Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin is a novel calcineurin inhibitor recently approved for the treatment of adults with active lupus nephritis (LN) in combination with background immunosuppressive therapy. Voclosporin has a favorable metabolic profile and a consistent dose-concentration relationship eliminating the need for therapeutic drug monitoring.
Previously reported results from the Phase 3 AURORA 1 study and the Phase 2 AURA-LV study showed that compared with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose steroids, the addition of voclosporin significantly increased the complete renal response (CRR) rate and reduced proteinuria, as measured by urine protein-creatinine ratio (UPCR), in patients with LN at approximately one year of treatment (48 weeks in AURA-LV and 52 weeks in AURORA 1).
We describe here the results of a post-hoc analysis of AURORA 1 to assess whether patients with recent onset LN treated with voclosporin respond similarly to the overall population.
Methods: Patients with a diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus according to ACR criteria, biopsy-proven (Class III, IV, or V ± III/IV) LN and proteinuria of ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2 mg/mg for pure Class V) were eligible to enroll in AURORA 1. Overall, 179 patients were randomized to the voclosporin (23.7 mg BID) arm and 178 patients were randomized to receive placebo treatment in the control arm. All patients received MMF (1 g BID) and low-dose oral steroids (tapered over 16 weeks to 2.5 mg/day).
In this post-hoc analysis, 45 patients in the voclosporin arm and 46 patients in the control arm were identified as having recent onset LN, defined as LN diagnosis within an estimated 6 months of study start based on reported year of diagnosis, study start date and date of biopsy. Disease duration and baseline clinical characteristics were evaluated and compared with the rest of the trial population to ensure the population was relevant to patients with recent onset disease seen in clinical practice (Table 1). Patients with biopsy pure class V LN (n=50) were excluded. Achievement of CRR (defined as UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg with stable renal function in the presence of sustained, low-dose steroids and no rescue medication) was assessed at approximately one year of treatment.
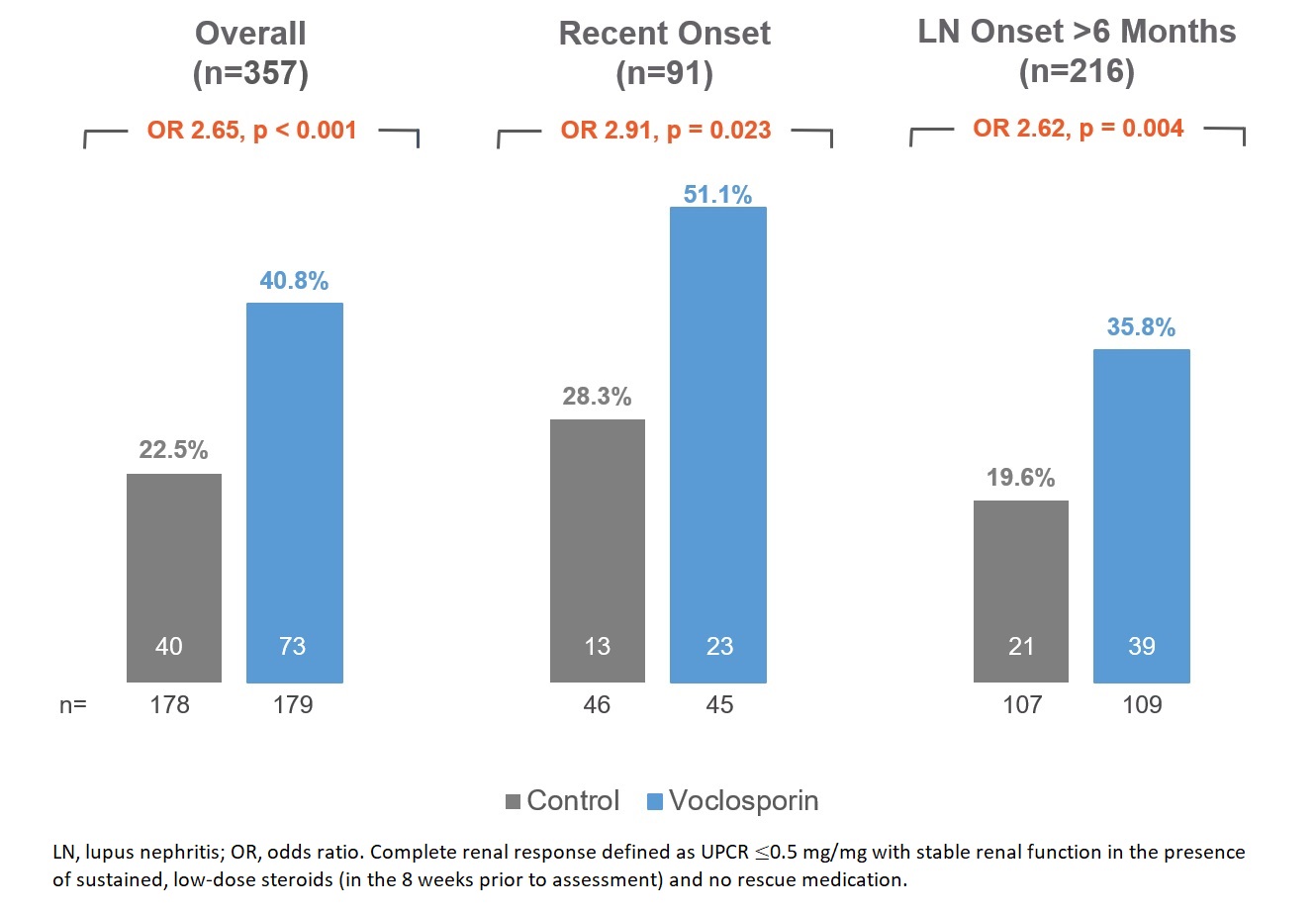
Results: Patients with recent onset LN (n=91) had a mean (SD) LN disease duration of 0.2 (0.1) years compared to 5.4 (5.3) years for the rest of the population (n=216); baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were similar between the treatment arms (Table 1). Among recent onset patients, CRR was significantly increased in the voclosporin arm compared to the control arm (CRR of 51.1% vs 28.3%, respectively; OR 2.91; p=0.023) at one year of treatment (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Patients with recent onset LN treated with voclosporin in combination with MMF and low-dose steroids had clinically meaningful reductions in proteinuria and achieved significantly higher rates of CRR compared to patients treated with MMF and low-dose steroids alone. The efficacy benefit of voclosporin in recent onset LN patients is comparable with the efficacy in the overall population of patients participating in the Phase 3 AURORA 1 study. This post-hoc analysis also suggests significant efficacy benefit in the population with much longer duration of LN.
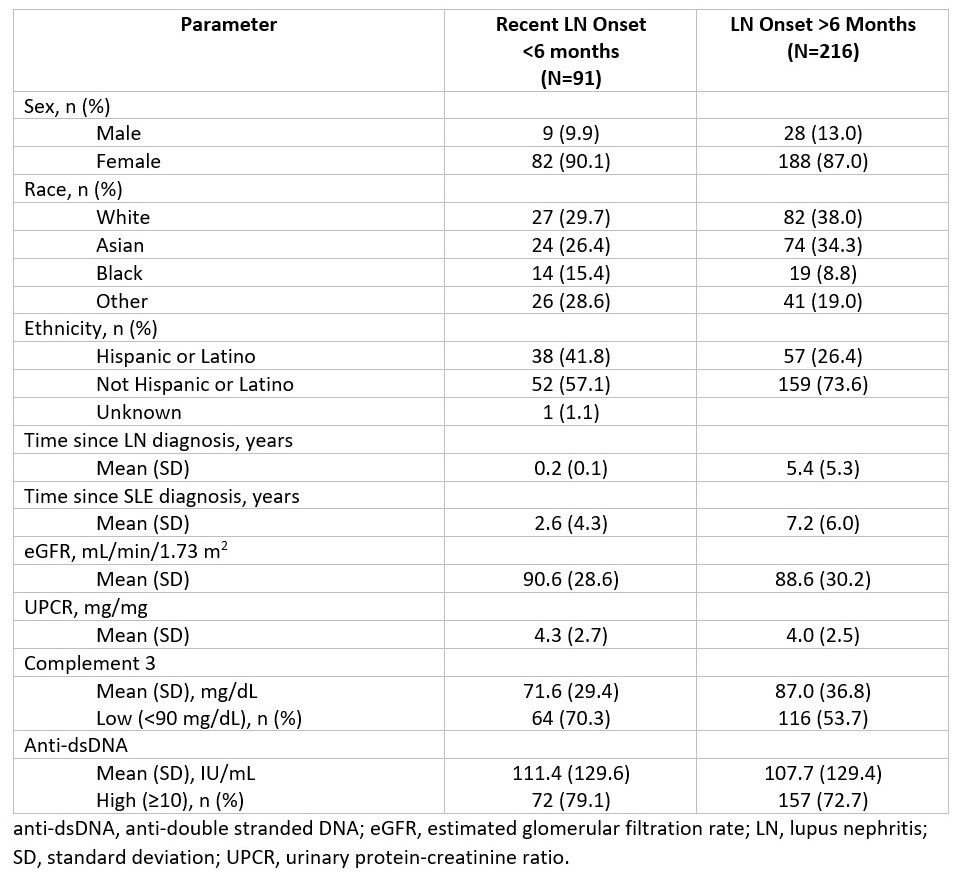 Table 1. Demographic and Baseline Characteristics
Table 1. Demographic and Baseline Characteristics
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mackay M, Truman M, England N, Birardi V, Mina-Osorio P. Efficacy of Voclosporin in Recent Onset Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-voclosporin-in-recent-onset-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-voclosporin-in-recent-onset-lupus-nephritis/