Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a heterogenous, multi-dimensional disease. Little is known about factors underpinning treatment intensification in routine practice. Treatment pathways are not well defined and need individual tailoring. The purpose of the ASSIST study was to investigate the prescribing practice for PsA in routine care and whether the use of the patient reported outcome (PRO), PsA Impact of Disease questionnaire (PsAID-12), impacted treatment decisions.
Methods: ASSIST was a cross sectional study of patients diagnosed with PsA (by a rheumatologist using CASPAR criteria). Patients were selected using systematic sampling with random starting numbers generated for each site. Participants were treated in their usual routine clinical practice, decisions on whether treatment was escalated, unchanged or reduced (and why) were recorded. The PsAID-12 questionnaire and additional PROs were provided to patients in one single study visit, during a routine clinic appointment. Univariable and multivariable analyses were performed to explain treatment escalation. There was no imputation of missing data.
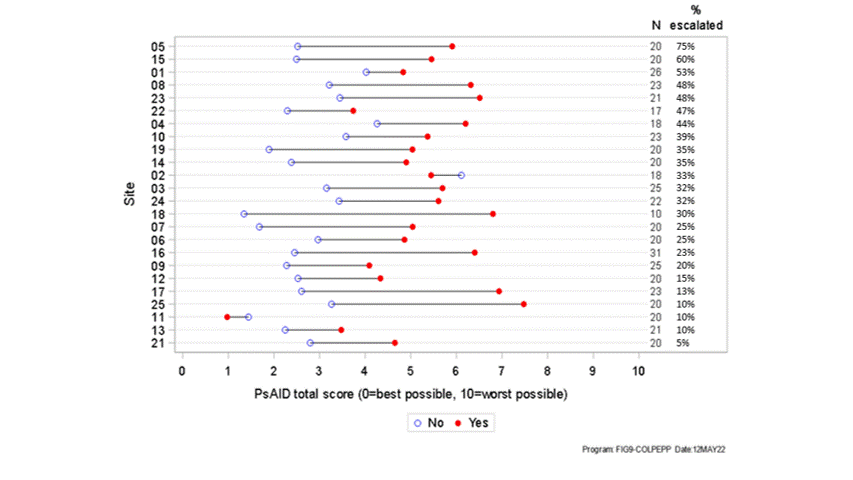
Results: 503 patients from 24 centres across five countries in Europe (49.1% F, 50.9% M) aged 18 years or above (mean age 53) participated in the survey between 12/07/2021-22/03/2022. Overall, treatment was changed for 182 patients (36.2%) with an increase in treatment being the most common type of change (160 patients, 31.8%). Treatment escalation was most common in the UK (51 patients, 47.7%) compared to other countries (31.5% of patients or fewer). In 22/24 sites, the mean PsAID score for patients with treatment escalation was higher than that for those with no escalation. (figure 1) The PsAID score was found to have statistically significant association with the odds of treatment escalation (OR: 1.58; p< 0.0001) – the estimated odds of treatment escalation increased by 58% with every 1-point increase in the score. A statistically significant relationship between treatment escalation and patient characteristics, physician characteristics, disease activity, disease impact was identified (Figure 2). Only age, tender joint count and comorbidity index were not significantly associated with treatment escalation. A high level of correlation was seen between a number of these variables, including physician’s global assessment of disease and the patient reported PsAID score. In most cases, the clinicians reported that the PsAID score did not significantly influence the decision on treatment escalation.
Conclusion: The PsAID score had a significant association with odds of treatment escalation. The greater the PsAID score, the more likely escalation in treatment. Several factors influenced treatment change indicating the complex decision making in routine clinics. Clinicians reported PsAID score did not impact treatment escalation in most cases, but a significant correlation between PsAID and physician global scores was seen. Our work highlights the influence of multiple factors on decision making when reviewing treatments for individuals with PsA providing insight into the management of patients with this complex condition.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coyle C, Whately-Smith C, Brooke M, Kiltz U, Lubrano E, Queiro R, Trigos D, Brandt-Juergens J, D'Angelo S, Delle Sedie A, Dernis E, Helliwell P, Ho P, Hueber A, JOVEN B, Koehm M, Montilla C, Packham J, PINTO TASENDE J, Ramirez Garcia F, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Scrivo R, twigg s, Welcker M, Wirth T, Gossec L, Coates L. How Does PsAID Implementation Affect Treatment Intensification and Patient Satisfaction in PsA? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-does-psaid-implementation-affect-treatment-intensification-and-patient-satisfaction-in-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/how-does-psaid-implementation-affect-treatment-intensification-and-patient-satisfaction-in-psa/