Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an effective, yet costly, drug for treatment of RA and PsA. Tofacitinib is metabolized mainly by the cytochrome P450-enzyme CYP3A4, and the manufacturer recommends to halve the dose of tofacitinib when patients use concomitant medication that strongly inhibits CYP3A4. Therefore, we hypothesized that coadministration of cobicistat, an CYP3A4-inhibitor approved for boosting of antiretroviral drugs, next to half dose tofacitinib would lead to pharmacokinetics equivalent to standard doses tofacitinib. The aim of this study was thus to investigate the bioequivalence of tofacitinib 5 mg and cobicistat 150 mg once daily (QD) compared to tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (BID) alone.
Methods: This open label, non-randomized, cross-over, bioequivalence study was performed between September 2019 and March 2021 in the Netherlands. Patients with RA or PsA, using tofacitinib and no other concomitant medication which could be significantly affected by cobicistat use, were included. After using tofacitinib 5 mg BID for at least 14 days, plasma samples of tofacitinib were collected pre-dose and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9 and 12 hours post-dose. After this first sampling day, patients switched treatment to tofacitinib 5 mg and cobicistat 150 mg QD. Two to six weeks after, plasma samples of both tofacitinib and cobicistat were collected at the same timepoints, with the addition of a sample at 24 hours post-dose. Bioequivalence of the average tofacitinib concentration (Cavg) was assessed of tofacitinib 5 mg with cobicistat 150 mg QD compared to tofacitinib 5 mg BID: the 90% confidence intervals of the geometric mean ratio of Cavg should be between 80% and 125% for bioequivalence. Secondary endpoints included efficacy (change in mean DAS28CRP measured at both sampling days), safety, and patient preference (7-point Likert Scale at study end).
Results: Twenty seven patients were included, of which five underwent adaptations to comedication prior to inclusion due to CYP3A4 interactions (Table 1). The geometric mean ratio for the Cavg was 84.8% (90% CI 75.1% – 95.6%), thus full bioequivalence could not be concluded. The change in mean DAS28CRP was 0.05, 95% CI -0.49 to 0.59. No serious adverse events occurred during the study. The majority of patients preferred the combination regime: 56% preferred combination therapy (score on Likert scale 5-7), 18% monotherapy (score 1-3) and 26% neutral (score 4), leading to a net promotor score of 38%.
Conclusion: Tofacitinib 5 mg with cobicistat 150 mg QD combination therapy was not bioequivalent to standard tofacitinib 5 mg BID. However, we think this combination treatment shows promise as a slightly reduced exposure is not expected to result in reduced efficacy, based on prior dose finding studies1, combined with the fact that both drugs are registered and readily available. In addition, there was no difference in disease activity and a clear preference by patients. Further research should focus on safety and efficacy at longer use.
1Lamba M, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun;101(6):745-753.
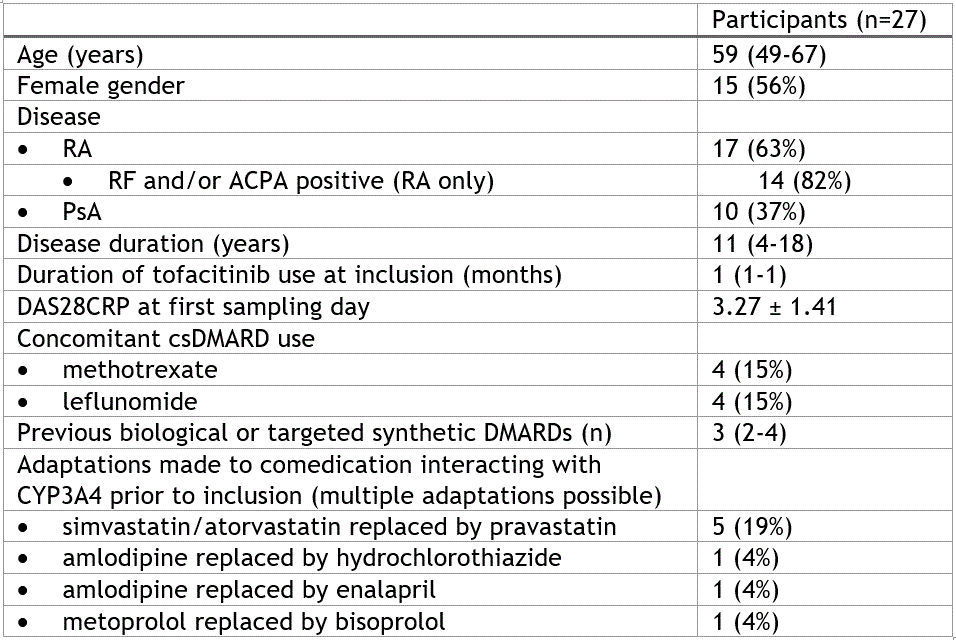 Table 1 Baseline characteristics. Either displayed as number (percentage), mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range). Percentages were calculated over the total number of participants unless indicated.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics. Either displayed as number (percentage), mean ± standard deviation or median (interquartile range). Percentages were calculated over the total number of participants unless indicated.
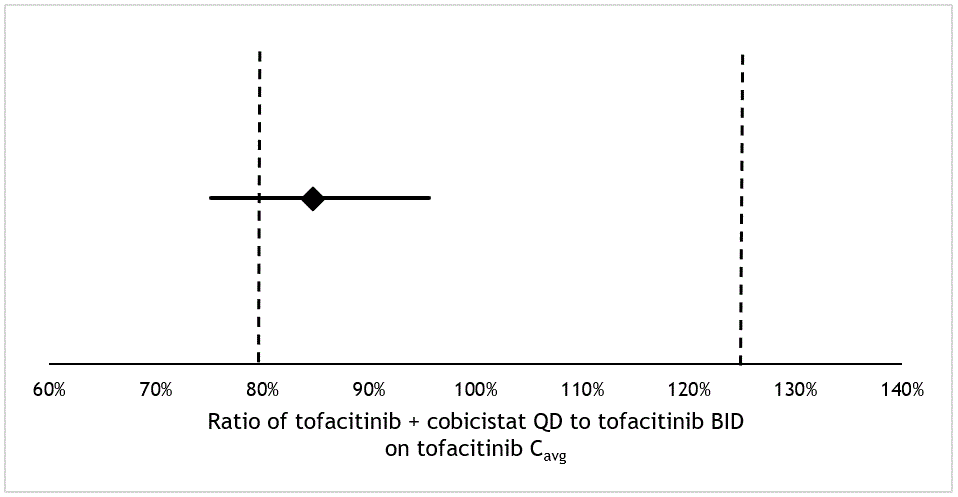 Figure 1 Visual representation of primary study result on bioequivalence. Geometric mean ratio with 90% confidence interval of the tofacitinib Cavg (tofacitinib 5 mg BID compared to tofacitinib 5 mg and cobicistat 150 mg QD) represented as horizontal line. Equivalence margins are represented as vertical dotted lines at 80% and 125%.
Figure 1 Visual representation of primary study result on bioequivalence. Geometric mean ratio with 90% confidence interval of the tofacitinib Cavg (tofacitinib 5 mg BID compared to tofacitinib 5 mg and cobicistat 150 mg QD) represented as horizontal line. Equivalence margins are represented as vertical dotted lines at 80% and 125%.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Togt C, Verhoef L, den Broeder N, ter Heine R, van den Bemt B, den Broeder A. Pharmacokinetic Boosting to Enable Once-Daily Reduced Dose Tofacitinib [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetic-boosting-to-enable-once-daily-reduced-dose-tofacitinib/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetic-boosting-to-enable-once-daily-reduced-dose-tofacitinib/
