Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus is a heterogenous autoimmune disease characterized by loss of immune tolerance, production of nucleic acid:autoantibody immune complexes, immune cell hyperactivation, and increased proinflammatory cytokine and interferon production. Interleukin receptor associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) is a serine/threonine kinase that modulates proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production downstream of toll-like receptors (TLRs) and IL-1 receptors (IL-1Rs) in immune cells. It is well established that TLR signaling (predominately TLR7 and TLR9) plays a key role in the pathogenesis of lupus1 and thus inhibition of IRAK4 represents a promising target for the therapeutic treatment of lupus.
The murine NZB/W model recapitulates many lupus-like disease pathologies including proteinuria, hyperactive B and T cells, high titers of autoantibodies, and splenic and kidney abnormalities2,3. Current standard of care treatments, including methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, and blockers of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) have demonstrated efficacy (e.g. improved survival and/or clinical pathologies) in this model2,3. Demonstrating beneficial effects of IRAK4 inhibition in this model would support clinical evaluation in lupus.
Methods: In this study we investigated the efficacy of GS-5718, a highly selective, competitive inhibitor of IRAK4, to improve survival and attenuate disease pathology in the murine NZB/W model of spontaneous lupus.
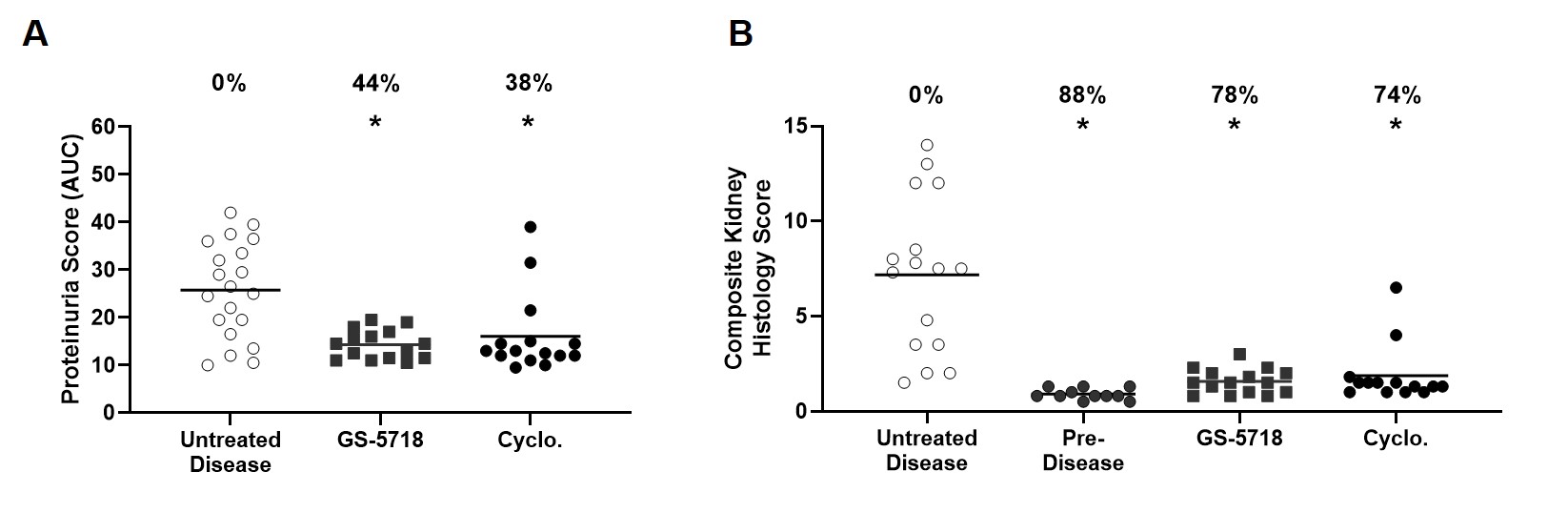
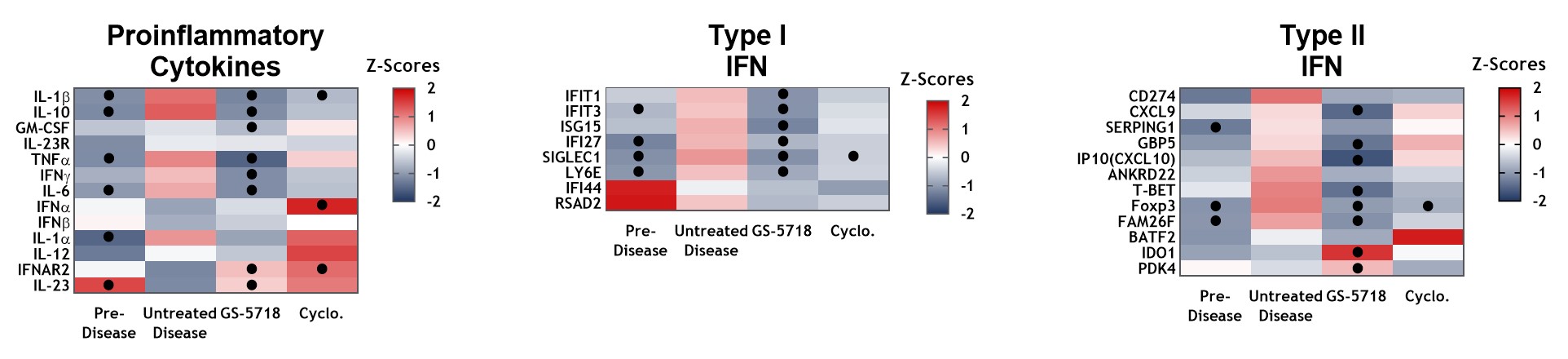
Results: GS-5718 treated animals displayed improved in-life disease outcomes, histological measures, and pharmacodynamically reduced multiple inflammatory endpoints. Administration of GS-5718 showed statistically significant improvements in survival and reduced proteinuria, splenomegaly, and serum cholesterol levels compared to control animals. Kidney histology revealed GS-5718 treatment decreased swelling, crescent formation and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining in glomeruli, protein casts in the cortex, and perivascular infiltration. These improvements in disease pathologies were accompanied by statistically significant reductions in peripheral cytokine production, kidney cytokine and interferon gene expression, and splenic immune cell infiltration.
Conclusion: GS-5718 treatment showed statistically significant improvements in survival and disease progression in a murine NZB/W spontaneous lupus model accompanied by improvements in pharmacodynamic inflammatory endpoints. These results suggest a pathological role for IRAK4 signaling in a pre-clinical mouse lupus model and supports further evaluation of GS-5718 for therapeutic intervention in lupus patients.
References
1 Devarapu, S. K. & Anders, H. J. Toll-like receptors in lupus nephritis. J Biomed Sci 25, 35 (2018).
2 Perry, D., Sang, A., Yin, Y., Zheng, Y. Y. & Morel, L. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011, 271694 (2011).
3 Celhar, T. & Fairhurst, A. M. Modelling clinical systemic lupus erythematosus: similarities, differences and success stories. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56, i88-i99 (2017).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yadon A, Gorney V, Hammond A, Grant E, Clarke A. The Clinical, Oral Small Molecule IRAK4 Inhibitor, GS-5718, Improves Survival and Reduces Disease Pathologies by Modulating Multiple Inflammatory Endpoints in the Murine NZB/W Model of Spontaneous Lupus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-oral-small-molecule-irak4-inhibitor-gs-5718-improves-survival-and-reduces-disease-pathologies-by-modulating-multiple-inflammatory-endpoints-in-the-murine-nzb-w-model-of-spontaneous-lup/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-oral-small-molecule-irak4-inhibitor-gs-5718-improves-survival-and-reduces-disease-pathologies-by-modulating-multiple-inflammatory-endpoints-in-the-murine-nzb-w-model-of-spontaneous-lup/