Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: Abstracts: B Cell Biology and Targets in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disease
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by various autoantibodies. In particular, targeting autoreactive B cells could be a promising therapy with minimal adverse effects and dependence on corticosteroids. Some phenotypically distinct B cell populations including IgD-, CD27-, CD11c+, and CXCR5lo double negative 2 (DN2) B cells, are expanded in lupus peripheral blood. DN2 B cells, which includes autoreactive B cells capable of differentiating into antibody secreting cells (ASCs), exhibit high intracellular expression of T-bet. Aiming to identify therapeutic targets in SLE, we found that phospholipase D4 (PLD4) is expressed on the surface of most plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) and less on the surface of B cells in healthy donors (HDs). PLD4 is believed to be an endolysosomal nuclease that regulates signals of toll-like receptors(TLRs) 7,8, and 9. We aimed to investigate the surface expression of PLD4 on B cells in SLE and to test PLD4+ B cells as a possible target for SLE treatment.
Methods: We developed monoclonal antibodies against PLD4. Flow cytometry was used to analyze PLD4 expression on several populations among peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from individuals with SLE (n = 40) and HDs (n = 11) classified by CD19, CD3, CD14, CD16, CD303, IgD, CD27, CD38, CD43, CD11c, and CXCR5. All SLE patients met ACR 1997 classification criteria. The prevalence of PLD4+ CD19+ B cells was compared between individuals with SLE and HDs, and their correlation with disease status was assessed. Furthermore, we investigated the intracellular expression of T-bet in SLE PLD4+ B cells. Certain compartments of B cells were isolated for culture to test their abilities to differentiate into ASCs by ELISpot.
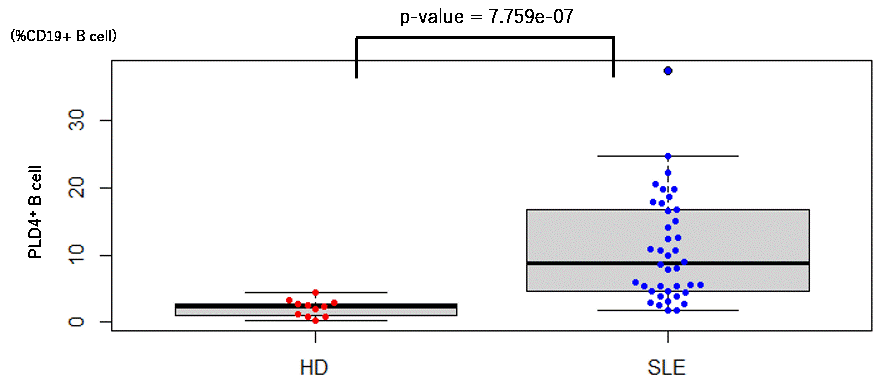
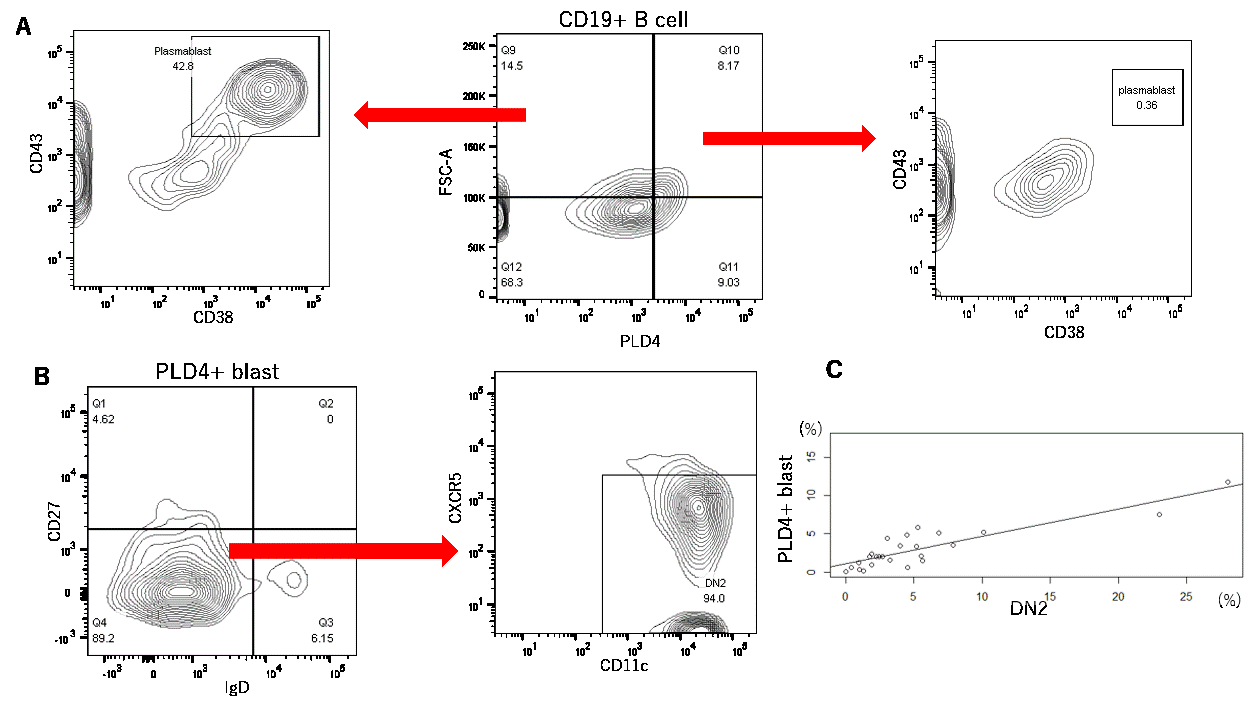
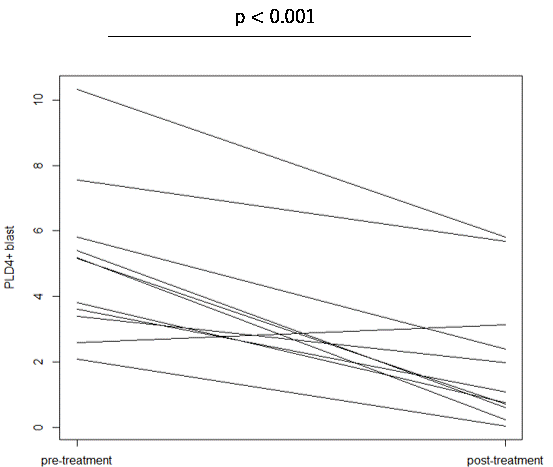
Results: Among PBMCs, PLD4 was expressed only on pDCs and B cells. The ratio of PLD4+ CD19+ B cells to the whole CD19+ B cells was significantly higher in individuals with SLE than in HDs (mean ± SEM%, 11 ± 1.2% in SLE vs 2.1 ± 0.37% in HD, P < 1.0×10-6). In terms of cell size represented on forward scatter area density plot (FSC-A,) a subset of PLD4+ B cells was comparable to CD38+ CD43+ plasmablasts. We considered PLD4+ large B cells as distinct blastic B cell populations and named them “PLD4+ blasts.” Up to 90% of PLD4+ blasts were CD11c+ and CXCR5lo DN2, but few were plasmablasts. The frequencies of PLD4+ blasts significantly correlated with those of DN2 (spearman = +0.79, P < 1.0 × 105). When divided into four compartments by PLD4 and FSC-A (PLD4+/- and blast/small), PLD4+ blasts were exclusively and highly positive for intracellular T-bet expression ( >75% in PLD4+ blast, < 50% in the other compartments, n = 2). In some cases of new-onset SLE, PLD4+ blasts significantly decreased after immunosuppressive therapy (5.0% vs 2.0%, P < 1.0×104, paired t-test). Finally, when sorted and cultured in vitro with TLR 7 or 9 ligands, PLD4+ blasts differentiated into ASCs secreting comparable or higher levels of IgG than whole CD19+ B cells.
Conclusion: PLD4+ B cells are expanded in SLE and those blastic highly overlap with DN2. Targeting cell surface PLD4 could be a novel therapeutic strategy for SLE.
SLE and healthy donors. SLE showed significant expansion of PLD4+ blasts.
A) “PLD4+ blasts” expanded in SLE are as large as plasmablasts, but include few plasmablasts.
B) PLD4+ blasts are mostly composed of DN2 B cells. C) The frequencies of DN2 and PLD4+blasts are significantly correlated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yasaka K, Yamazaki T, Sato H, Shirai T, Fujii H, Ishii T, Harigae H. Phospholipase D 4 Is a Novel Surface Marker of a Distinctive B Cell Population Overlapping with Double Negative 2 B Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phospholipase-d-4-is-a-novel-surface-marker-of-a-distinctive-b-cell-population-overlapping-with-double-negative-2-b-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/phospholipase-d-4-is-a-novel-surface-marker-of-a-distinctive-b-cell-population-overlapping-with-double-negative-2-b-cells/