Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
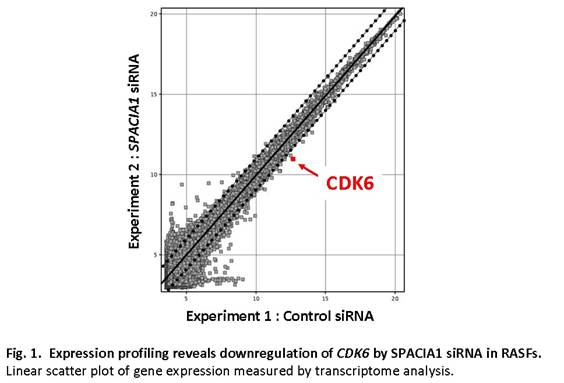
Background/Purpose: SPACIA1 is a novel gene associated with abnormal synovial proliferation. We have already shown that SPACIA1 could be involved in the progression of synovitis in vivo. We previously reported that SPACIA1 siRNA inhibited the proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs) and delayed the cell cycle at the G1 phase. These findings indicate that SPACIA1 is tightly linked to functional genes at the G1 phase; however, the molecular mechanism is still unclear. In particular, CDK6 was found by transcriptome analysis to be downregulated in RASFs that were transfected with SPACIA1 siRNA (Fig. 1.). In the present study we investigated the mechanisms involved in the SPACIA1-related regulation of CDK6 gene expression in vitro.
Methods : RASFs were transfected with control siRNA or SPACIA1 siRNA. Seventy-two hours after transfection, we examined the expression of several key regulators of G1 phase mRNA and protein production by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. To determine the processes responsible for SPACIA1 down-regulation of CDK6 expression, the basal luciferase activity of pGV-basic2 luciferase reporter containing the CDK6 5′-upstream region was analyzed by luciferase assay in cells treated with control siRNA or SPACIA1 siRNA. To determine whether the stability of CDK6 mRNA is regulated by SPACIA1, we compared mRNA decay rates of CDK6 transcripts analyzed by qRT-PCR at different time points following control/SPACIA1 siRNA- and actinomycin D (Act-D)-treatment.
Results : Among the key regulators of the G1 phase, the only gene to be significantly reduced by SPACIA1 siRNA was CDK6, which was reduced to half of its control expression. The basal luciferase activity of the reporter containing the Cdk6 5′-upstream region averaged 8 to 10-fold higher activity than the promoter-less pGV-basic2 luciferase vector. The Cdk6 5′-upstream region could function as a promoter, however, CDK6 promoter activity was not affected by SPACIA1 knockdown. Knockdown of SPACIA1 accelerated the degradation of CDK6 mRNA in the presence of Act-D relative to control siRNA. After 60min of Act-D treatment, 40% of CDK6 mRNA was reduced by SPACIA1 siRNA, but, not control siRNA. This indicates that SPACIA1 is involved in regulation of CDK6 mRNA decay.
Conclusion: We identified that SPACIA1 regulates the functional gene, CDK6, at the G1 phase, and found that the presence of SPACIA1 is due to alterations in CDK6 mRNA turnover.
Disclosure:
R. Komatsu,
None;
R. Fujii,
None;
T. Sato,
None;
Y. Yamano,
None;
K. Yudoh,
None;
M. Beppu,
None;
K. Nishioka,
None;
T. Nakajima,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cdk6-transcripts-expression-control-by-the-synoviocyte-proliferation-gene-spacia1/