Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
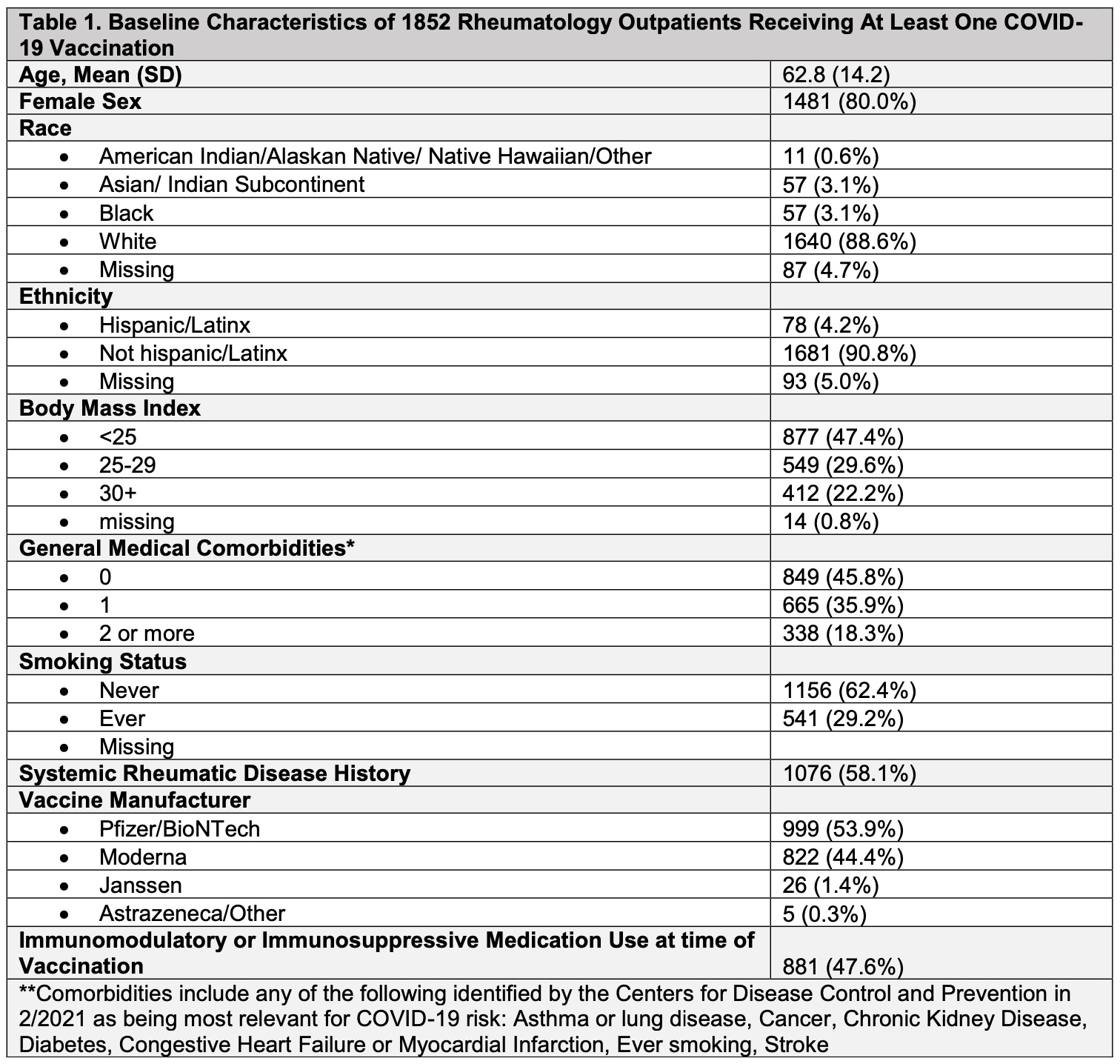
Background/Purpose: Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 is important for patients with systemic rheumatic diseases (SRDs), who may be at increased risk of severe outcomes post-COVID-19 infection. However, as patients with SRDs were not included in vaccine trials, limited data exist on post-vaccine adverse events in the SRD population. We evaluated the prevalence of adverse events post- SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in rheumatology outpatients from New York City.
Methods: We emailed a secure web-based survey on March 5, 2021 to 7,505 patients aged ≥18 years evaluated at least once between 2018-2020 by a rheumatologist at a single Rheumatology Division in New York City. We included individuals who received at least one vaccine dose. ICD-10-CM codes were used to identify SRD diagnoses. We collected data on sociodemographics, medical comorbidities, and medication use at time of vaccination. Patients were asked to report adverse events defined as “symptoms within 1 week” of receiving each vaccine dose. Patients were asked to report symptoms they did not attribute to an SRD flares, which were reported separately.
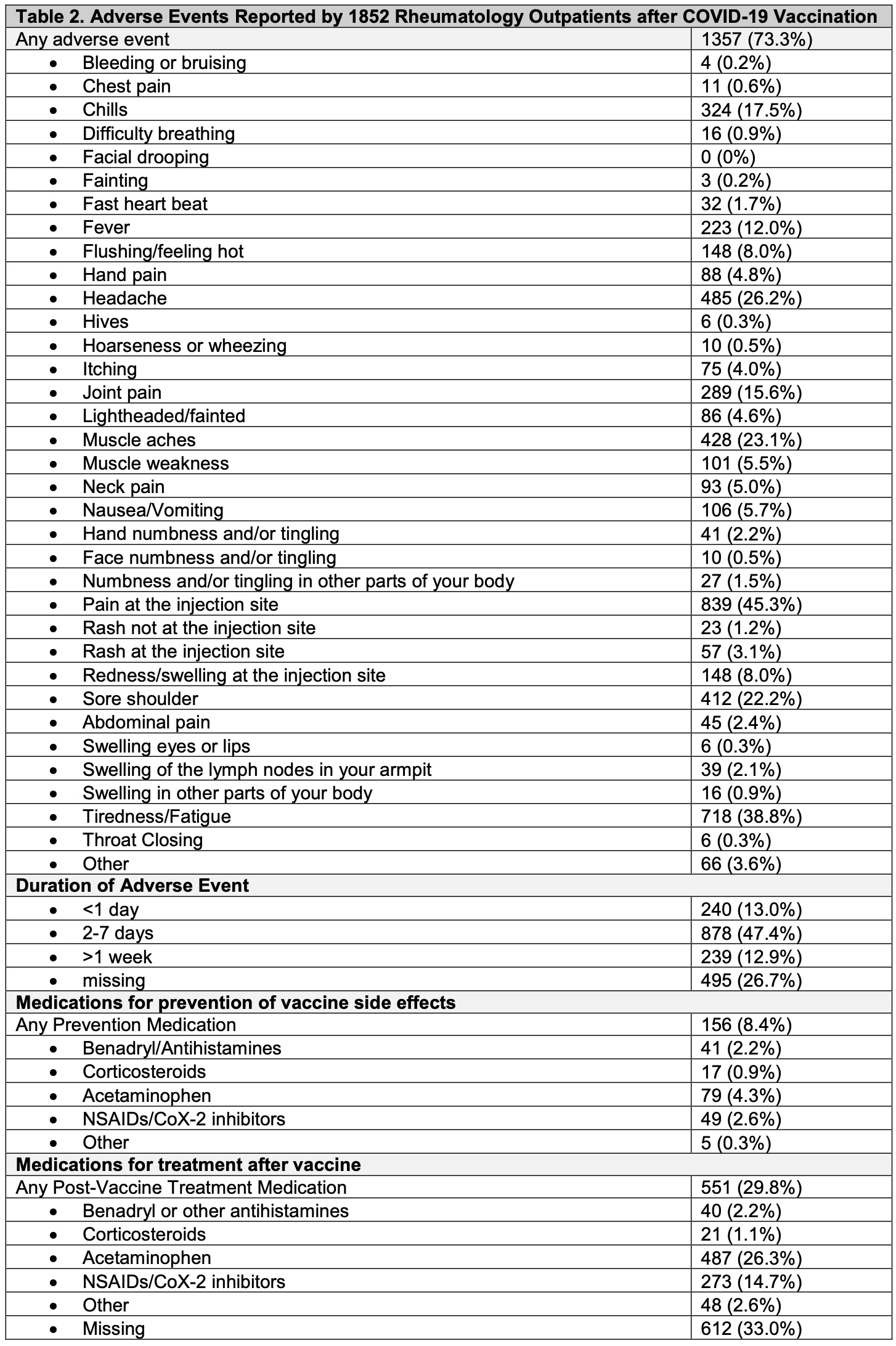
Results: As of May 17, 2021, 1852 respondents (24.7% response rate) had received at least one COVID-19 vaccine dose (53.9% Pfizer vaccine, 44.4% Moderna, 1.4% Janssen, 0.3% Astrazeneca). Mean age of respondents was 62.8 [14.2] years; 80% female; 88.6% White; 4.2% Hispanic/Latinx ethnicity). 1173 patients received two vaccine doses and 679 patients received only the first dose. 1076 patients (58.1%) met an ICD-10-CM algorithm for an SRD. Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory medications were used by 47.6% of individuals at the time of vaccination. Adverse events at the first or second vaccine dose were reported by 1357 (73.3%) individuals, and most commonly included pain at injection site (45.3%), fatigue (38.8%), headache (26.2%), muscle aches (23.1%), sore shoulder (22.2%). 14.4% of respondents reported only local injection site reactions (i.e. pain, swelling, redness, rash) at either vaccine dose. Severe symptoms such as throat closing, wheezing, fainting, chest pain, difficulty breathing, bleeding, and swelling of the eyes, lips or other parts of body were reported by less than 1%. Medications to prevent vaccine side effects were used by 8.4% of patients (Table); after vaccination, only 2 patients (0.1%) required use of epinephrine and 21 patients (1.1%) used corticosteroids for symptom relief. 35 patients (1.9%) reported seeking medical attention (i.e. urgent care, ER or hospital) after any vaccination. Typical adverse event duration was 2-7 days (47.4%); 13% experienced symptoms < 1 day, and 13% experienced symptoms >1 week.
Conclusion: Interim data from our cohort demonstrate that 73.3% of rheumatology patients experienced a local or systemic adverse event post-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, similar to estimates from Pfizer BioNTech vaccine clinical trial data. Symptoms were typically transient (< 7 days) and consisted predominantly of common side effects such as injection site pain, fatigue, headache, and myalgias. Less than 1% of patients experienced more serious post-vaccination events, which is reassuring and may help inform vaccine decision making for rheumatology patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barbhaiya M, Jannat-Khah D, Levine J, Do H, Lally L, Bykerk V, Mandl L. Adverse Events After SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination Among Rheumatology Outpatients in New York City [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-events-after-sars-cov-2-vaccination-among-rheumatology-outpatients-in-new-york-city/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-events-after-sars-cov-2-vaccination-among-rheumatology-outpatients-in-new-york-city/