Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I (0387–0413)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: High resolution computed tomography (conventional CT) represents the diagnostic gold standard for systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). A low-dose 9-slices (reduced) CT protocol was previously shown to be a highly sensitive tool to screen for ILD and to classify it into limited or extensive according to the Goh et al visual staging system (1). Histogram-based densitometry analysis is an automated quantitative evaluation of SSc-ILD, with mean lung attenuation, skewness, and kurtosis as main variables, recently merged into a Computerized Integrated Index (CII) (2). CII has shown good discrimination of SSc-ILD presence and association with the Goh et al staging on conventional CT. We aimed at testing the CII in reduced CT, in comparison to conventional CT, in discriminating for the presence and severity of SSc-ILD.
Methods: We analyzed prospectively collected conventional and reduced CT images of SSc patients followed at our tertiary referral center. The Goh et al staging (limited vs extensive ILD) was applied by an experienced radiologist. Conventional and reduced CT images were analyzed using the free-source software Horos to obtain the CII, named conventional and reduced CII respectively. We measured the association between CIIs and categories using generalized estimating equations (GEE). The predictive ability of CIIs was assessed in a ROC analysis.
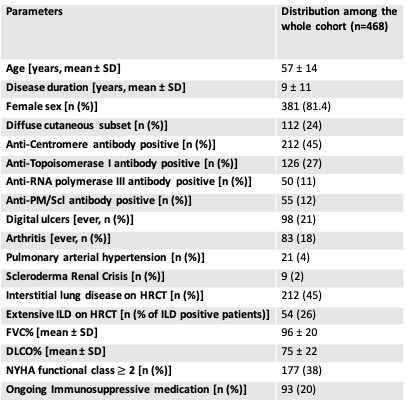
Results: We enrolled 468 SSc patients, further described in the table 1: 427 had undergone at least one conventional CT (total 719 CTs), 345 at least one reduced CT (total 814 reduced CTs). Both CT and reduced CT images were available at the same visits for 243 patients (total 294 conventional + reduced CTs). The three groups were comparable in terms of ILD prevalence and extensive ILD (48% vs 45% vs 48% and 25% vs 21% vs 20%, in conventional CT, reduced CT and conventional + reduced CTs groups, respectively).
Both conventional and reduced CII significantly differentiated ILD vs non-ILD (mean conventional CII-0.46±0.15vs 0.67±0.09, p< 0.001 and mean reduced CII -0.50±0.17 vs 0.48±0.11, p< 0.001, respectively). Similarly, they separated limited vs extensive ILD (mean conventional CII -0.12±0.14 vs -1.48±0.21, p< 0.001, and mean reduced CII -0.25±0.13 vs -1.71±0.20, p< 0.001, respectively).
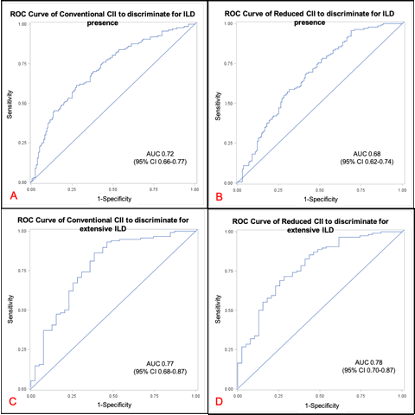
The two CIIs similarly predicted the presence of ILD [conventional CII AUC 0.72 (95% CI 0.66-0.77) vs reduced CII AUC 0.68 (95% CI 0.62-0.74); p=0.28, Figure 1A-B]. A similar performance was shown for extensive vs limited ILD [conventional CII AUC 0.77 (95% CI 0.68-0.87) vs reduced CII AUC 0.78 (95% CI 0.70-0.87), p=0.86, Figure 1C-D].
A cut-off for conventional CII< -0.96 (85% sensitivity, 62% specificity) or a reduced CII< -1.85 (85% sensitivity, 54% specificity) was chosen for an optimal sensitivity to detect extensive ILD.
Conclusion: We validated the ability of the CII to detect the presence of ILD and identified cut-offs for both conventional and reduced CII to discriminate between extensive versus limited ILD. Further validation of the proposed cut-offs is ongoing to further support its use in clinical practice and research.
References: 1) Goh et al, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 2)Bocchino et al, Sci Rep 2019
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
BRUNI C, Garaiman A, Tofani L, Jordan S, Mihai C, Dobrota R, ELHAI M, Becker M, Matucci-Cerinic M, Distler O. A Histogram-based Densitometry Index to Support the Identification and the Assessment of Severity of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis: Applicability in Conventional and Low-dose Computed Tomography [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-histogram-based-densitometry-index-to-support-the-identification-and-the-assessment-of-severity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-applicability-in-conventional-and-low-dose-compute/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-histogram-based-densitometry-index-to-support-the-identification-and-the-assessment-of-severity-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-systemic-sclerosis-applicability-in-conventional-and-low-dose-compute/