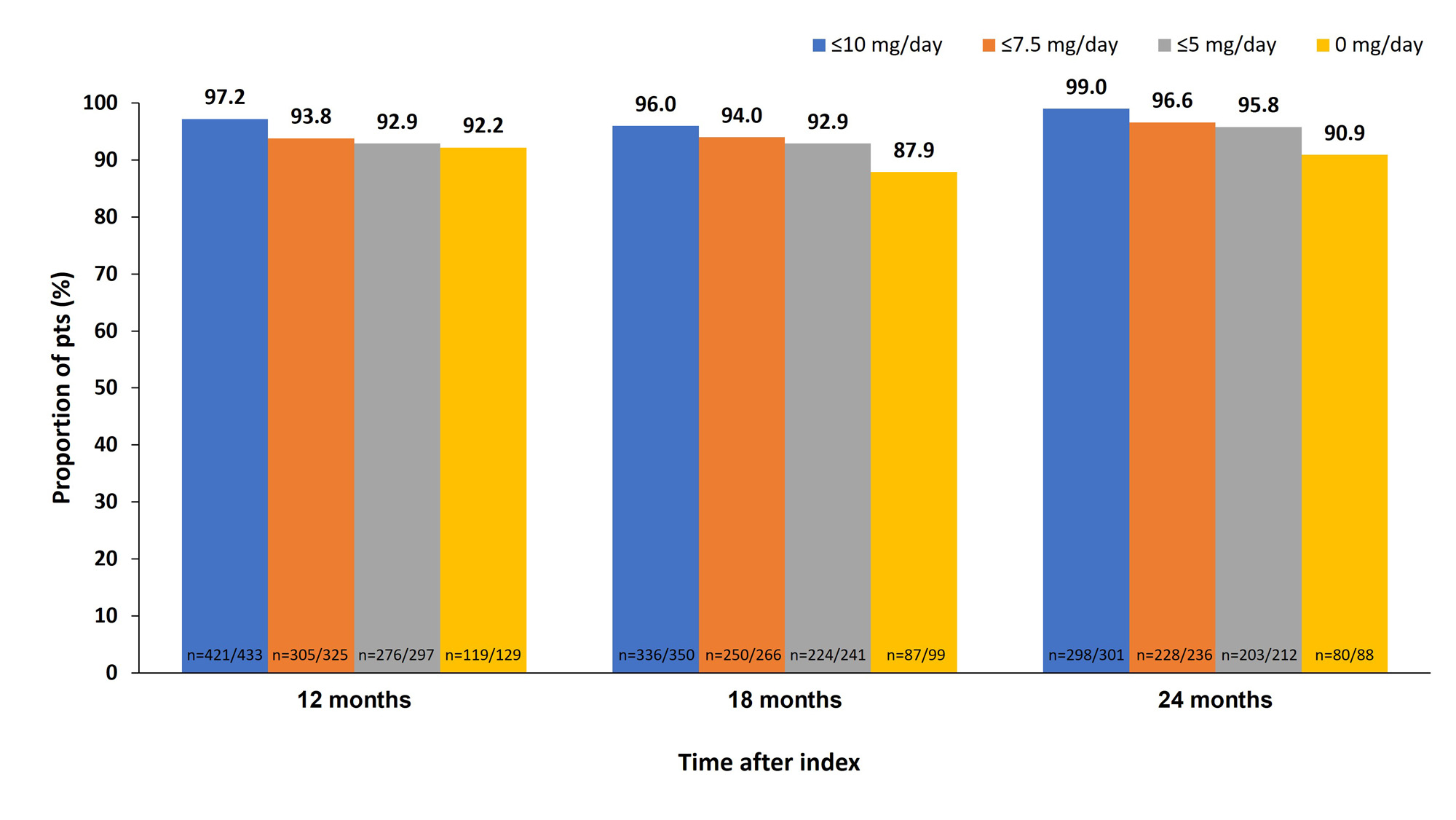
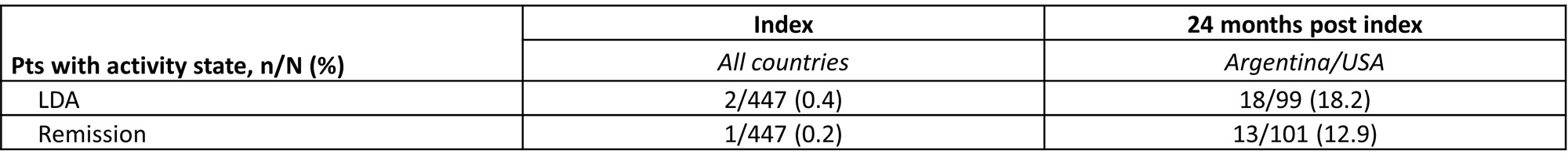
At index, median (interquartile range) OCS dose was 10.0 (5.0, 20.0) mg/day; 14.5% were receiving an OCS dose of >20 mg/day and 41.0% >10 mg/day. The proportion of pts receiving OCS dose ≤7.5 mg/day increased from 38.5% at index to 69.4% at 6 months, 80.0% at 12 months, 83.7% at 18 months, and 92.1% at 24 months (data after 6 months for pooled Argentina/USA only; Figure 1A). A similar trend was seen among those who were receiving >10 mg/day at index (Figure 1B). Over 87% of pts maintained the same OCS low dose threshold at 12, 18, and 24 months as at 6 months after index (Figure 2). At index (N=447), 0.4% of pts were in LDA state and 0.2% in remission. At 24 months, 18.2% and 12.9% achieved LDA and remission, respectively (Table).
Conclusion: These data demonstrate a steroid-sparing effect of long-term BEL use, which was evident from 6 months and maintained over 24 months, as well as an improvement of disease activity indices in pts with SLE, further supporting the effectiveness of IV BEL in real-world SLE clinical management.
Funding: GSK References:
1 Collins CE et al. Rheumatol Ther 2020;7:949–65
2 Fanouriakis A et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:736–45
3 Golder V et al. Rheumatol 2020;59:(Suppl5)v19–v28
4 Franklyn K et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:1615–21
5 van Vollenhoven et al. Lupus Sci Med 2021;8:e000538
OCS dose=prednisone equivalent.
*Among pooled pts in Argentina and the USA where data were captured beyond 6 months post index.
OCS dose=prednisone equivalent.
*Among pooled pts in Argentina and the USA where data were captured beyond 6 months post index.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moldaver D, Anderson S, Bracher M, Levy R, Quasny H, Wood R, Wild R, Cusmano A, Rottier E. Impact of up to 24 Months Intravenous (IV) Belimumab (BEL) Treatment on Steroid Use and Disease Activity in Patients with SLE in Clinical Practice: Additional Post Hoc Pooled Analysis of Multicountry OBSErve Cohort Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-up-to-24-months-intravenous-iv-belimumab-bel-treatment-on-steroid-use-and-disease-activity-in-patients-with-sle-in-clinical-practice-additional-post-hoc-pooled-analysis-of-multicountry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-up-to-24-months-intravenous-iv-belimumab-bel-treatment-on-steroid-use-and-disease-activity-in-patients-with-sle-in-clinical-practice-additional-post-hoc-pooled-analysis-of-multicountry/