Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Metabolic and Crystal Arthropathies – Basic and Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease lacks recommendations on treatment strategies. This study reports on treatment modalities used in European tertiary hospitals for the management of patients with chronic CPPD disease.
Methods: Charts from patients with a diagnosis of chronic CPPD disease were retrospectively reviewed. Chronic CPPD disease was defined as persistent CPP crystal inflammatory arthritis lasting for more than 3 months and/or recurrent ( >2 episodes/year) acute episodes of CPP crystal arthritis. Patients came from 4 centers in France, 1 in Spain and 2 in Italy. All treatments started from the 1st of January 2015 were recorded.
Baseline characteristics of patients were collected, including clinical presentation, items for CPPD diagnosis, disease activity (Patient Global Assessment (PGA) 0-10 on a numeric scale), quality of life on a 0 to 4 Likert scale, and treatments before 2015. The median number [inter-quartile range] of treatments used prior to each new treatment initiated was noted. Visits at baseline, months 3, 6, 12 and 24 were recorded for each new treatment initiated. Treatment efficacy was assessed with a 0 to 4 Likert scale according to the data from the files of the patients. If the treatment was discontinued before the 24 months visit, the date and cause was recorded.
Results: A total of 129 patients were included in the study (n = 66 in France, n = 21 in Spain, and n = 42 in Italy), cumulating n=194 treatments initiated since 2015, and a mean number of 1.8 (±0.9) treatments per patient. Mean age was 69.6 ± 13.1 years, n = 83 (64.3%) were females, duration of symptoms before the first recorded treatment was 16.8 (±27.1) months. Overall, n = 85 (65.9%) patients presented with persistent CPP crystal inflammatory arthritis and n = 83 (64.3%) presented with recurrent acute episodes of CPP crystal arthritis flares. Mean PGA at baseline was 6.6 ± 1.5, resulting in impaired quality of life (< 4 on the Likert scale) in 94.6% of patients.
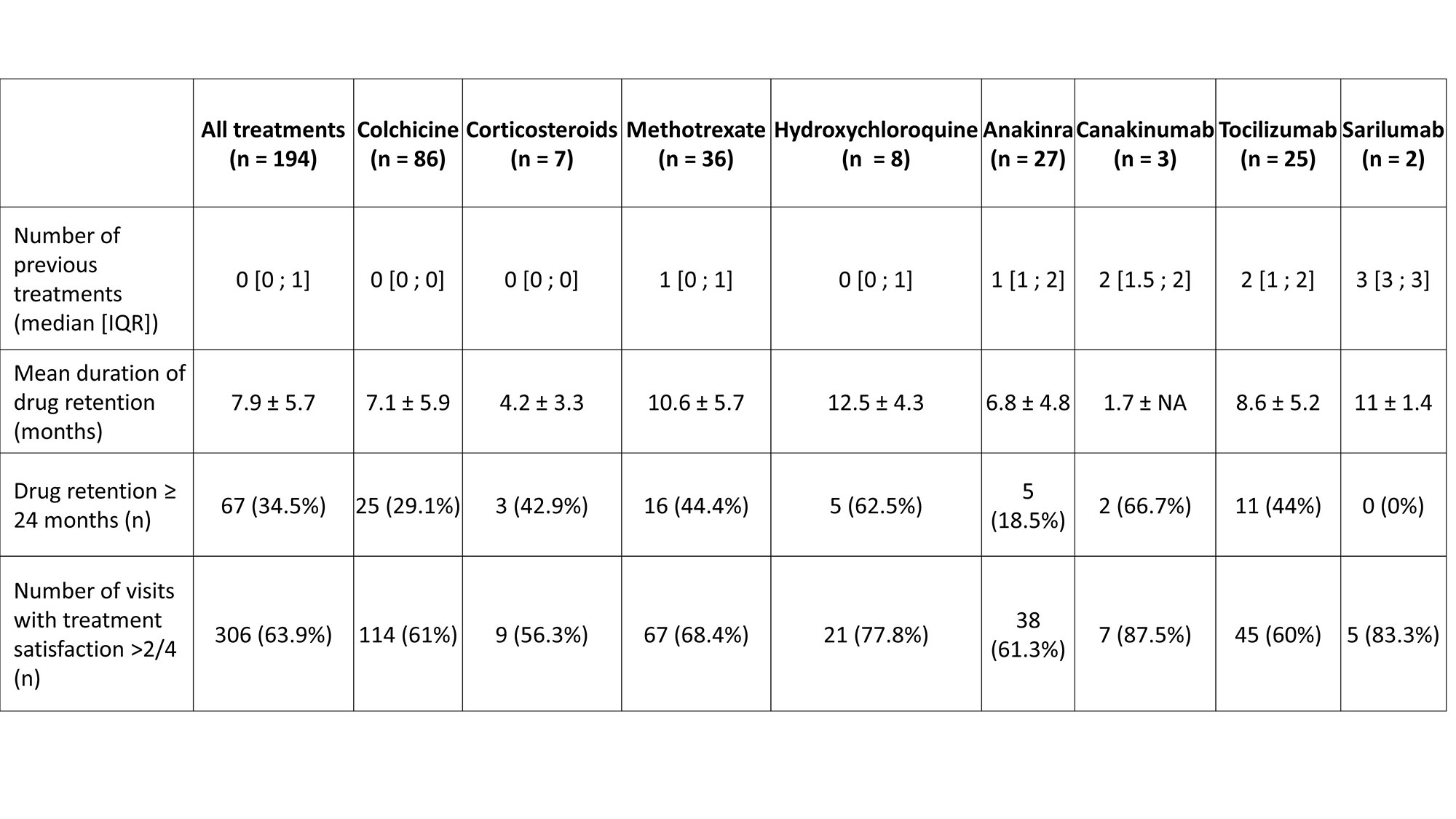
The most frequent first-line therapy was colchicine in n= 83 (72.8%) patients (mainly 1mg QD (57.8%) and 0.5mg QD (33.7%) QID). At 24 months, n = 49 (59.0%) of patients were still on colchicine, n = 25 (30.1%) had discontinued colchicine for inefficacy, n = 4 (4.8%) for intolerance, and n = 5 (6.0%) for prolonged symptom remission.
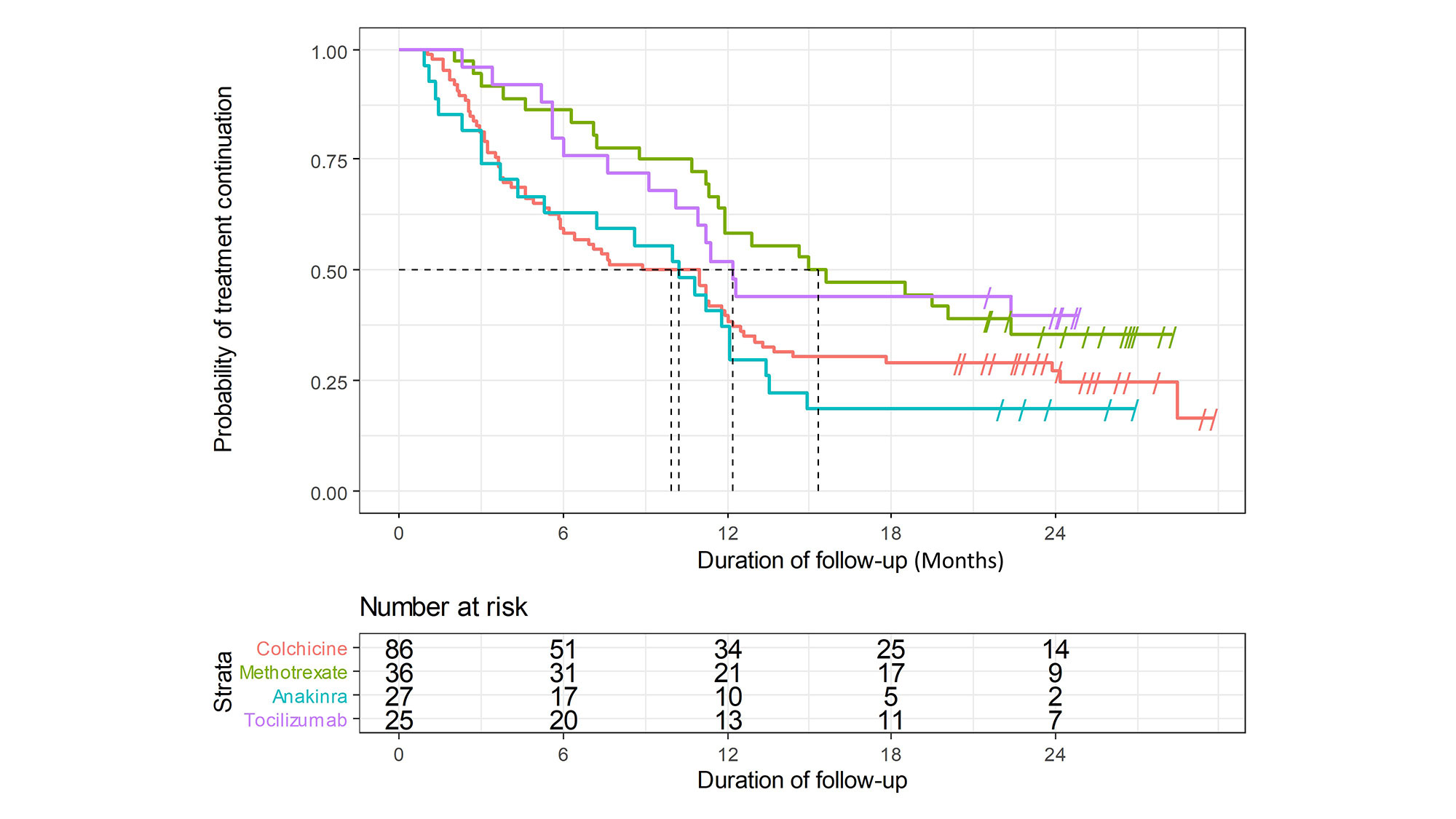
The median position of each treatment in the therapeutic strategy, drug retention and treatment efficacy are reported in Table 1. Treatment retention for drugs with at least 20 initiations are reported in Figure 1. Combination of treatments was prescribed in 35 patients (27.1%), mostly using corticosteroids (n = 20, 66.7% of combinations).
Conclusion: This study shows that long term colchicine is the most frequent first-line therapy prescribed for chronic CPPD disease in a variety of European centers. Methotrexate is still significantly used, while anakinra and tocilizumab are the most frequent biological therapies. Although this is an uncontrolled study, our results call for adequately powered clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate, colchicine and biological agents in persistent CPP crystal arthritis and recurrent acute CPP crystal arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Damart J, Sirotti S, Andrès M, Cipolletta E, Filippou G, Carboni D, Filippucci E, Diez P, Abhishek A, Latourte A, Ea H, Ottaviani S, Letarouilly J, Desbarbieux R, Graf S, Norberciak L, Richette P, Pascart T. Therapeutic Strategies for Patients with Chronic Manifestations of Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-strategies-for-patients-with-chronic-manifestations-of-calcium-pyrophosphate-deposition-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-strategies-for-patients-with-chronic-manifestations-of-calcium-pyrophosphate-deposition-disease/