Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Dermatologic symptoms of PsA can substantially impact patient (pt) health‑related quality of life (HRQoL);1 itch is the most commonly reported, and among the most bothersome of, symptoms.2 In pts treated with tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA,3,4 improvements were observed in itch, Physician Global Assessment of Psoriasis (PGA‑PsO), and HRQoL measures;5 however, the relationships between these outcomes have not been quantified. This post hoc analysis aimed to evaluate and quantify relationships between dermatologic symptoms and HRQoL in pts with PsA.
Methods: Data were pooled from 2 Phase 3 trials of pts with active PsA receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily, or placebo (12‑month OPAL Broaden [NCT01877668]; and 6‑month OPAL Beyond [NCT01882439]).3,4 A repeated measures longitudinal model assessed relationships between Itch Severity Item (ISI; numeric scale 0 [no itching]–10 [worst possible itching]), PGA‑PsO (5‑point severity scale defined by descriptors of erythema, induration, and scaling), and Patient’s Global Skin Assessment (PSA; 100‑mm Visual Analog Scale [VAS]) as predictors, and Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI; general dermatology questionnaire) and Short Form‑36 Health Survey version 2 (SF‑36v2) domains (physical functioning, role‑physical, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social functioning, role‑emotional, mental health, Physical Component Summary, Mental Component Summary) as outcomes. Each longitudinal model included one predictor and one outcome.
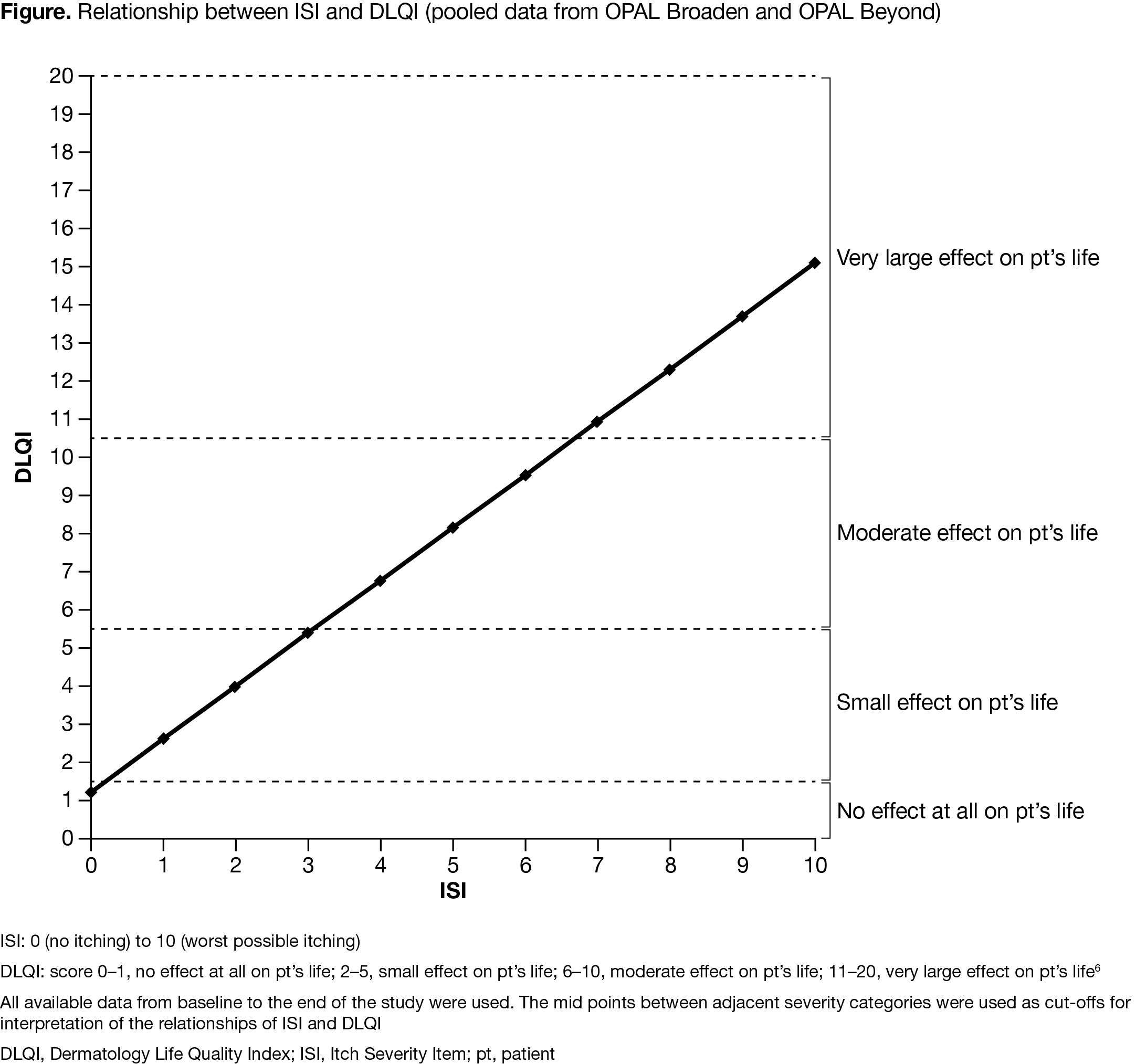
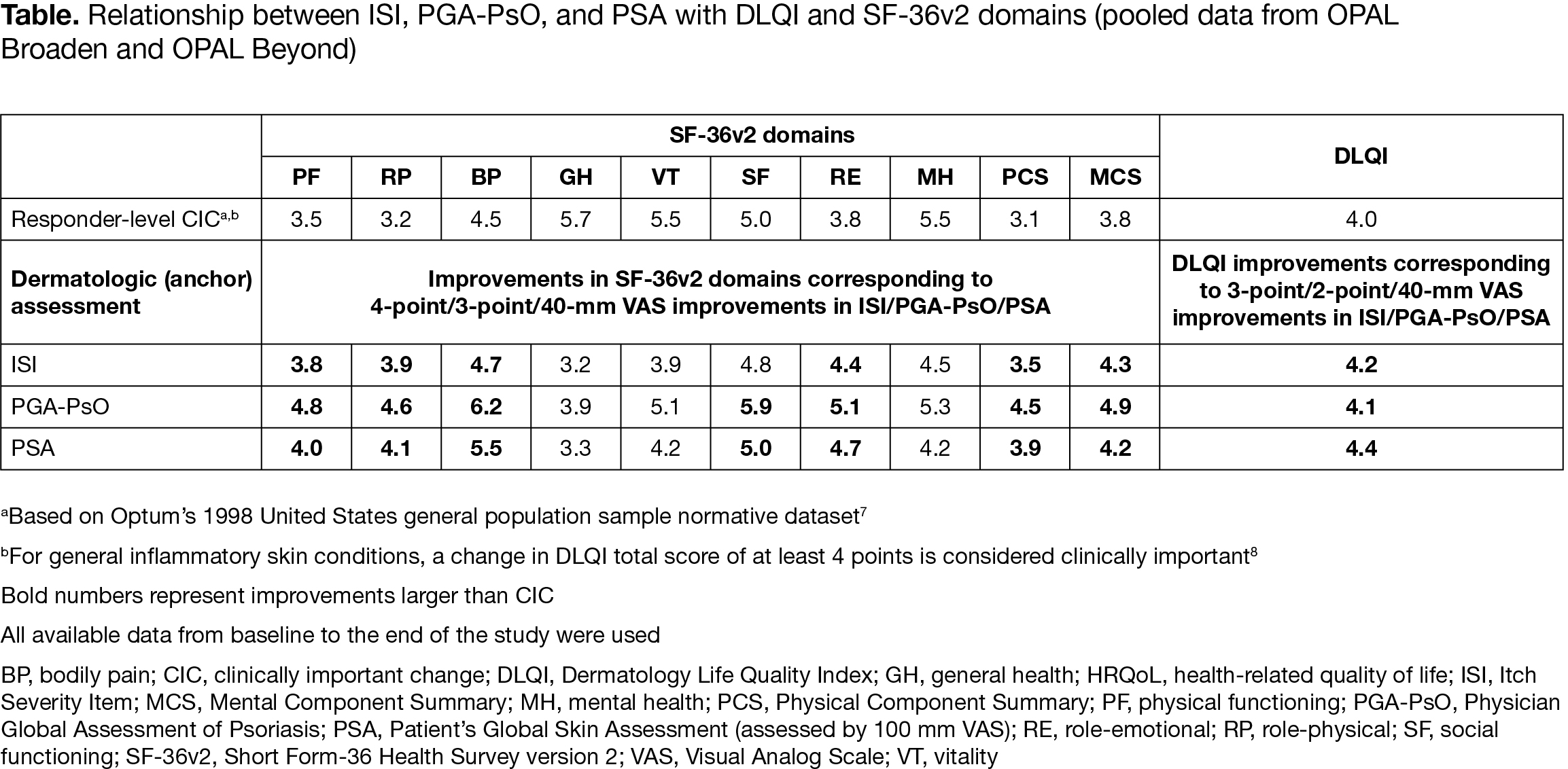
Results: An approximately linear relationship was observed between ISI, PGA‑PsO, and PSA with total DLQI score, and each SF‑36v2 domain. There was a direct relationship between itch severity (measured by ISI), severity of illness (measured by PGA‑PsO), and pts’ perception of disease (measured by PSA) and general dermatology QoL (measured by DLQI; Figure), as well as between ISI, PGA‑PsO, and PSA and SF‑36v2 domains. 3‑point/2‑point/40‑mm VAS improvements from baseline (BL) in ISI/PGA‑PsO/PSA, respectively, were associated with clinically meaningful improvements in DLQI ( > 4 points; Table). 4‑point/3‑point/40‑mm VAS improvements from BL in ISI/PGA‑PsO/PSA were generally associated with clinically important improvements across SF‑36v2 domains (Table). A 4‑point ISI improvement was associated with a 4.7‑point improvement in SF‑36v2 bodily pain domain.
Conclusion: Substantial and quantifiable links exist between dermatologic symptoms and HRQoL in pts with PsA; physical and mental domains are ameliorated by tofacitinib. These findings help to inform pt care and pt‑centered research.
1. Merola JF et al. Rheumatol Ther 2019; 6: 33-45.
2. Lebwohl MG et al. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014; 70: 871-81.
3. Mease P et al. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 1537-50.
4. Gladman D et al. N Engl J Med 2017; 377: 1525-36.
5. Merola JF et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2020; 34: 2809-20
6. Hongbo Y et al. J Invest Dermatol 2005; 125: 659-64.
7. Ware JE, Jr. et al. User’s manual for the SF-36v2® health survey (2nd ed.) 2007
8. Basra MK et al. Dermatology 2015; 230: 27-33.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by K Thompson, CMC Connect, funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Bushmakin A, Cappelleri J, Young P, Germino R, Merola J, Yosipovitch G. Relationships Between Dermatologic Symptoms and Health-related Quality of Life in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Post Hoc Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-dermatologic-symptoms-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationships-between-dermatologic-symptoms-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-post-hoc-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/