Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
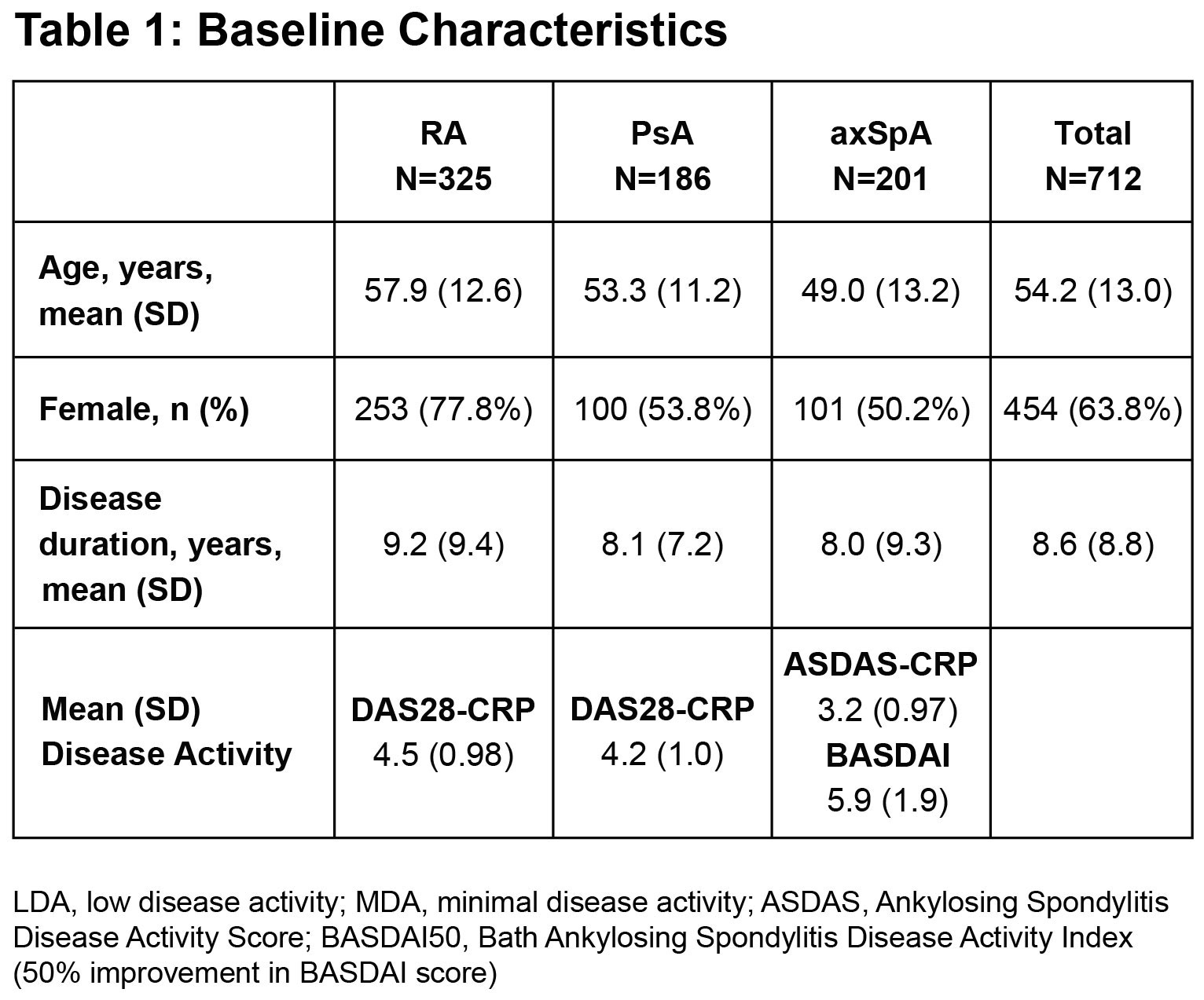
Background/Purpose: Patients with inflammatory arthritis often experience secondary non-response to a first-line tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor (TNFαi). GO-BEYOND is a study program comprised of 6 observational, prospective studies conducted across Europe in patients (pts) with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), or axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) to evaluate the effectiveness of golimumab (GLM) after an inadequate response to a previous TNFαi. We conducted a pooled analysis of structured data from these studies to provide a more precise estimate of GLM effectiveness for each of these rheumatic diseases.
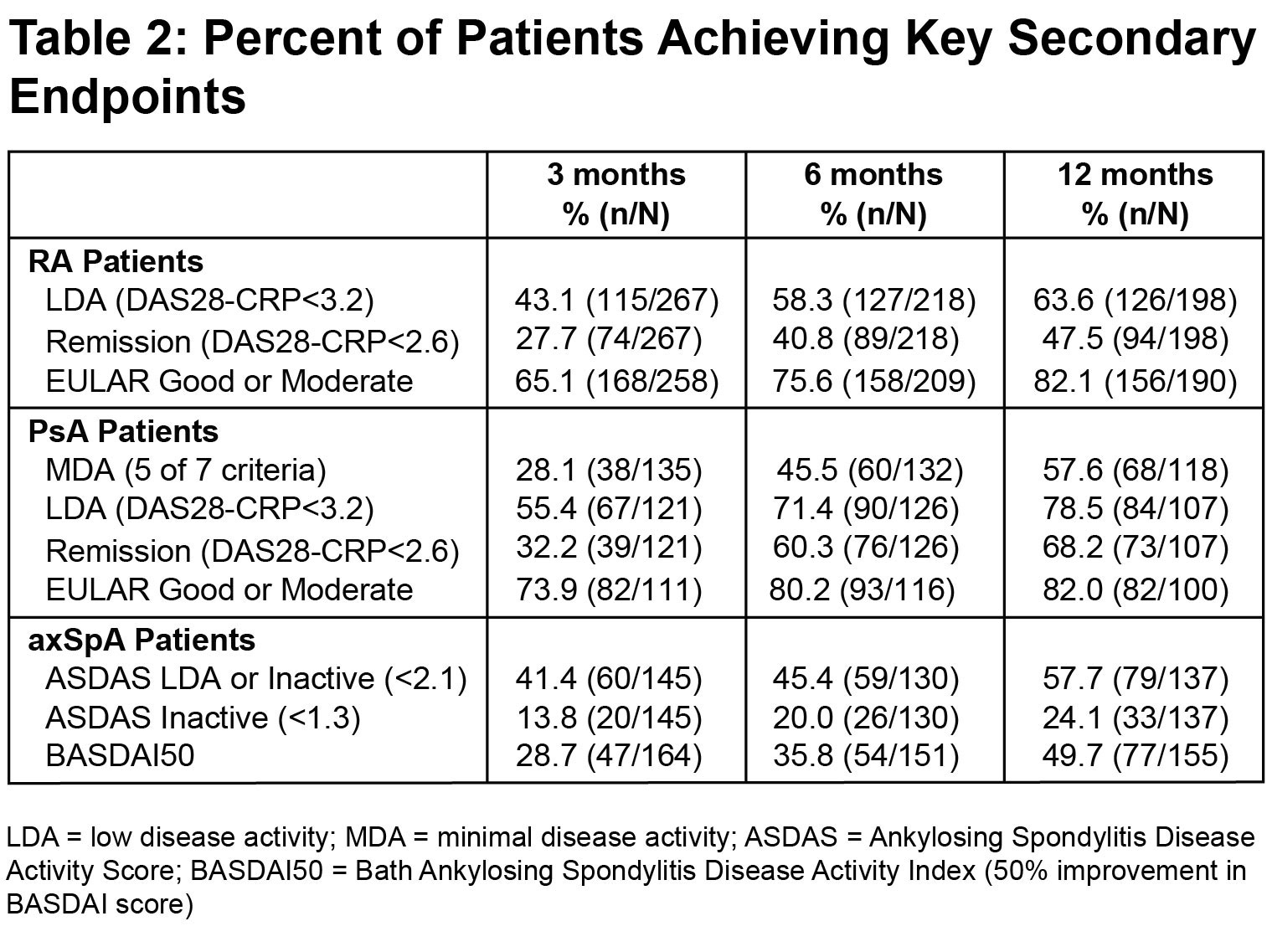
Methods: The individual studies in GO BEYOND included common disease-specific primary and secondary endpoints, including quality of life (QoL) assessments, thereby allowing for a pooled analysis. Pts were previously treated with one TNFαi (pts who used >1 TNFαi were excluded) and demonstrated secondary failure for loss of efficacy, tolerability (e.g., injection-site reactions), or inconvenience (e.g., injection frequency). Primary TNFαi non-responders were ineligible. Pts were followed for up to 12 months, with protocol-specified analyses based on observed data reported (i.e., the sub-populations of patients with available data for each endpoint). The primary endpoints (PE) were assessed at 6 months, as the proportion of pts achieving the following: low disease activity (LDA, DAS28-CRP< 3.2) in RA; Minimal Disease Activity (MDA, fulfillment of 5 of 7 outcome measures) in PsA; and Inactive or Low Disease Activity (ASDAS< 2.1) in axSpA. Secondary efficacy endpoints assessed disease activity through multiple indices at 3, 6 and 12 months, and QoL after 6 and 12 months with the EQ-5D-3L visual analogue scale (VAS). Treatment persistence was an exploratory endpoint. A more stringent, supportive analysis using non-responder imputation (NRI) was also performed for the primary endpoint. Adverse events (AE) were monitored.
Results: A total of 712 pts were included: 325 with RA, 201 with axSpA and 186 with PsA. Baseline characteristics are reported in Table 1. The most common prior TNFαi were etanercept (41.6%) and adalimumab (31.7%); the most common reason for switching was loss of efficacy (76.8%). The % (n/N) of pts who achieved the PE were 58.3% (127/218) in RA, 45.5% (60/132) in PsA, and 45.4% (59/130) in axSpA; results for the NRI analyses are also shown in the Figure. Improvements in disease activity were also observed at 3 and 12 months (Table 2). The mean EQ-5D-3L VAS health score increased over time, showing improved QoL (Figure). Treatment persistence rates (n/N) at 3, 6 and 12 months were 84.7% (603/712), 73.9% (526/712), and 67.8% (483/712). There were no new safety signals observed; serious AEs occurred in 4.4% and serious infections in 1% of pts.
Conclusion: This pooled analysis of six European studies in patients with active RA, PsA or axSpA who experienced secondary failure to an initial TNFαi showed that treatment with GLM was effective and represented a valid second-line option. GLM provided clinically relevant improvements in disease activity and QoL through the observation period and showed high persistence, with two-thirds of patients remaining on treatment at 12 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Govoni M, Batalov A, Boumpas D, D'Angelo S, De Keyser F, Flipo R, Kellner H, Leroi H, Khalifa A. Effectiveness of Golimumab in the Treatment of Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, or Axial Spondyloarthritis Who Failed Initial TNFα Therapy: A Pooled Analysis of European Prospective Observational Studies (the GO BEYOND Program) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-golimumab-in-the-treatment-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-or-axial-spondyloarthritis-who-failed-initial-tnf%ce%b1-therapy-a-pooled-analysis-of-eur/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-golimumab-in-the-treatment-of-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-psoriatic-arthritis-or-axial-spondyloarthritis-who-failed-initial-tnf%ce%b1-therapy-a-pooled-analysis-of-eur/