Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster II: Psoriatic Arthritis I (1329–1363)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Reaching control or improvement on enthesitis domain in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is challenging, and it continues to be a priority for patients (pts) and rheumatologists. Upadacitinib (UPA) has demonstrated efficacy across key manifestations, including enthesitis, in pts with active PsA with inadequate response to non-biologic or biologic DMARDs from the SELECT-PsA Clinical trials program 1,2. The objective of this analysis was to further estimate UPA 15 mg qd effects on enthesitis using different assessment tools through 56 weeks (W).
Methods: The SELECT-PsA 1 and 2 primary results were described elsewhere 1,2. For the purpose of this analysis, the UPA 15 mg arms were pooled from the two studies to 56W (continuous UPA), the PBO arms to W24 and the PBO to UPA 15 arms from 24W to 56W.
Enthesitis resolution was assessed as proportion of pts achieving LEI =0 and/or SPARCC=0 at each timepoint for patients with LEI >0 or SPARCC > 0 at baseline (BL). Change from BL in LEI and SPARCC scores was also assessed at each timepoint. Residual enthesitis sites and maintenance of an enthesitis-free state were assessed through 56W. Non-responder imputation was used for binary endpoints and mixed-effect model repeated measures (MMRM) for continuous endpoints.
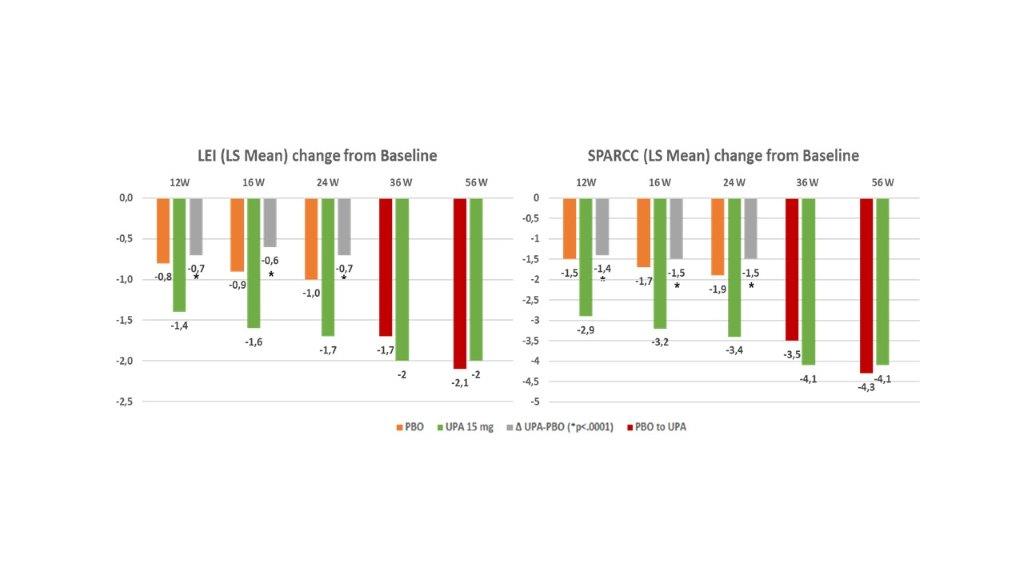
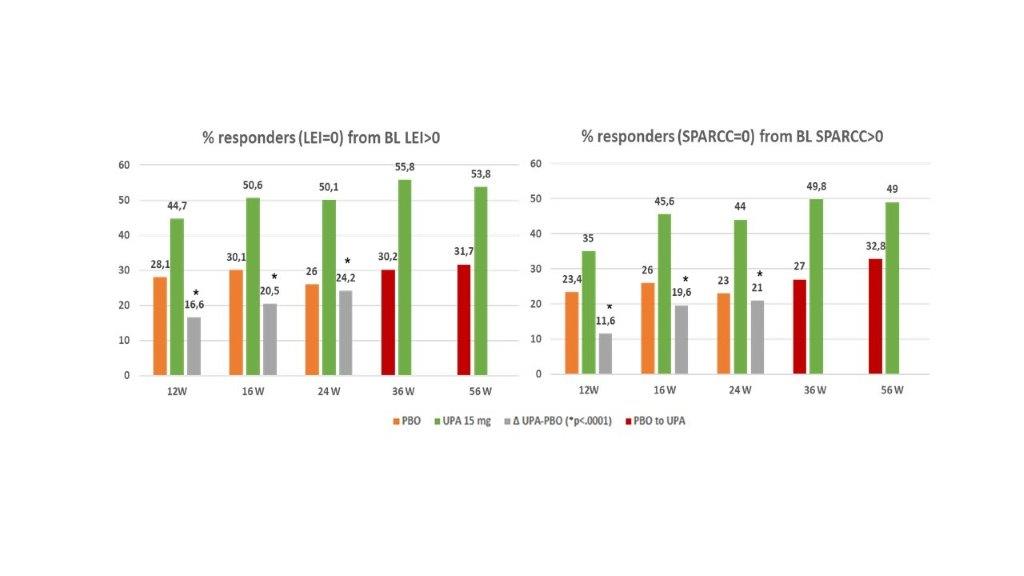
Results: Pooled population comprised 639 UPA 15 mg pts and 635 PBO pts. A significantly greater improvement in LEI and SPARCC scores (change from baseline) was observed with UPA 15 mg QD vs PBO as early as 12W to 24W, (nominal P< 0.0001; Figure 1) and results were either sustained or increased through 56W. A higher proportion of pts treated with UPA in comparison to PBO achieved complete resolution of enthesitis as assessed with LEI=0 or SPARCC=0 (nominal P<0.0001, Figure 2) and “LEI + SPARCC=0” (nominal p=0.0003 at 12W and p< 0.0001 at 16W / 24W). Resolution of enthesitis was sustained or increased through 56W, particularly in the continuous UPA 15 mg arm. Maintenance rate of an enthesitis-free state after LEI resolution at week 24 for UPA 15 mg continuous arm was: 84.2% at 36W, 80.2% at 56W, and with 72.3% remaining in remission at both 36W and 56W. Similarly, SPARCC assessment showed a 81.4% maintenance rate at 36W, 78.2% at 56 W, and 69.5% at both 36 W and 56W. For partial responders (pts experiencing a reduction in LEI or SPARCC but not achieving enthesitis resolution at 24W), UPA 15 mg still showed improvement over placebo for all components of LEI (or SPARCC) at 24W, with no specific refractory sites identified (Figure 3). For subjects with LEI=0 at baseline, Upa 15 mg also showed higher proportion of prevention of enthesitis versus placebo up to 24W, (between 12W and 24W the proportion of pts with LEI=0 for UPA ranged from 84.7% to 80.1% while for PBO ranged from 76% to 58.8%; nominal p< 0.05).
Conclusion: In pts with active PsA who had inadequate response to non-biologic or biologic DMARDs, UPA 15 mg achieved a rapid and comprehensive impact on enthesitis, across individual entheseal sites and with a high rate of maintenance of an enthesitic free state after resolution.
 Figure 3: Residual Enthesitis sites at 24W among Subjects Not Achieving Full Resolution
Figure 3: Residual Enthesitis sites at 24W among Subjects Not Achieving Full Resolution
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cantini F, Marchesoni A, Marando F, Gualberti G, Novelli L, Curradi G, McDearmon-Blondell E, Gao T, Salvarani C. Upadacitinib Effects on Entheseal Domain in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients – a Pooled “post-hoc” Analysis from Two Phase III Studies (Select PsA 1 and 2) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-effects-on-entheseal-domain-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-from-two-phase-iii-studies-select-psa-1-and-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/upadacitinib-effects-on-entheseal-domain-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-from-two-phase-iii-studies-select-psa-1-and-2/