Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Treatment: New Agents, Old Agents (1458–1463)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:30PM-3:45PM
Background/Purpose: We previously reported 24-wk results of a phase 2b trial of iberdomide, a high-affinity cereblon ligand that promotes proteasomal degradation of Ikaros (IKZF1) and Aiolos (IKZF3), 2 key transcription factors linked to SLE. The study (NCT03161483) met its primary endpoint at wk 24.1 Results through wk 52 are reported here.
Methods: Adults (N=288) with autoantibody-positive SLE and SLEDAI 2K scores ≥6 were randomized (2:2:1:2) to oral iberdomide (0.45, 0.3, 0.15 mg) or placebo (PBO) daily, added to background lupus therapy. At wk 24, patients (pts) on PBO were re-randomized to iberdomide 0.3 or 0.45 mg, while pts on iberdomide continued their original regimens. Efficacy analyses were based on the intent-to-treat population, including all pts who were randomized at wk 0 and received ≥1 dose of study drug.
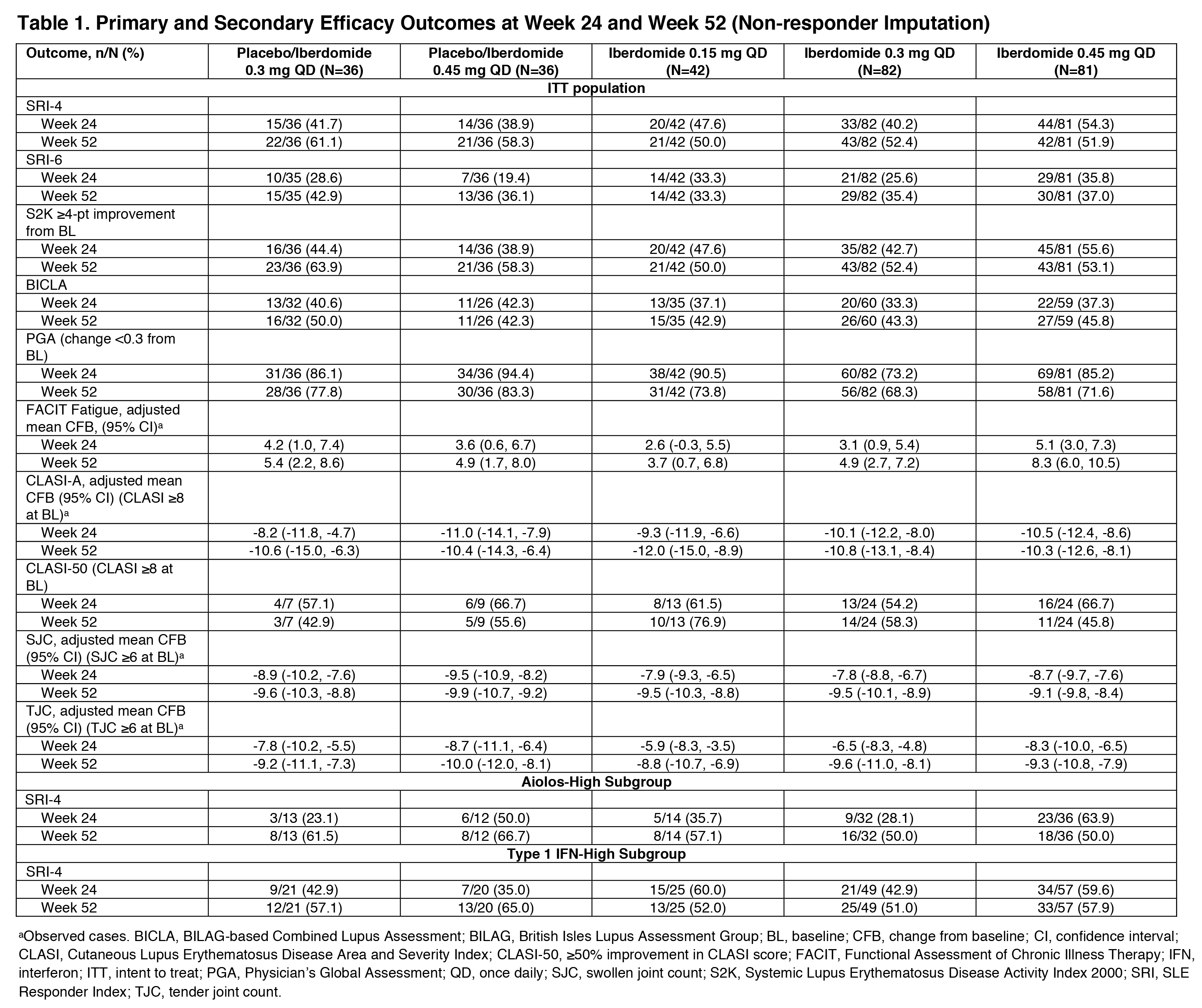
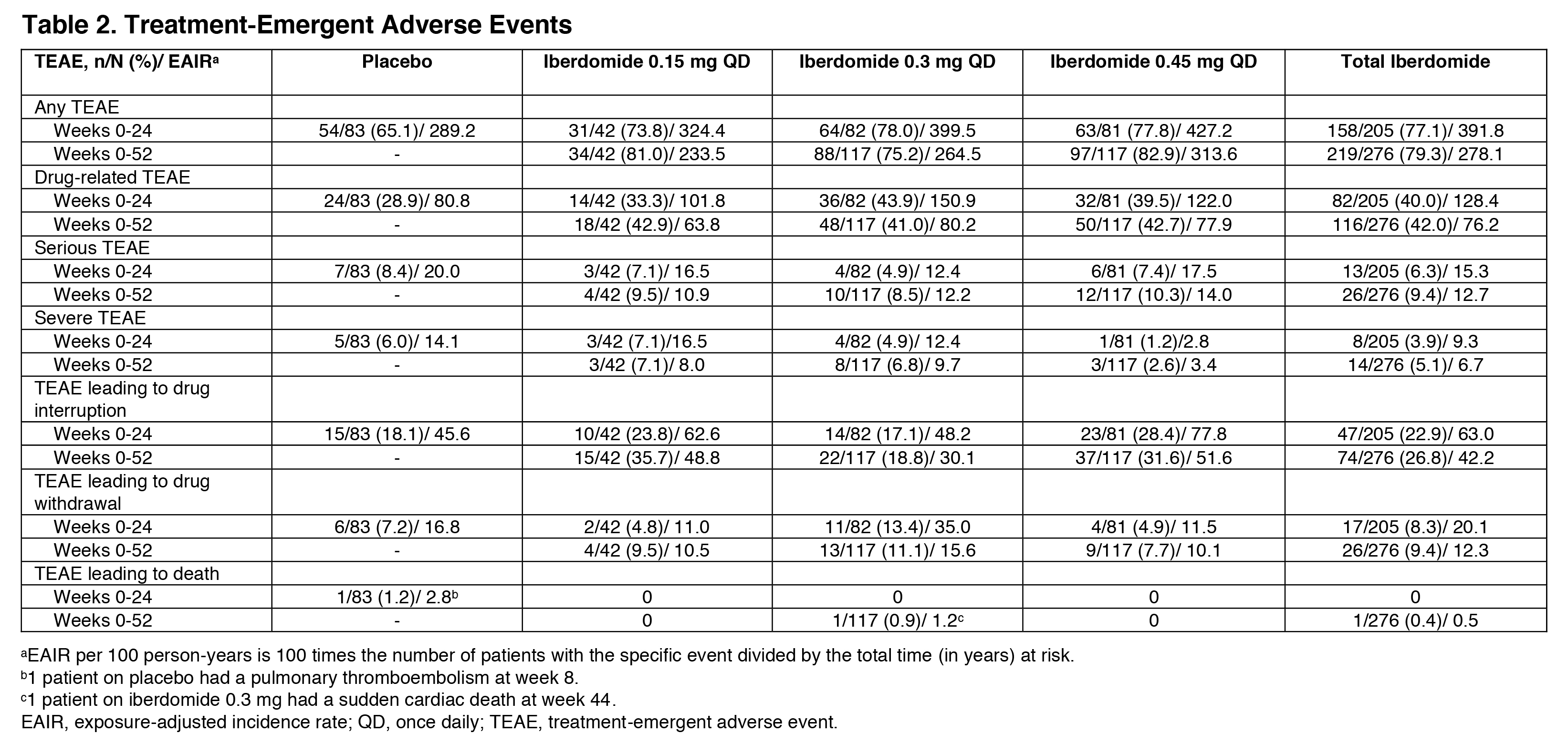
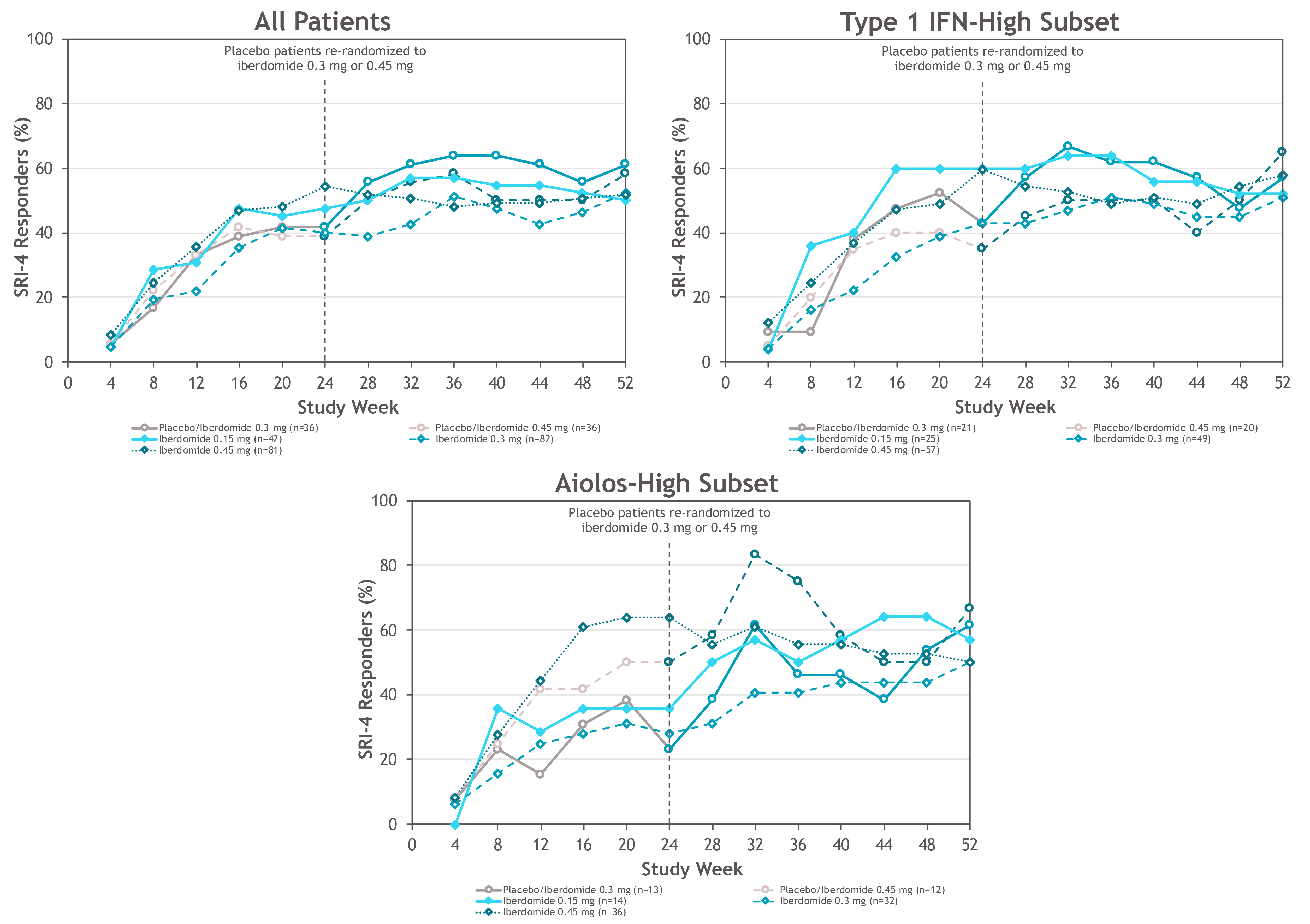
Results: 214 (87.0%) pts completed 52 wks. As previously reported, the primary endpoint, SRI-4 response at wk 24, was achieved by 54.3% of pts on iberdomide 0.45 mg vs. 34.9% on PBO (stratified difference, 19.4%; P=0.011). At wk 52, the proportions of SRI-4 responders were sustained or improved in all groups originally randomized to iberdomide: 0.45 mg (wk 24: 54.3% vs. wk 52: 51.9%), 0.3 mg (40.2% vs. 52.4%), and 0.15 mg (47.6% vs. 50.0%) (Figure). Of wk 24 SRI-4 responders, response was maintained at ≥70% of the visits through wk 52 by 75.0%, 81.8%, and 70.0% in the 0.45-mg, 0.3-mg, and 0.15-mg groups. Increased proportions of pts attained SRI-4 response after switching from PBO to 0.3 mg (41.7% vs. 61.1%) or from PBO to 0.45 mg (38.9% vs. 58.3%) (Figure). In the iberdomide 0.3-mg group and the 2 PBO switching groups, improvements in the proportions meeting SRI-6 and ≥4-point decrease in SLEDAI-2K at wk 52 were observed (Table 1). In pts originally randomized to iberdomide, there were trends of increased BICLA responses and improved swollen/tender joint counts at wk 52 (Table 1). In the 0.3-mg and 0.45-mg groups, the enhanced SRI-4 responses at wk 24 in the prespecified subsets of pts with Type 1 IFN high signatures at baseline were similar or improved at wk 52 and also achieved by pts switching from PBO to iberdomide (Figure and Table 1). In Aiolos-high pts at baseline, enhanced responses were observed at wk 52 in the 0.15-mg and 0.3-mg groups and PBO switching groups, but response rates were not sustained in the 0.45-mg group. There were no increases in exposure-adjusted incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), TEAEs leading to drug interruption or withdrawal, or serious AEs (SAEs) (Table 2). Most TEAEs were mild to moderate in severity, the most common being urinary tract infection (14.9%), upper respiratory tract infection (11.2%), and neutropenia (9.8%). Neutropenia was reversible and rarely led to discontinuation (1.4%). One pt on iberdomide (0.3 mg) had an SAE of varicella zoster pneumonia with full recovery.
Conclusion: Iberdomide treatment of pts with SLE was associated with sustained clinical benefits in multiple measures of disease activity up to wk 52. Enhanced clinical responses in pts with IFN-high and Aiolos-high signatures were also observed at 52 wks. Iberdomide was well tolerated with safety data consistent with that reported at wk 24.
Reference:
1. Merrill J, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72 (suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merrill J, Werth V, Furie R, van Vollenhoven R, Majdan M, Weiswasser M, Korish S, Liu Z, Schafer P, Delev N. Sustained Efficacy and Safety of Iberdomide to Week 52 in Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in a Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-efficacy-and-safety-of-iberdomide-to-week-52-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-in-a-phase-2-randomized-placebo-controlled-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-efficacy-and-safety-of-iberdomide-to-week-52-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-in-a-phase-2-randomized-placebo-controlled-study/