Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Selenium plays an indispensable role in the process of antioxidant and antiinflammation. Oxidative stress and inflammation have been hypothesized to be involved in the pathogenesis of cartilage degeneration. We sought to explore the association between serum selenium levels and the prevalence of radiographic osteoarthritis (ROA) in a large population-based study.
Methods: Subjects aged 50 years or older were from the Xiangya Osteoarthritis (XO) Study, a community-based observational study. Serum selenium concentration was measured by inductively coupled plasma-dynamic reaction cell-mass spectrometry. ROA was defined as a Kellgren/Lawrence score ≥ 2 for at least one knee, hip or hand joint. The association between serum selenium levels and ROA were evaluated by conducting logistic and spline regression.
Results: A total of 1,032 participants (women: 52.5%; mean age: 63.1 years; ROA prevalence: 45.4%) were included. Compared with the lowest tertile, odds ratios (ORs) for ROA were 0.69 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.51 to 0.93) and 0.56 (95% CI: 0.41 to 0.75) in the second and third tertiles of serum selenium, respectively (P for trend < 0.05) (Table 1). Adjusting for potential confounders did not change the results materially. In addition, subjects with lower serum selenium levels had a higher prevalence of OA in a dose-response-relationship manner (P = 0.005) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Subjects with lower levels of serum selenium, even within the normal range, had higher prevalence of ROA in a dose-response relationship manner, suggesting that selenium may have a preventive or therapeutic potential for OA.
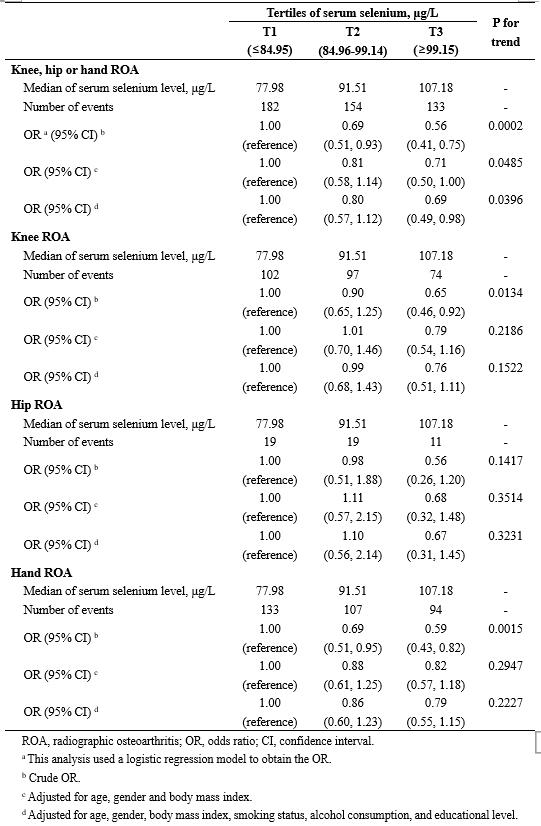 Table 1. Association between serum selenium levels and radiographic knee, hip or hand ROA (1,032 participants)
Table 1. Association between serum selenium levels and radiographic knee, hip or hand ROA (1,032 participants)
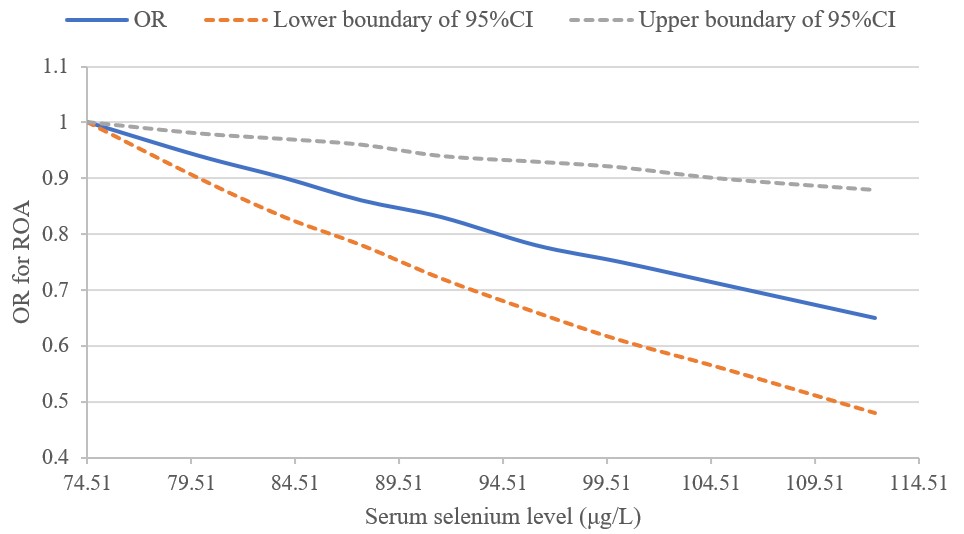 Figure 1. Dose-response relationship between serum selenium level and the odds ratio (OR) for radiographic knee, hand or hip radiographic osteoarthritis (ROA). CI, confidence interval.
Figure 1. Dose-response relationship between serum selenium level and the odds ratio (OR) for radiographic knee, hand or hip radiographic osteoarthritis (ROA). CI, confidence interval.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang N, Xie M, Zeng C, Yang T, Yang Z, Wang Y, Li J, Tian J, Yang T, Lei G. Association Between Serum Selenium Level and the Prevalence of Osteoarthritis: Data from the Xiangya Osteoarthritis Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-serum-selenium-level-and-the-prevalence-of-osteoarthritis-data-from-the-xiangya-osteoarthritis-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-serum-selenium-level-and-the-prevalence-of-osteoarthritis-data-from-the-xiangya-osteoarthritis-study/
