Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0543–0581) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Monogenic lupus is associated with specific gene mutations, most commonly reported in TREX1, DNASE1L3, DNASE2, and SAMHD1. However, their phenotypes are not well reported.
Methods: Patients < 16 years of age, satisfying classification criteria for SLE (SLICC 2012) or incomplete lupus1 (ILE)( ANA (titer ≥1:80) and any 1 of acute/ subacute/ chronic cutaneous lupus, oro-nasal ulcers, alopecia, synovitis, serositis, neurologic or renal manifestation or 2 of hematologic, immunologic manifestations, family history of autoimmune rheumatic disease (AIRD) or lupus-like disease(LLD) as per treating physicians opinion, in whom a monogenic cause was suspected due to consanguinity in parents, young age of onset, familial history, recurrent infections, skeletal abnormalities were subjected to clinical exome sequence. Data was retrieved from outpatient and inpatient records. Those with pathogenic variants or with variant of unknown significance but with the same mutation identified in parents were analysed.
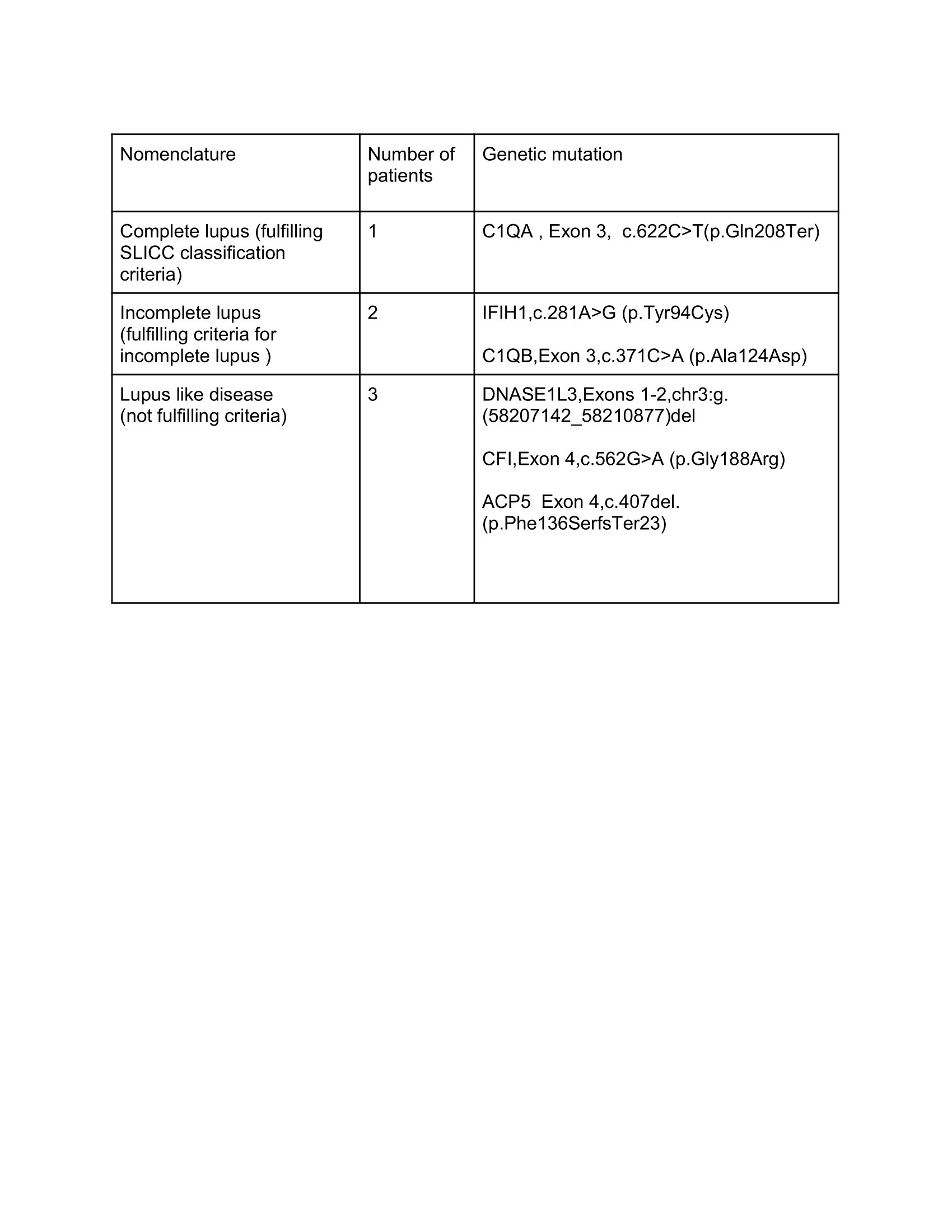
Results: Clinical exome revealed mutations in 6 of 7 patients tested (Table 1). The mean age of the patients was 5.3 years( range 2-12) and mean duration of follow-up was 10.8 months (range 4- 21). One patient with a mutation in C1QA gene fulfilled the SLICC-CC (acute cutaneous lupus, oral ulcers, myelitis, lupus nephritis). She also experienced recurrent infections (thigh cellulitis and thumb abscess).
Two patients met the criteria for ILE. One had AIHA, ILD, and low complements and shared a heterozygous mutation in the IFIH1 gene with her mother. The other had oral ulcers, discoid rash, and mutation in C1QB mutation.
Three patients had LLD. One had DAH (diffuse alveolar haemorrhage) and mutation in DNASE1L3 gene, another had urticarial skin rash and low complements with a mutation in CFI gene, and third had AIHA (autoimmune hemolytic anemia), leucopenia, and spondyloenchondroplasia with mutation in ACP5 gene. All, except patient with DNASE1L3 mutation, were ANA positive. None had a family history of AIRD.
Conclusion: We report on 6 patients with mutations in C1QA, C1QB, DNASE1L3, CFI, IFIH1, and ACP5. In 3 with known mutations for monogenic lupus (C1QB, DNASE1L3, ACP5) SLE SLICC criteria were not met. One child presented with DAH. Others had lupus-like autoimmune features and features atypical for ILE eg ILD. Monogenic lupus will allow better research into pathways of disease.
Reference: 1.Lambers WM. Incomplete Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: What Remains After Application of ACR and SLICC criteria? Arthritis Care Res 2020;72(5):607–14.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yerram K, Shanigaaram K, Deshpande G, Parikh A, Ramavath A, Gollakota N, Manthri R, Rajasekhar L. Monogenic Lupus: Clinical Phenotypes and Genetic Mutations in a Cohort of Pediatric Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/monogenic-lupus-clinical-phenotypes-and-genetic-mutations-in-a-cohort-of-pediatric-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/monogenic-lupus-clinical-phenotypes-and-genetic-mutations-in-a-cohort-of-pediatric-patients/