Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The ORAL Surveillance study highlighted risks of cardiac events, thromboembolism (VTE), and cancer associated with Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi). The aim of this study was to understand the effect that these data have had on practice patterns by describing the characteristics of patients initiating advanced therapies for RA including tofacitinib (TOFA), TNF inhibitors (TNFi), and non-TNFi agents before and after the release of safety data in January 2021 and to evaluate characteristics associated with discontinuation among active users at the time that the data was released.
Methods: This was a national, retrospective study of US Veterans with RA receiving advanced therapies between April 2019 through September 2022. This period was divided into two 664-day periods, one before and one after the January 2021 press release. Eligible patients had ≥1 diagnosis code for RA and initiated a TNFi, non-TNFi, or TOFA. Patient characteristics were defined for each therapy initiation including a comorbidity index (RDCI), and individual comorbidities were categorized using Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Clinical Classification Software. We tested for interaction within regression models to determine whether changes observed in characteristics (standardized differences) for TOFA users were different from changes observed for the other therapies. We also determined the time to discontinuation for active users at the time of the press release, censoring for death and end of follow-up. We used Cox models adjusted for age, sex, and duration on therapy to evaluate for associations between patient characteristics and therapy discontinuation, testing for interactions with TOFA vs. TNFi.
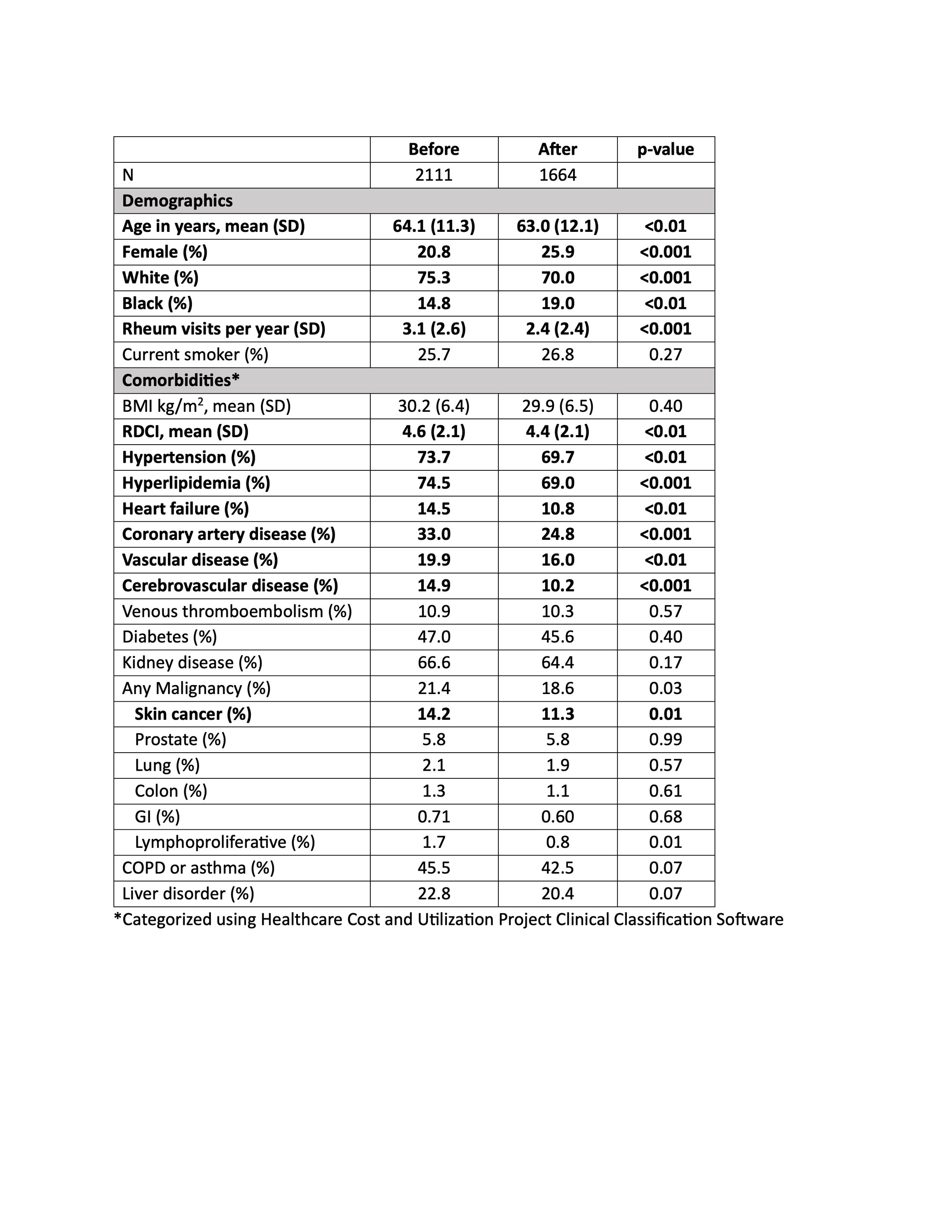
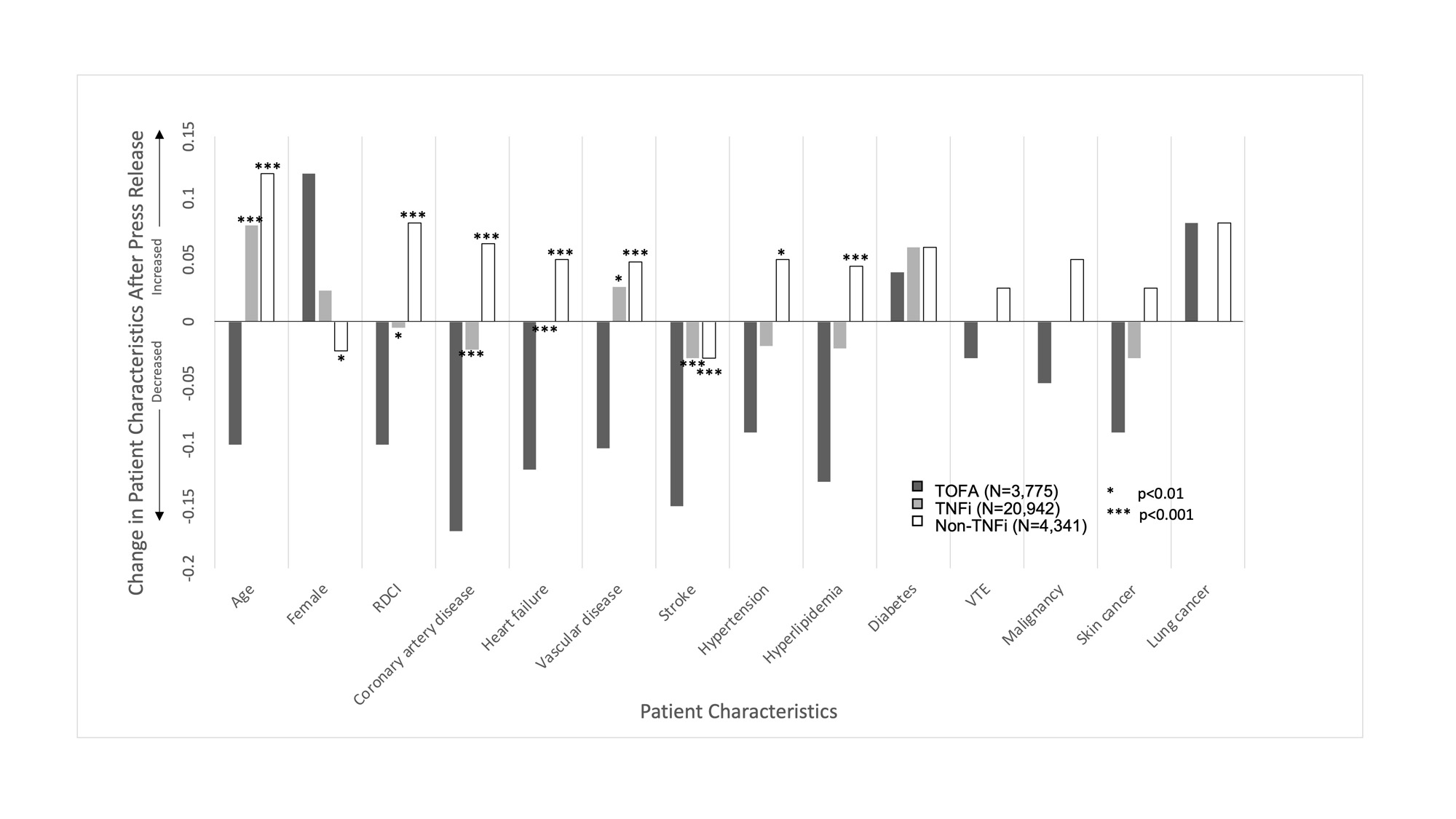
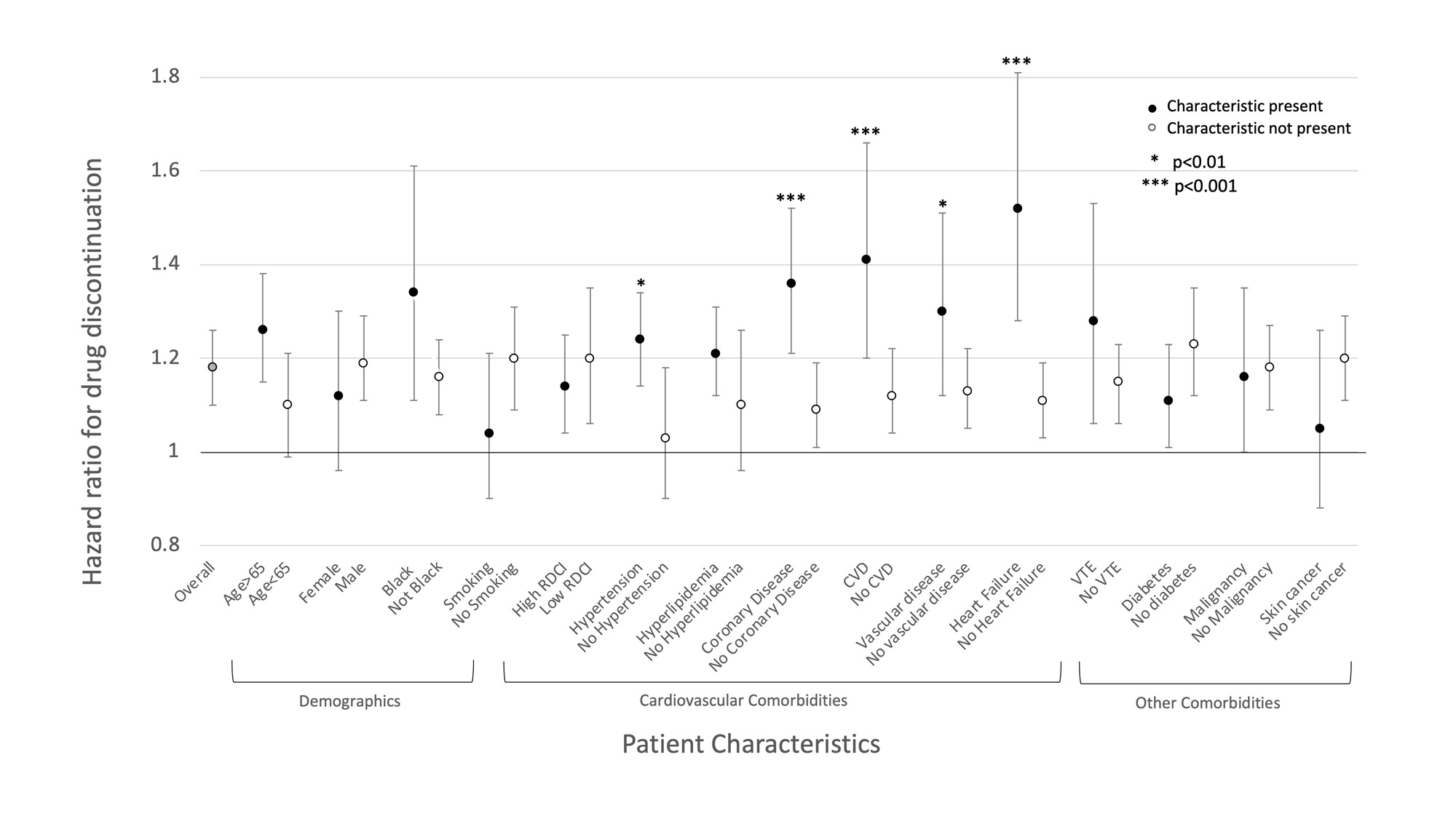
Results: When comparing patients initiating TOFA before (N=2111) and after (N=1664) January 2021, there were decreases in mean age (64.1 vs 63.0), the proportion of men (20.8% vs 25.9%), mean RDCI score (4.6 vs 4.4), and the proportion with cardiovascular comorbidities and skin cancer (Table 1) (all p< 0.01). These changes were significantly different from those observed for patients initiating TNFi or non-TNFi biologic drugs (p for interaction with therapy < 0.05) (Figure 1). In contrast, changes in VTE, smoking, and malignancies, including skin cancer, were not significantly different between TOFA initiators and initiators of other therapies. Among active users, the likelihood of discontinuation was higher among TOFA (N=2295, HR: 1.18 [1.10, 1.26], p< 0.001) compared to TNFi (N=12,042). The higher rate of TOFA discontinuation was more pronounced in the presence of cardiovascular comorbidities (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Shifts toward younger age, female sex, lower comorbidity, and lower rates of cardiovascular diseases were observed in patients initiating TOFA after the release of safety data. There was a lower proportion of VTE and malignancy as well, which did not reach significance. TOFA users, particularly those with cardiovascular comorbidities, were more likely than TNFi users to discontinue ongoing therapy following the release. These data suggest the ORAL Surveillance trial affected prescribing practices, with particular attention to those at high cardiovascular risk.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Song S, England B, Sauer B, George M, Wallace B, Cannon G, Mikuls T, Baker J. Changes in Characteristics of Patients Initiating and Discontinuing Advanced Therapies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Following Release of Safety Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-characteristics-of-patients-initiating-and-discontinuing-advanced-therapies-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-following-release-of-safety-data/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/changes-in-characteristics-of-patients-initiating-and-discontinuing-advanced-therapies-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-following-release-of-safety-data/