Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Basic Science (0944–0947)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-9:15AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriasis (PsO) is an inflammatory, immune-mediated skin disorder affecting ~3% of the population worldwide. It is associated with multiple comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis (PsA), which occurs in up to a third of patients. While genes contribute to the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease, twin studies demonstrate substantial discordance in PsO and PsA, suggesting that epigenetics and environmental factors play a significant role. In fact, there is increasing evidence that the microbiome has an impact on psoriatic disease pathogenesis. However, prior investigations were performed in populations of unrelated individuals and could not discern environmental from genetic influences. To characterize the host-microbiome relationship, we studied the gut and skin microbiome of monozygotic (MZ) twins discordant for psoriatic disease in order to determine disease-specific microbial perturbations that are independent of host-genes.
Methods: Stool and skin swabs were collected from subjects with psoriatic disease and their unaffected MZ twin siblings (pairs=9, n=18). Non-lesional (NL) or healthy skin was swabbed at three separate sites: bicep, scalp, and elbow/forearm. Fecal samples underwent shotgun metagenomic sequencing to deeply characterize the gut microbiome taxonomy and functional pathways at high resolution. Sequences were processed with the HUMAnN and MetaPhlAn2 pipelines. Skin swab samples underwent 16S rRNA sequencing to characterize the cutaneous bacterial microbiome. Forward sequences were processed with the QIIME2 pipeline and SILVA reference database. Downstream computational analysis was performed using several libraries in R, including DESeq2.
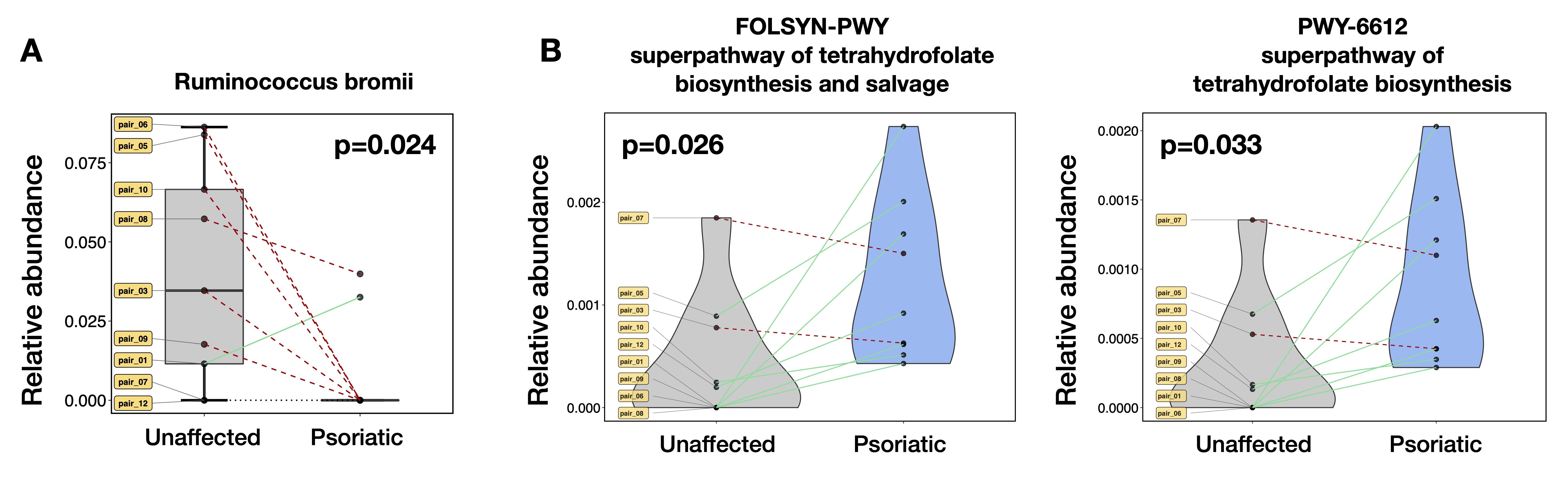
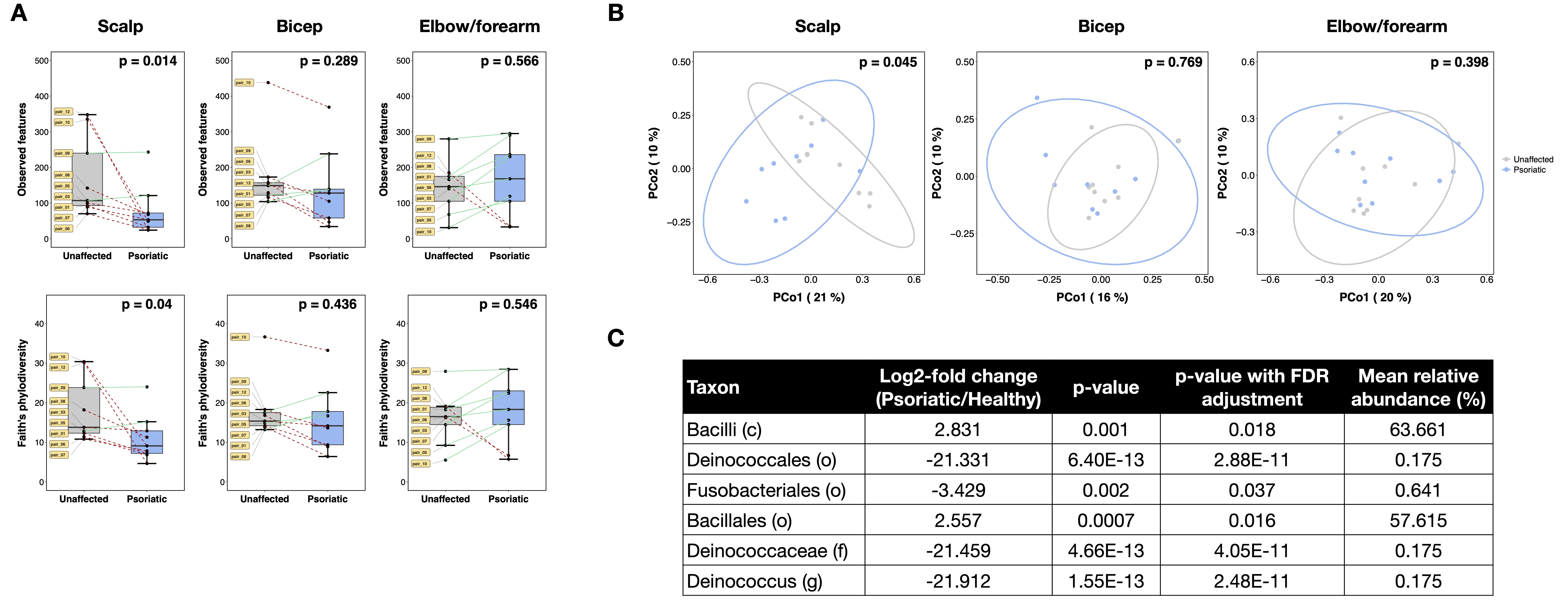
Results: In gut samples, the relative abundance of Ruminococcus bromii species was significantly reduced and two pathways related to tetrahydrofolate biosynthesis were upregulated in psoriatic twins compared to their corresponding unaffected siblings (Fig 1; p< 0.05, Mann-Whitney). In NL skin samples from psoriatic twins, there was a significant reduction in alpha diversity and beta diversity differences in microbial communities of the scalp, but not the bicep or elbow/forearm, compared to healthy samples from unaffected twins (Fig 2A-B; p< 0.05, Mann-Whitney and Permanova). Differential analysis of taxa in the scalp identified a higher abundance of the Bacillales order and related taxa, as well as a lower abundance of the Deinococcus genus and related taxa in psoriatic twins compared to their unaffected siblings (Fig 2C; p< 0.05 with FDR correction).
Conclusion: This is the first study exploring microbial differences in MZ twins discordant for psoriatic disease. In agreement with our previous results, we found that Ruminococcus is reduced or virtually absent in the gut of psoriatic patients, and may therefore be associated with psoriatic disease. Additionally, we discovered that even healthy-appearing NL skin of psoriatic subjects, particularly in the scalp, exhibited microbial perturbations and decreased diversity compared to unaffected twins. A further understanding of these changes and their downstream effects should shed light into the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease beyond genetic susceptibility.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Manasson J, Stapylton M, Medina R, Castillo R, Vasudevanpillai Girija P, Heguy A, Ubeda C, (MATR) M, Clemente J, Scher J. A Characterization of the Gut and Cutaneous Microbiome of Monozygotic Twins Discordant for Psoriatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-characterization-of-the-gut-and-cutaneous-microbiome-of-monozygotic-twins-discordant-for-psoriatic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-characterization-of-the-gut-and-cutaneous-microbiome-of-monozygotic-twins-discordant-for-psoriatic-disease/