Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Eye involvement is an important cause of morbidity in rheumatology patients. Inflammatory eye diseases include conditions like scleritis, uveitis, retinitis and orbital inflammation. The complexity of these conditions requires specialized care resulting in significant financial burden for patients and the healthcare system. Identifying this financial burden is the first step towards developing strategies to address it. However, there is a lack of national data for the health care cost associated with inflammatory eye diseases. This study assesses health care cost due to ocular inflammatory diseases using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS), a nationally representative sample of hospital discharges in the United States.
Methods: We have conducted a retrospective analysis of the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) from 2016-2019. Patients with a primary diagnosis of uveitis and ocular inflammation were identified using International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes. NIS is the largest all payer database developed by the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) in the US and is ideal for investigating national estimates for health care cost. Healthcare costs are identified by analyzing aggregate and average hospital charges, aggregate and average hospital cost and length of stay.
Charge is the amount hospital billed and cost is the actual cost of hospital stay. Charges are converted to costs using cost-to-charge ratios based on hospital accounting reports from the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). Descriptive statistics are used to present the demographics and cost characteristics of patients.
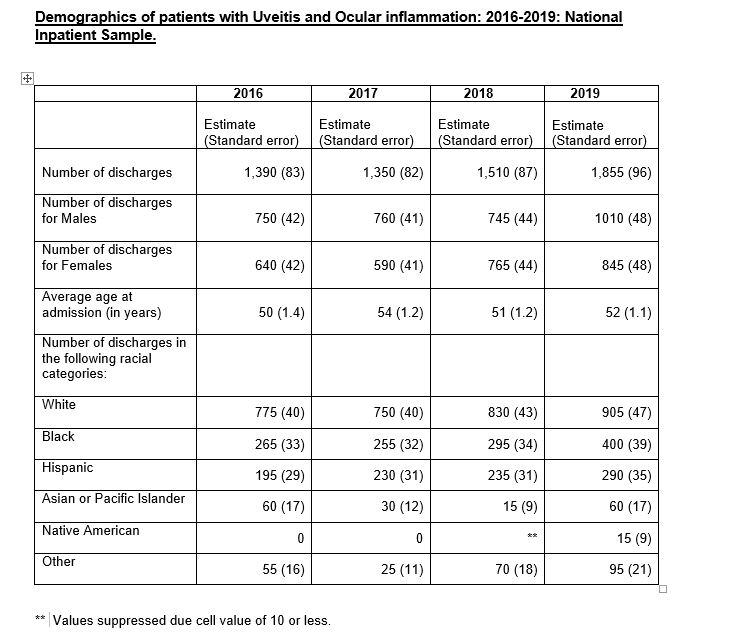
Results: A total of 6105 uveitis and ocular inflammation related hospitalizations were identified in the NIS database from 2016-2019. The average age of patients during the study period ranged between 50-54 years and a higher number of patients were males. The mean length of hospital stay was 6.3 (±.5) days.
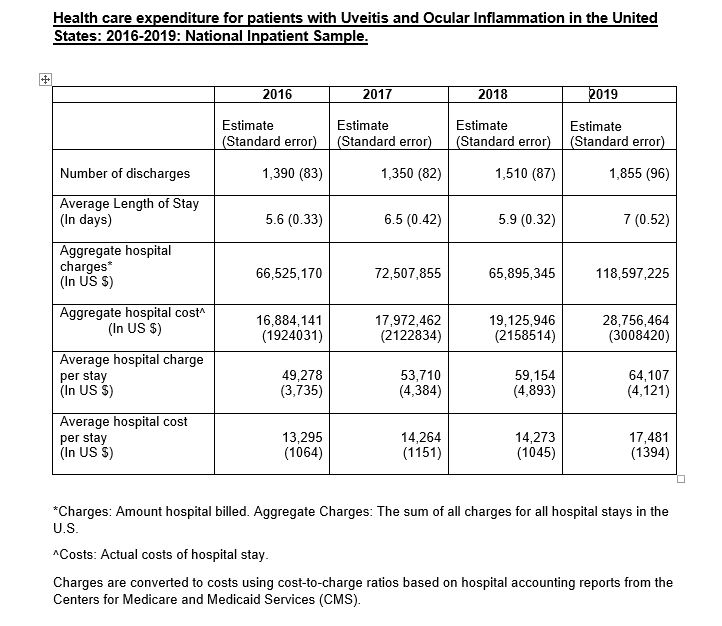
The total healthcare costs for uveitis and ocular inflammation related hospitalizations for the years 2016-2019 was $ 82,739,013 and it increased from the years 2016 to 2019. Breakdown of patient demographics, total and aggregate hospital charges, total and aggregate hospital cost and length of stay for individual years from 2016-2019 are shown in the table.
Conclusion: Inflammatory eye diseases impose substantial economic burden on both the patients and the healthcare system. Identifying the financial impact will help patients and healthcare providers in making informed treatment decisions. Further research is necessary to identify the cost-effectiveness of management strategies for inflammatory eye diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chauhan K, Scaife S, Buhnerkempe M. Understanding the Economic Impact of Autoimmune Eye Disease in the United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/understanding-the-economic-impact-of-autoimmune-eye-disease-in-the-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/understanding-the-economic-impact-of-autoimmune-eye-disease-in-the-united-states/