Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPD) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (RA-LPD) have unique pathophysiological features. More than half of the cases of RA-LPD undergo spontaneous regression after the discontinuation of disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), whereas approximately 33% of these cases relapse. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection is especially involved in the pathophysiology of RA-LPD. The current study was conducted with whole RNA transcriptome analysis using the peripheral blood of patients developing RA-LPD to investigate the pathophysiology of RA-LPD.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples of the patients with RA-LPD were obtained between May 2013 and October 2018 from 30 hospitals in Japan. Whole transcriptome sequencing was performed using the Ion AmpliSeq Human Gene Expression Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and an IonS5 XL sequencer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The kit covers the expression levels of 20,802 human RefSeq genes (based on UCSC hg19). Differential gene expression analysis was performed by Transcriptome Analysis Console (TAC) software (ver. 4.0.3, Thermo Fisher Scientific) with |FC| > 2-fold difference and at p < 0.1. A Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was performed to identify pathways enriched in the Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark gene set. A nominal p value of < 0.05 and an FDR (false discovery rate) q value of < 0.25 were considered statistically significant.
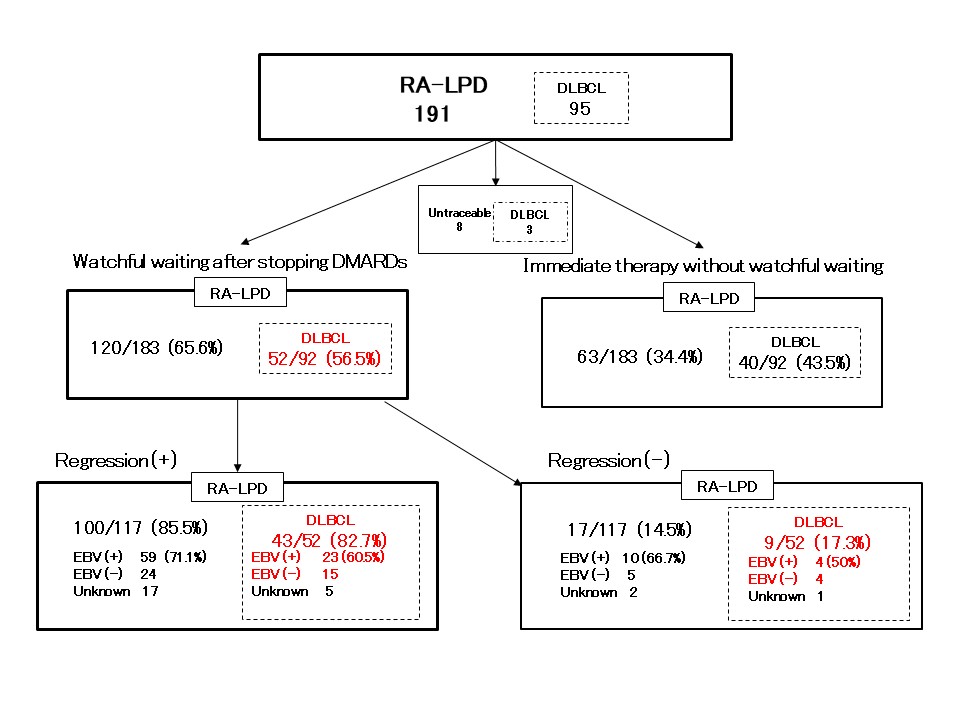
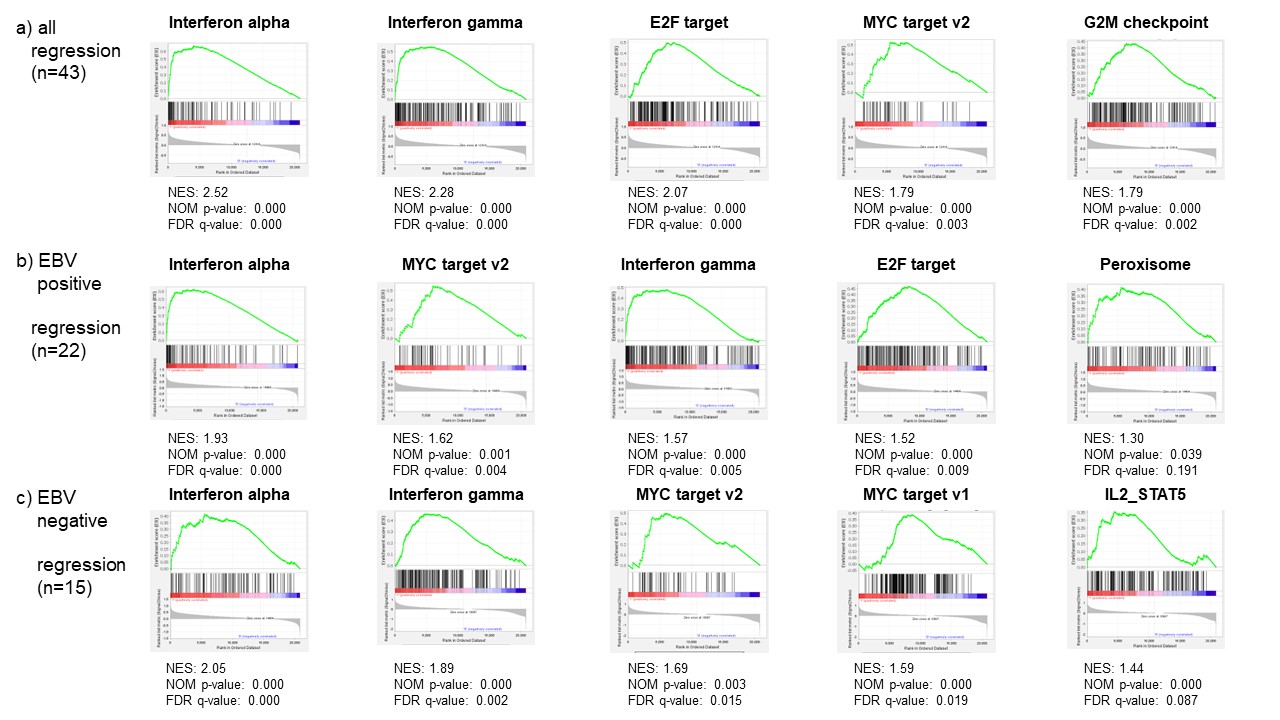
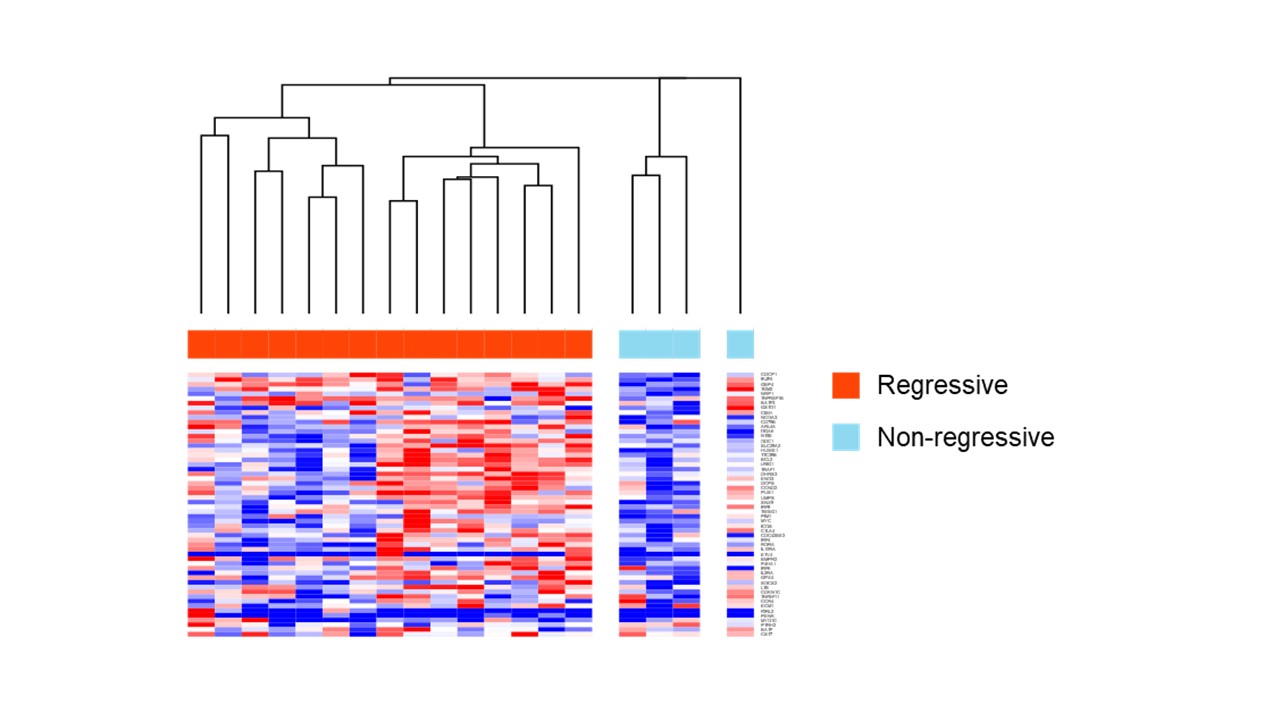
Results: In total, 211 cases (191 RA-LPD cases and 20 non-LPD RA cases) were analyzed. The flow diagram of the study is shown in Figure 1. We grouped diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cases into two groups; regression cases (n = 43), which regressed spontaneously after stopping DMARDs and non-regression cases (n = 9), which did not regress. Gene expression levels were compared between the two groups. GSEA analysis showed that interferon alpha and gamma pathways were enhanced in regression cases (Figure 2a). To investigate mechanisms of regression in EBV-negative cases, we performed further analysis according to EBV infection status. (EBV positive, n= 22; EBV negative, n= 15). The interleukin-2-STAT5 (IL2-STAT5) pathway was enhanced in regression cases without EBV infection, which was suggested to be a unique mechanism for regression in EBV-negative RA-LPD (Figure 2b, c). The heatmap (Figure 3) shows that genes related to IL2-STAT5 were expressed highly in regression cases without EBV infection. Additionally, expression levels of some genes related to the IL2-STAT5 pathway were significantly different between regression and non-regression EBV-negative cases. This result suggests that these genes may serve as new liquid markers for regression in EBV-negative RA-LPD.
Conclusion: The current study showed that interferon-alpha and gamma pathways were upregulated in the regression cases with DLBCL of RA-LPD. Moreover, the study revealed a unique mechanism related to IL2-STAT5 for regression of EBV-negative cases. Our research further suggested new potential markers for regression in EBV-negative cases.
Cases analyzed in this study are written in red. RA-LPD: lymphoproliferative disorders in rheumatoid arthritis; DLBCL: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; DMARD: Disease modifying anti rheumatic drug; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
TSUJII A, SAKAI K, OHSHIMA S, SAEKI Y, YAGITA M, MIYAMURA T, Katayama M, HIRAMATSU Y, HIGA S, HIRANO F, ICHIKAWA K, CHIBA N, SUGIYAMA T, IHATA A, TSUTANI H, TAKAHI K, MIGITA K, MORI S, YOSHIKAWA N, UEDA A, NAGAOKA S, SETOGUCHI K, SUGII S, ABE A, SUGAYA T, SUGAHARA H, TSUNODA S, IIZUKA N, YOSHIHARA R, YABE H, FUJISAKI T, MORII E, SAITO K, Matsui K, TOMITA Y, FURUKAWA H, Tohma S, NISHIO K, HOSHIDA Y. Parsing Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders via Whole RNA Transcriptome Analysis: Multi-center Study in Japan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/parsing-pathophysiology-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-lymphoproliferative-disorders-via-whole-rna-transcriptome-analysis-multi-center-study-in-japan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/parsing-pathophysiology-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-lymphoproliferative-disorders-via-whole-rna-transcriptome-analysis-multi-center-study-in-japan/