Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA), an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy and safety through 14 weeks in the SELECT-AXIS 1 study in biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-naïve patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS).1 The objective of this analysis was to evaluate the efficacy of UPA 15 mg once daily (QD) in selected subgroups of patients with AS based on different baseline characteristics.
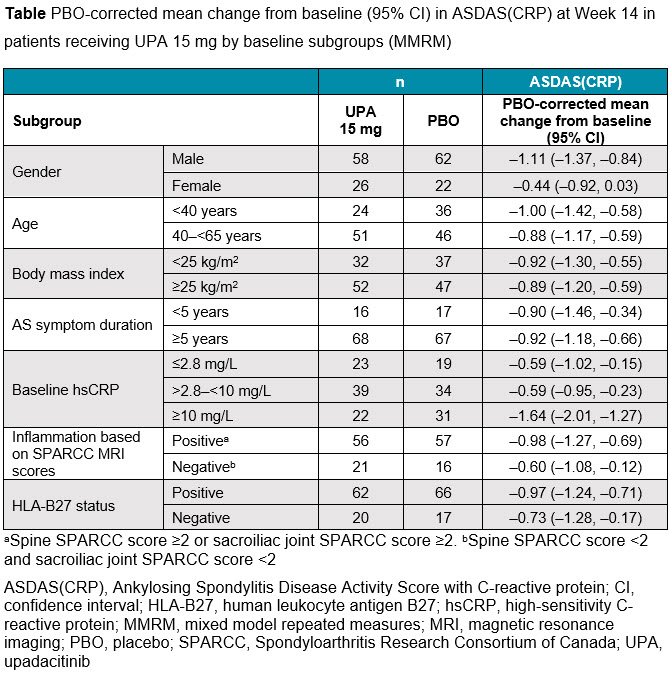
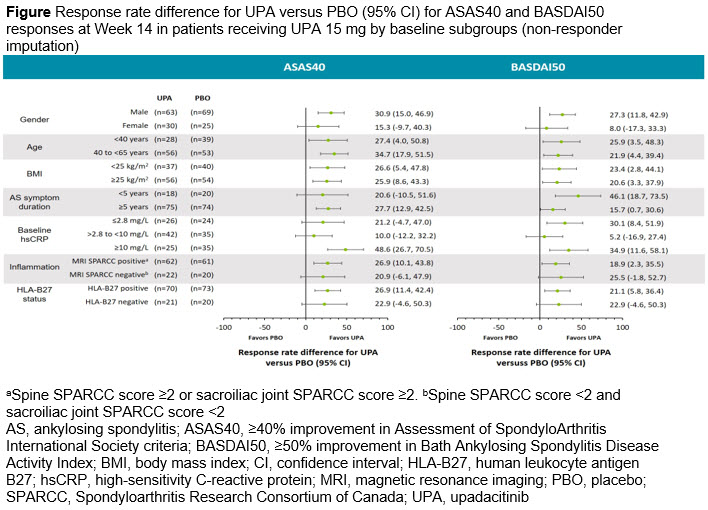
Methods: In SELECT-AXIS 1, patients were randomized to 14 weeks of blinded treatment with UPA 15 mg QD or placebo (PBO). This post hoc analysis evaluated the proportions of patients achieving ≥40% improvement in Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society criteria (ASAS40), ≥50% improvement in the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI50), and change from baseline in Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with C-reactive protein (ASDAS[CRP]) at Week 14 across subgroups based on the following baseline patient characteristics: gender, age, body mass index, AS symptom duration, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Magnetic Resonance Imaging index, and human leukocyte antigen B27 status. For missing data, non-responder imputation analysis was used for ASAS40 and BASDAI50, and mixed model repeated measures analysis was used for ASDAS(CRP).
Results: Baseline disease characteristics were balanced between the treatment groups at randomization, as previously reported.1 ASAS40 and BASDAI50 response rates at Week 14 were numerically higher with UPA 15 mg versus PBO across the demographic and disease characteristic subgroups evaluated (Figure), including some subgroups with small sample sizes, such as patients with disease duration < 5 years and female patients. Improvements from baseline in ASDAS(CRP) were also consistently greater with UPA 15 mg versus PBO across the subgroups evaluated (Table).
Conclusion: Within subgroups evaluated, most patients with active AS receiving UPA 15 mg demonstrated greater improvements versus PBO in disease activity measures assessed by ASAS40, BASDAI50, and change from baseline in ASDAS(CRP). There was some evidence that gender, AS symptom duration, and baseline CRP levels seemed to influence outcomes, though results should be interpreted with caution due to small sample sizes for some subgroups.
Reference: 1. van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet 2019;394:2108–17.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Van den Bosch F, Poddubnyy D, Stigler J, Ostor A, D'Angelo S, Navarro-Compán V, Song I, Gao T, Ganz F, Gensler L. Influence of Baseline Demographics on Improvements in Disease Activity Measures in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Receiving Upadacitinib: A Post Hoc Subgroup Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-baseline-demographics-on-improvements-in-disease-activity-measures-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-receiving-upadacitinib-a-post-hoc-subgroup-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/influence-of-baseline-demographics-on-improvements-in-disease-activity-measures-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-receiving-upadacitinib-a-post-hoc-subgroup-analysis/