Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is mainly described based on the individual domains or clinical components of the disease.1,2 The aim of this post hoc analysis was to identify hypothesis-free clusters of phenotypes according to patients’ clinical features and characteristics at baseline (BL) using data from the guselkumab Phase 3 DISCOVER-1 and -2 clinical trials of patients with PsA.
Methods: Data from bio-naïve patients with active PsA treated with guselkumab 100 mg either every 4 or 8 weeks in DISCOVER-1 and -2 were retrospectively analyzed. Non-negative matrix factorization was applied as an unsupervised machine learning technique to identify clusters of PsA phenotypes, with BL characteristics and clinical observations as input features. Clusters are described here according to their characteristics and clinical features, including the relation to achievement of minimal disease activity (MDA) at Weeks 24 and 52 (W24; W52).
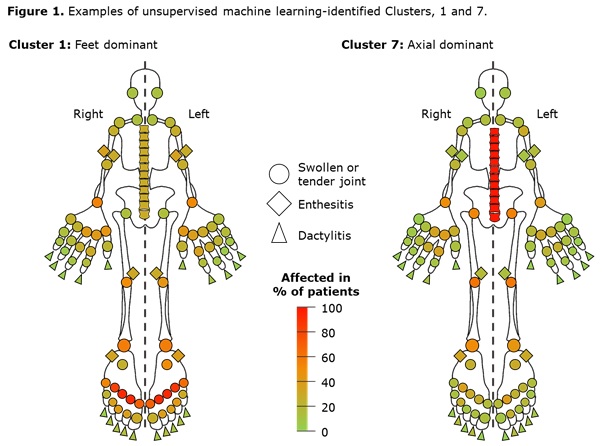
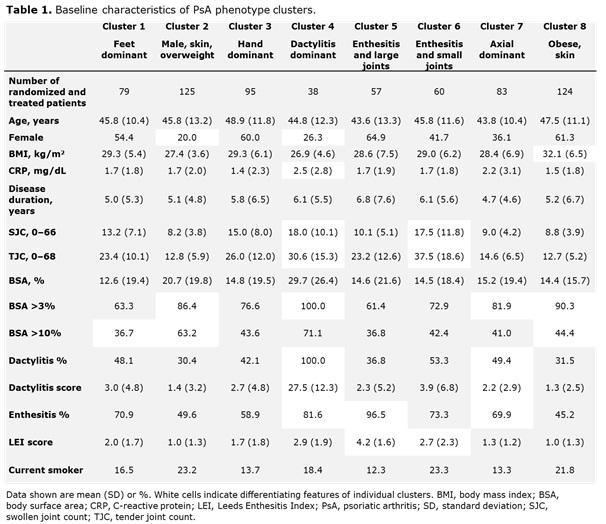
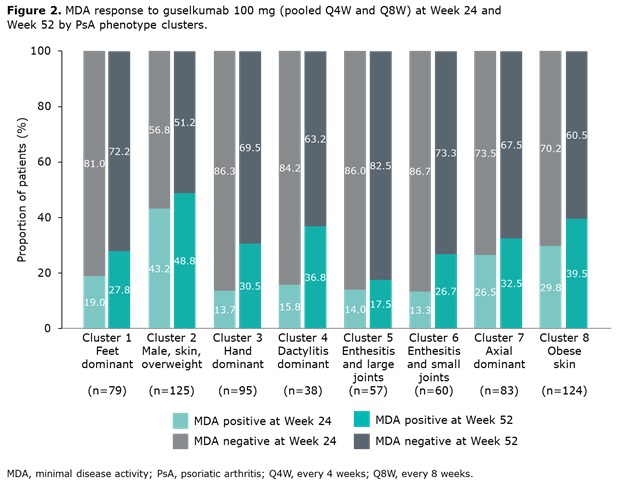
Results: Data from 661 bio-naïve patients were pooled. Eight distinct clusters of PsA phenotypes were identified. Cluster 1 was characterized by a high frequency of lower limb involvement, notably foot/ankle, and the lowest rates of severe skin involvement (Figure 1). Cluster 2 was characterized by high skin involvement, the lowest proportion of females, and the highest proportion of overweight patients (70% body mass index [BMI] 25–< 30). Cluster 3 was characterized by a high burden of disease in the hands/wrists. Cluster 4, the smallest cluster, was distinguished by the highest degree of dactylitis involvement; second highest proportion of male patients; and the highest proportion of patients with ≥3% body surface area (BSA) psoriasis involvement. Cluster 5 was differentiated based on the highest proportion of patients with enthesitis at BL. Large joint involvement was also common in this cluster. Cluster 6 was characterized by a high level of involvement of small joints in the hands and feet, but a low mean dactylitis score. Presence of nail involvement (78%) and enthesitis at BL were also common in this cluster. Cluster 7 was characterized by axial involvement at BL (100%); nearly one-half of patients with dactylitis, two thirds with enthesitis and the majority with BSA ≥3% at BL (Figure 1). Cluster 8 was characterized by low rates of joint involvement, high rates of more extensive skin involvement, and the highest proportion of obese patients (67% with BMI >30; Table 1). MDA response rates at W24 and W52 were highest in Cluster 2 and lowest in Cluster 5. Clusters 3 and 4 were characterized by low MDA response rates at W24 that increased at W52 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Unsupervised machine learning was able to identify 8 clusters of PsA phenotypes with significant differences in demographic and clinical features, including patterns of involvement of joint, skin/nail, dactylitis, and enthesitis manifestations as well as MDA responses. These clusters seem to differ in their initial vs. later responses to guselkumab. Further analysis will clarify which MDA domains play a role in this response kinetics.
1. Coates C et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016; 68: 1060–1071.
2. Gossec L et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71: 4–12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richette P, Vis M, Ohrndorf S, Tillett W, Neuhold M, van Speybroeck M, Theander E, Noel W, Shawi M, Kollmeier A, Zabotti A. Identification of PsA Phenotypes with Machine Learning Analytics Using Data from a Phase 3 Clinical Trial Program of Guselkumab in a Bio-naïve Population of Patients with PsA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-psa-phenotypes-with-machine-learning-analytics-using-data-from-a-phase-3-clinical-trial-program-of-guselkumab-in-a-bio-naive-population-of-patients-with-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-psa-phenotypes-with-machine-learning-analytics-using-data-from-a-phase-3-clinical-trial-program-of-guselkumab-in-a-bio-naive-population-of-patients-with-psa/