Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia (SAB) has high mortality.[1] We have previously identified an approximately doubled risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA),[2] but the role of anti-rheumatic treatments and disease activity remains disputed.[3,4]
We aimed to explore impact of treatment with glucocorticoids, biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) and of disease activity on the risk of SAB in RA patients.
Methods: We performed a case-control study nested in a nationwide cohort of RA patients (DANBIO, positive predictive value of RA=96%) with no history of SAB. Cases had a first-time microbiologically verified SAB during 2010-2018. Controls were incidence density matched (age and sex) at time of SAB (index date). We linked data from DANBIO (e.g. disease activity, anti-rheumatic treatment) to other national registries (to identify e.g. comorbidities, prescriptions, socioeconomic status). Users of oral glucocorticoids and bDMARDs 0-2 years before the index date were identified in DANBIO or by relevant prescriptions. Daily dose of oral glucocorticoids at the index date was 1) retrieved from DANBIO or 2) estimated from the latest prescription. Risk associated with treatment and disease activity was assessed by multivariate conditional logistic regression. For treatments, the number needed to harm (NNH) was calculated using the fully adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) and the incidence rate (IR) in the cohort (NNH=(1/(OR-1)*IR). Missing data was handled by multiple imputation.
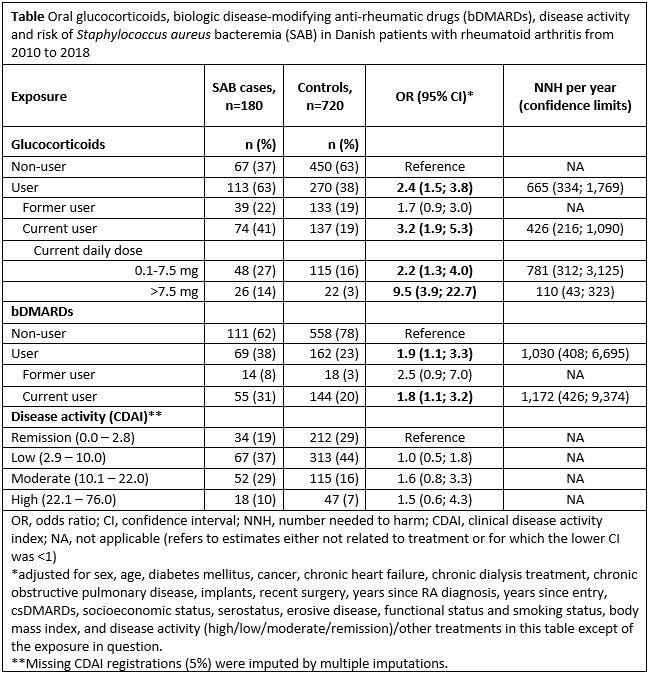
Results: We observed 180 cases among 30,479 RA patients (IR 106.7/100,000 person-years) and matched 720 controls (53% women, median age 73 years, IQR 65;80). For cases, orthopedic implants were frequent (53%/34% for cases/controls), many had recent surgery (38%/5%), longstanding RA (13 years (6;21)/8 (4;14)), bone erosions (48%/39%), moderate (29%/16%) or high (10%/7%) disease activity, and used glucocorticoids (41%/19%) and bDMARDs (31%/20%). Risk of SAB increased dose-dependently for current users of oral glucocorticoids (adjusted OR=9.5 95% CI (3.9; 22.7) for >7.5 mg/day) (Table). For bDMARDs, adjusted OR was 1.8 (1.1; 3.2) for current use and 2.5 (0.9; 7.0) for former use. Correspondingly, the NNH was 110 for current use of glucocorticoids >7.5mg/day and 1,172 for current bDMARD use. For disease activity, adjusted ORs were above 1 (statistically non-significant) for moderate and high disease activity compared with remission (Table).
Conclusion: Oral glucocorticoids were associated with a dose-dependent increased risk of SAB and use of >7.5 mg/day appeared to be a clinically relevant risk factor for SAB with a relatively small number of patients needed to be exposed for one extra case to occur. Use of bDMARDs was associated with increased risk, however, the NNH was ten-fold higher than for higher dose glucocorticoids. Disease activity had minor impact. These results emphasize that glucocorticoids >7.5 mg/day should be prescribed with caution.
REFERENCES
1 Laupland KB et al. doi:10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03903.x
2 Dieperink SS et al. doi:10.1080/03009742.2022.2049057
3 Sams M et al. doi:10.1007/s00296-015-3239-8
4 Smit J et al. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.04.023
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dieperink S, Glintborg B, Mehnert F, Nørgaard M, Oestergaard L, Benfield T, Torp-Pedersen C, Petersen A, Hetland M. The Increased Risk of Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteremia in Rheumatoid Arthritis – What Is the Impact of Glucocorticoids, Biologic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs and Disease Activity: A Danish Nationwide Nested Case-Control Study in the DANBIO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-increased-risk-of-staphylococcus-aureus-bacteremia-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-what-is-the-impact-of-glucocorticoids-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-and-disease-activity-a/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-increased-risk-of-staphylococcus-aureus-bacteremia-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-what-is-the-impact-of-glucocorticoids-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-and-disease-activity-a/