Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 12:00PM-12:50PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a disease involves the complex interplay of many genes, reflected in more than one hundred loci linked with disease risk by genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Decoding GWAS is, therefore, a promising strategy to identify novel drug targets in SLE. However, most of the identified disease-associated hits are noncoding single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), and cannot be distinguished from others that reside incidentally within risk loci. To address this longstanding challenge of finding the real functional regulatory SNPs (fSNPs) from GWAS hits in SLE, we utilized an unbiased high-throughput screen method to investigate GWAS hits.
Methods: From 4 GWAS for SLE (Gateva, Sandling et al. 2009, Bentham, Morris et al. 2015, Morris, Sheng et al. 2016, Langefeld, Ainsworth et al. 2017, Zhang, Zhang et al. 2018), 87 disease-associated SNPs were chosen as lead SNPs and SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD)(R2>0.8) with them are also included as the screening library. In a total of 2176 SNPs were screened by three different high-throughput methods, SNP-seq (Li, Martinez-Bonet et al. 2018), H3K4me3 epigenetic modification (Trynka, Sandor et al. 2013), and Combined Annotation Dependent Depletion (CADD) (Rentzsch, Witten et al. 2018). Top candidates from the screening were further tested for regulatory function by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and luciferase reporter assay to get the final fSNPs candidates. Then through bioinformatics binding motif prediction and mass spectrometry for oligo pulldown assay, the transcriptional factor that might bind to the fSNPs was found and later validated by CHIP-qPCR, western blot for oligo pulldown assay as well as supershift assay.
Results: Fifty-four candidate fSNPs from 2176 SNPs after three screening methods were found to be possible regulatory variants and tested for regulatory function. After EMSA, 9 SNPs showed allelic specific binding to proteins from both BL2 cells (B cell line) and PBMC nuclear extract. Six out of these 9 SNPs showed allelic differential gene expression in luciferase reporter assay in a B cell line (Daudi). After bioinformatics predictions as well as mass spectrometry for oligo pulldown assay, two fSNPs (rs2297550 and rs9907966) were found to be able to bind to transcriptional factor IKZF1 and YBX1 in B cells respectively by allelic specific pulldown assay, CHIP-qPCR, and EMSA-supershift assay.
Conclusion: Our unbiased high-throughput screening for SLE GWAS hits, followed by a step-wise validation leads to the identification of real functional regulatory SNPs that are capable of binding to transcriptional factors and regulate gene expression, which establish a working model to bridge the gap between SLE GWAS and disease mechanism.
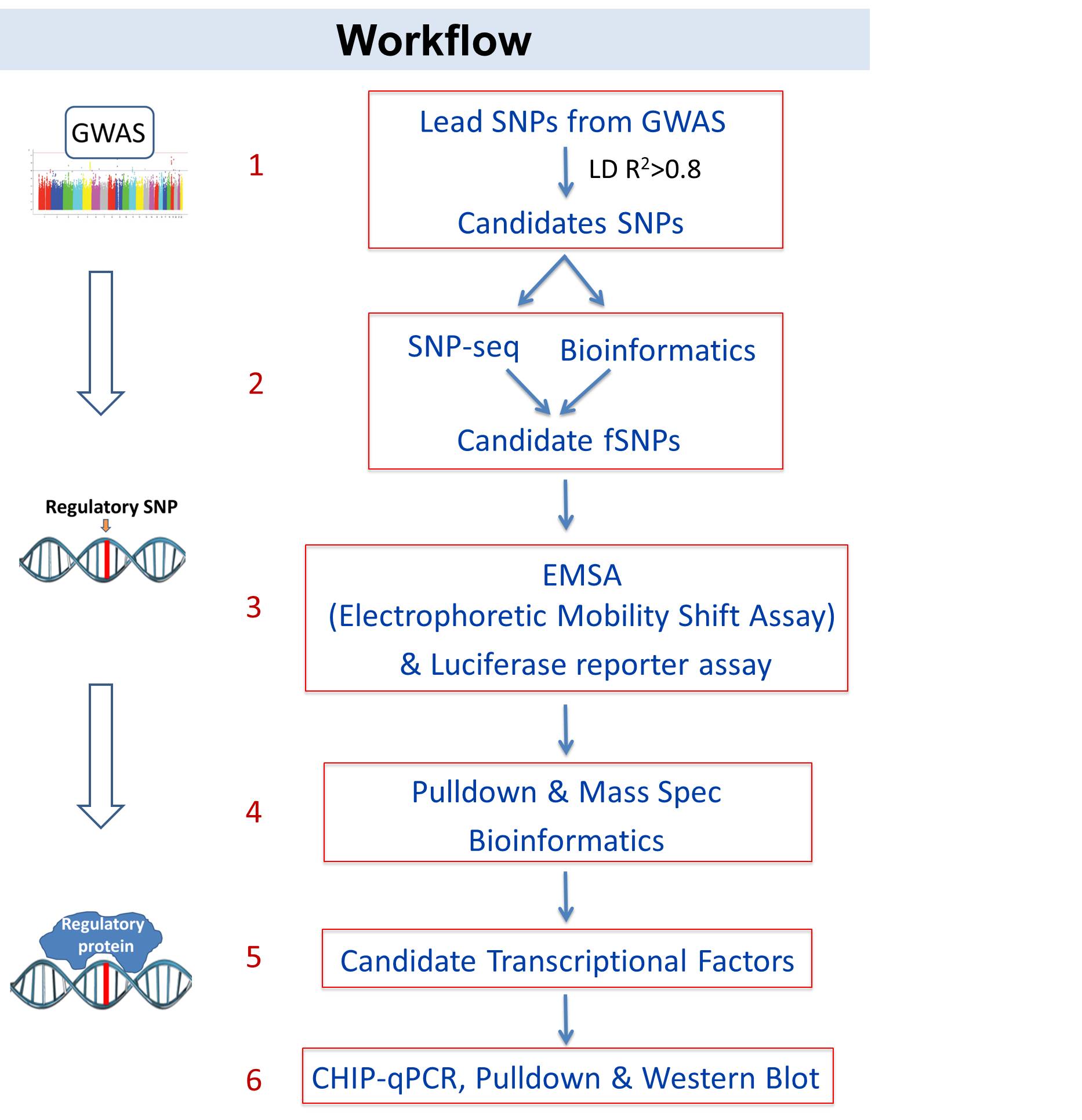 Fig 1. Workflow of identify variant-protein associations. 1-3: Identify novel regulatory variants that modulate SLE risk; 4-6: identify variant-protein associations in SLE.
Fig 1. Workflow of identify variant-protein associations. 1-3: Identify novel regulatory variants that modulate SLE risk; 4-6: identify variant-protein associations in SLE.
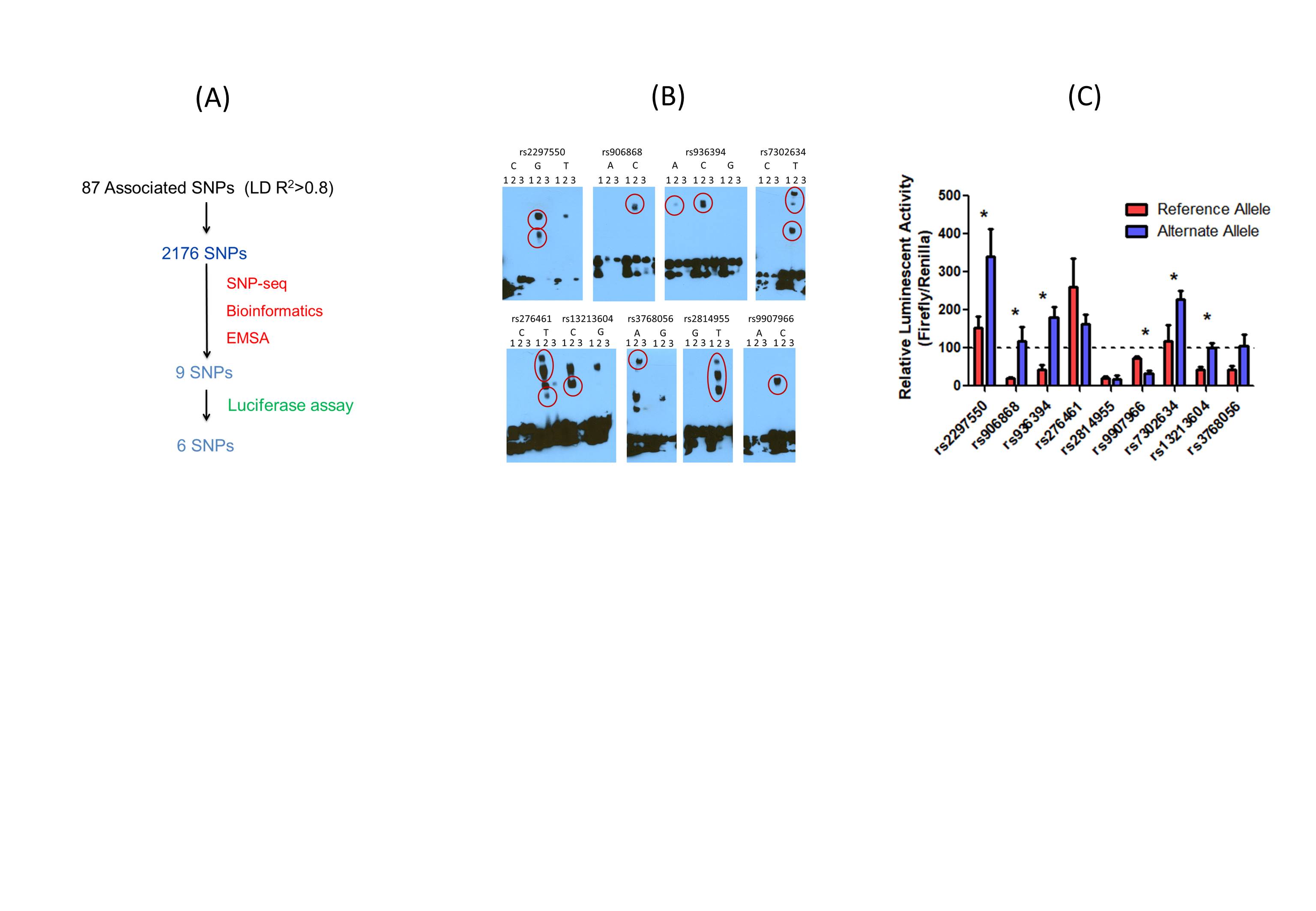 Fig 2. Identify Novel Regulatory Variants that Modulate SLE risk. (A): SNPs associated with SLE screening, 6 out of 2176 are found to be regulatory variants; (B): EMSA for 9 SNPs candidates that show allele-specific gel shift/binding (shown as red dots).1: biotinylated oligo alone; 2: biotinylated oligo with nuclear extract; 3: oligo with nuclear extract and non-biotinylated competitor. (n = 3 independent biological replicates with similar results). (C): Luciferase reporter assay shows allelic specific regulatory activity for 6 SNPs associated with SLE (* represents p < 0.05).
Fig 2. Identify Novel Regulatory Variants that Modulate SLE risk. (A): SNPs associated with SLE screening, 6 out of 2176 are found to be regulatory variants; (B): EMSA for 9 SNPs candidates that show allele-specific gel shift/binding (shown as red dots).1: biotinylated oligo alone; 2: biotinylated oligo with nuclear extract; 3: oligo with nuclear extract and non-biotinylated competitor. (n = 3 independent biological replicates with similar results). (C): Luciferase reporter assay shows allelic specific regulatory activity for 6 SNPs associated with SLE (* represents p < 0.05).
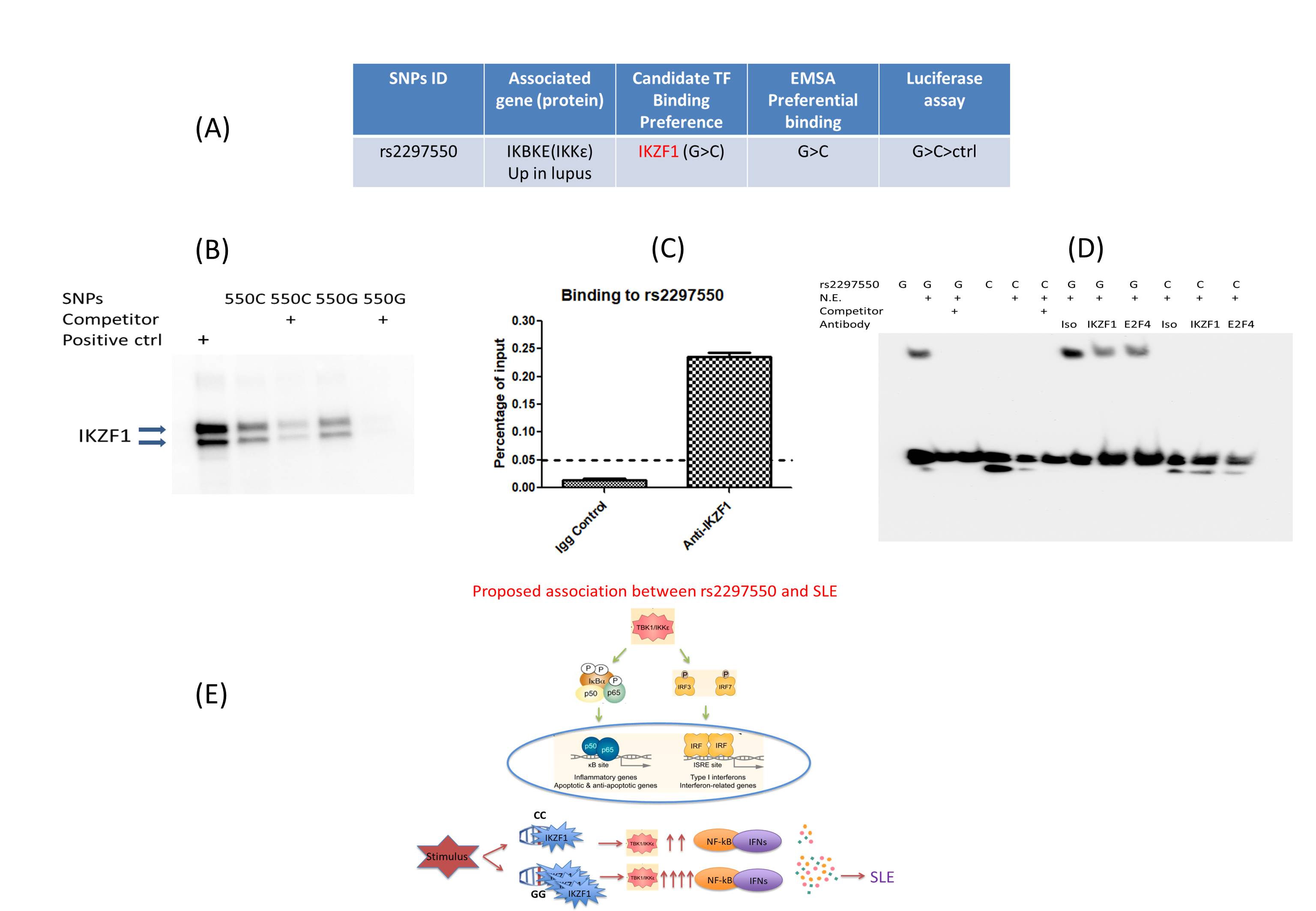 Fig 3. Identify Novel variant-protein association in SLE. (A): Table shows candidate TF (IKZF1) bound to variant rs2297550 after pulldown assay & MS and bioinformatics prediction. (B, C, D): Pulldown assay & WB and Chromatin Immunoprecipitation–qPCR and EMSA supershift assay show IKZF1 binds rs2297550, more specifically to G allele than C. (D): Proposed association between rs2297550 and SLE.
Fig 3. Identify Novel variant-protein association in SLE. (A): Table shows candidate TF (IKZF1) bound to variant rs2297550 after pulldown assay & MS and bioinformatics prediction. (B, C, D): Pulldown assay & WB and Chromatin Immunoprecipitation–qPCR and EMSA supershift assay show IKZF1 binds rs2297550, more specifically to G allele than C. (D): Proposed association between rs2297550 and SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Q, Martínez M, Weirauch M, Nigrovic P. High-throughput Identification of Functional Regulatory SNPs Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-identification-of-functional-regulatory-snps-associated-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-identification-of-functional-regulatory-snps-associated-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
