Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: PsA is an inflammatory rheumatic disease with manifestations including synovitis and enthesitis. During extensive study programs, IXE has shown a treatment effect across domains affected by PsA. Ixekizumab (IXE) is an IL17A inhibitor approved for the treatment of active PsA and axial SpA.
We sought to determine whether there is any association between the improvement of synovitis with that of enthesitis from baseline (BL) through week (wk) 52 in patients (pts) with PsA treated with IXE. Additionally, the association between the improvement of synovitis and enthesitis on health-related quality of life and patient-reported outcomes was investigated.
Methods: Data from SPIRIT-P1 (NCT01695239), SPIRIT-P2 (NCT02349295) and SPIRIT-H2H (NCT03151551) were analyzed. These were randomized, phase 3 trials involving pts with active PsA either biologic DMARD-naïve (P1, H2H); or who were TNF-inhibitor-experienced (P2).
We examined the patient population randomized to IXE-treatment (80 mg of ixekizumab every 4 weeks [IXEQ4W]), that had both synovitis and enthesitis at BL. For each study, a standardization procedure was applied to each study data in order to overcome the differences in score range between LEI and SJC. The Pearson correlation coefficient between improvement from BL in enthesitis and synovitis was calculated at each time point.
The mean improvement in the SF-36 Physical Component Summary score [PCS], the Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity [Pt GA], and the EuroQOL five dimensions [EQ5D]-visual analogue [VAS] score) was calculated over time for pts who reached or did not reach resolution of both enthesitis and synovitis at wk 52.
Missing data were imputed with modified Baseline Carried Out Forward (mBOCF) for continuous outcomes. Non-responder imputation was used for pts with missing resolution of enthesitis or synovitis.
Results: At BL, 68 (63% of patients treated with IXEQ4W in the ITT population), 68 (56%) and 159 (56%) pts from P1, P2 and H2H respectively, had both synovitis and enthesitis. In all 3 trials, the standardized mean change from baseline in synovitis and enthesitis showed a similar pattern over time (Figure 1). When statistically significant, Pearson correlation coefficient values ranged from 0.16 to 0.40 (Table), indicating a positive association between mean improvement in synovitis and enthesitis.
Pts were grouped according to whether they achieved resolution of both synovitis and enthesitis at wk 52, either or neither. We observed an improvement of SF-36 over the 52 wks regardless of the resolution of synovitis or enthesitis. The most pronounced improvement was shown by pts achieving resolution of both synovitis and enthesitis followed by the pts achieving one or the other (Figure 2). There was no difference in the trajectories for EQ5D and PtGAD in pts regardless of resolution of synovitis and/or enthesitis (data not shown).
Conclusion: Across the SPIRIT trials, treatment with IXE led to the significant improvement in synovitis and enthesitis with a positive association between the improvement of both. Furthermore, those pts that resolve both measures at wk 52, experienced an earlier and greater improvement in the SF-36 Physical Component Scale.
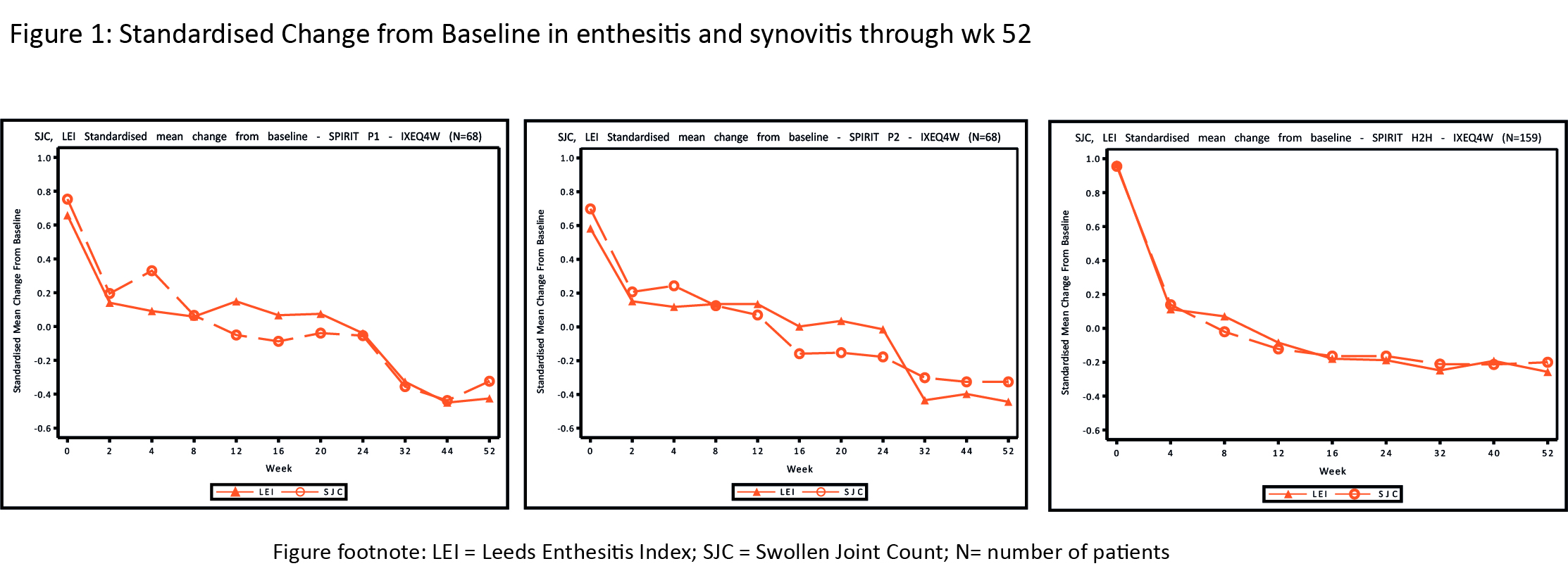 Figure footnote: LEI= Leeds Enthesitis Index; SJC = Swollen Joint Count; N = number of patients
Figure footnote: LEI= Leeds Enthesitis Index; SJC = Swollen Joint Count; N = number of patients
 Table footnote: Correlation coefficients range from -0.05 to 0.40. A more intense color represents a higher correlation.
Table footnote: Correlation coefficients range from -0.05 to 0.40. A more intense color represents a higher correlation.
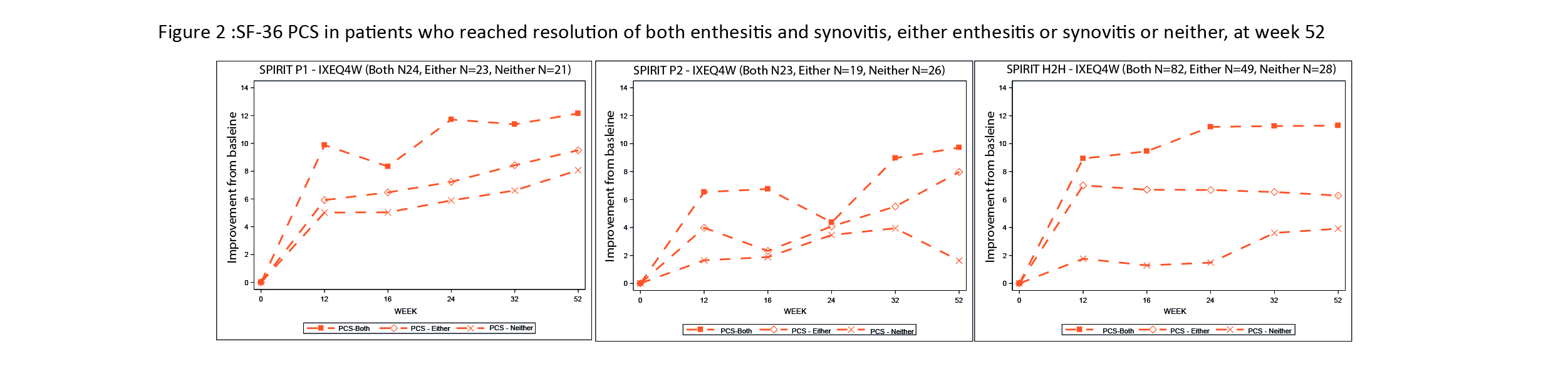 Figure footnote: Both = patients who achieved resolution of both enthesitis & synovitis at wk 52; Either = patients who achieved either resolution of enthesitis or synovitis at wk 52; Nf number of patients; Neither = patients who did not achieve resolution of enthesitis nor synovitis at wk 52; PCS – Physical Component Score
Figure footnote: Both = patients who achieved resolution of both enthesitis & synovitis at wk 52; Either = patients who achieved either resolution of enthesitis or synovitis at wk 52; Nf number of patients; Neither = patients who did not achieve resolution of enthesitis nor synovitis at wk 52; PCS – Physical Component Score
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kristensen L, McGonagle D, Rudwaleit M, Kameda H, Holzkaemper T, El Baou C, Smolen J. Association of the Improvement of Synovitis and Enthesitis with Quality of Life/Patient Reported Outcomes in Patients with PsA Treated with Ixekizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-the-improvement-of-synovitis-and-enthesitis-with-quality-of-life-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-psa-treated-with-ixekizumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-the-improvement-of-synovitis-and-enthesitis-with-quality-of-life-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-psa-treated-with-ixekizumab/
