Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Sjögren's Syndrome – Basic & Clinical Science Poster (0296–0322)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Dry mouth and eyes are the main clinical features of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), although a minority of patients present without sicca manifestations and isolated cases of oral or ocular dryness are rare. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether isolated mouth or eye dryness constitute distinct clinical phenotypes of SS.
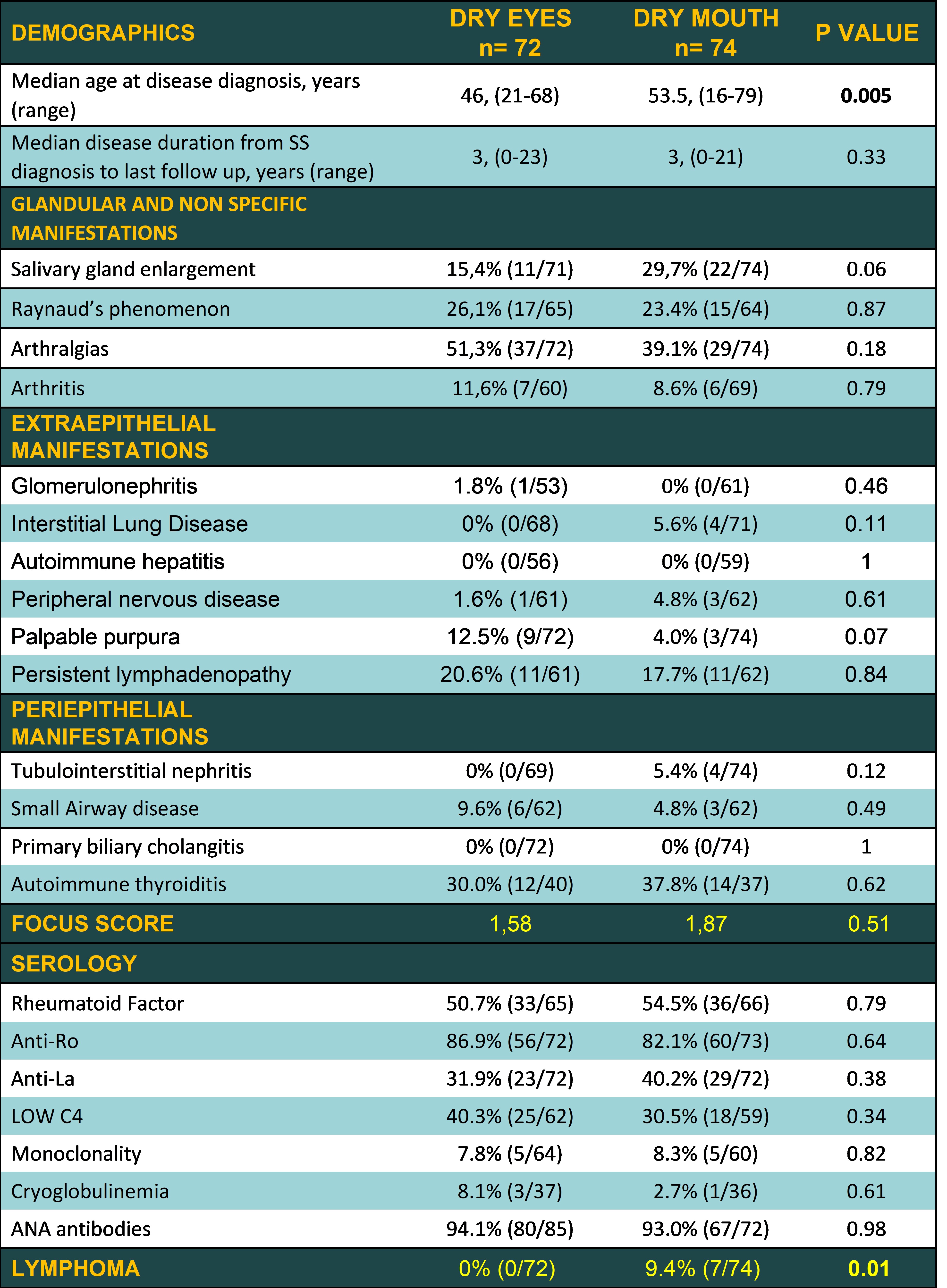
Methods: From a total population of 1765 consecutive patients fulfilling the 2016 ACR-EULAR criteria for SS, who were followed-up in 4 centers from Greece and Italy (Universities of Athens, Pisa, Harokopio and Ioannina) (PAHI group), those with isolated mouth or eye dryness, were identified and matched according to age at SS diagnosis, gender and disease duration from SS diagnosis to last follow up in a 1:2 ratio, with SS patients exhibiting both oral and ocular dryness. The 2 study groups of isolated dryness were defined as follows: a) patients with ocular dryness without oral dryness and b) patients with oral dryness without ocular dryness as documented by the AECG validated questionnaires. Cumulative data regarding glandular (dry mouth, dry eyes, parotid gland enlargement) and extra-glandular manifestations (Raynaud’s phenomenon, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias/arthritis, palpable purpura, liver involvement, kidney involvement, lymphoma), serology (anti Ro/SSA, anti La/SSB, rheumatoid factor, cryoglobulinemia, low C4 complement levels) and histologic features (focus score) were recorded and compared between each study group with their matched SS controls and between the 2 study groups as well. Statistical analysis for categorical data was performed by Fisher exact test or χ2 square test accordingly and numerical data with Man Whitney test.
Results: Seventy-two patients with isolated ocular dryness and 74 with isolated oral dryness were identified and compared with 144 and 148 SS controls, respectively. The median disease duration of both study groups was 3 years [range: 0-23 (ocular dryness group) and 0-21 (oral dryness group)] while the median age of SS diagnosis was 46 years old (range: 21-68) and 53,5 (range: 16-79) respectively. SS patients with isolated eye dryness had statistically significant lower frequency of salivary gland enlargement (35,4% vs 28,7%, p=0,05) and lymphoma (0% vs 11,3%, p=0,001) (Table 1) while in SS patients with isolated oral dryness arthralgias (39,1% vs 65,5%, p= 0,0003) and arthritis (8,6% vs 20,3%, p= 0,05) appeared less frequently, compared to their SS controls, respectively. After comparing the 2 study groups, it was found that SS patients with isolated oral dryness were diagnosed at older age (median: 53,5 vs 46 years old, p=0,005) and were more prone to develop lymphoma (9,4% vs 0%, p=0,01) compared to patients with isolated ocular dryness, without any difference in classical lymphoma predictors, including focus score (Table 2).
Conclusion: Patients with isolated ocular or oral mucosa dryness constitute 8% of total SS population and those with isolated dry eyes display lower frequency of lymphoma.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chatzis L, Goules A, Baldini C, Pezoulas V, Argyropoulou O, Voulgari P, Kouvelioti S, Fotiadis D, Skopouli F, Moutsopoulos H, Tzioufas A. The Clinical Phenotype of Isolated Ocular and Oral Dryness in Sjogren Syndrome, Fulfilling the 2016 ACR-EULAR Classification Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-phenotype-of-isolated-ocular-and-oral-dryness-in-sjogren-syndrome-fulfilling-the-2016-acr-eular-classification-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-phenotype-of-isolated-ocular-and-oral-dryness-in-sjogren-syndrome-fulfilling-the-2016-acr-eular-classification-criteria/