Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Repository corticotropin injection (RCI, Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals) is a naturally sourced complex mixture of adrenocorticotropic hormone analogs and other pituitary peptides approved for the treatment of SLE flares and as maintenance therapy. This post hoc analysis of patient-reported outcomes (PROs) from a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled study of RCI in patients with persistently active SLE despite use of moderate-dose glucocorticoids (GCs) was conducted to assess RCI-dependent quality of life (QOL) improvements (NCT02953821).
Methods: Patients were ≥18 years old with active SLE (≥4 of 11 ACR criteria; SLEDAI-2000 [SLEDAI-2K] ≥6) and moderate-severe rash and/or arthritis by BILAG despite stable GC doses (7.5-30 mg/d prednisone equivalent), antimalarials, NSAIDs for ≥4 weeks (Ws), and/or immunosuppressants for ≥8 Ws before screening. Patients were randomized to 80 U RCI subcutaneously or PBO every other day to W4 followed by twice-weekly dosing to W24. Stable GC doses were required through W16 with optional taper from W16 to W24. Primary analyses evaluated the change from baseline (BL) in the LupusQOL and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI)-Lupus questionnaires through W24. Post hoc analyses stratified these results by BL SLEDAI-2K (< 10 vs ≥10), Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Disease Area and Severity Index-Activity [CLASI-A (< 11 vs ≥11)], and BILAG (< 20 vs ≥20) scores and by BILAG-based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA) response (patients with BICLA responses at both W20 and W24). Analyses were performed in the modified intention-to-treat population (mITT-P; patients who received ≥1 dose of study drug and contributed any post-BL efficacy data).
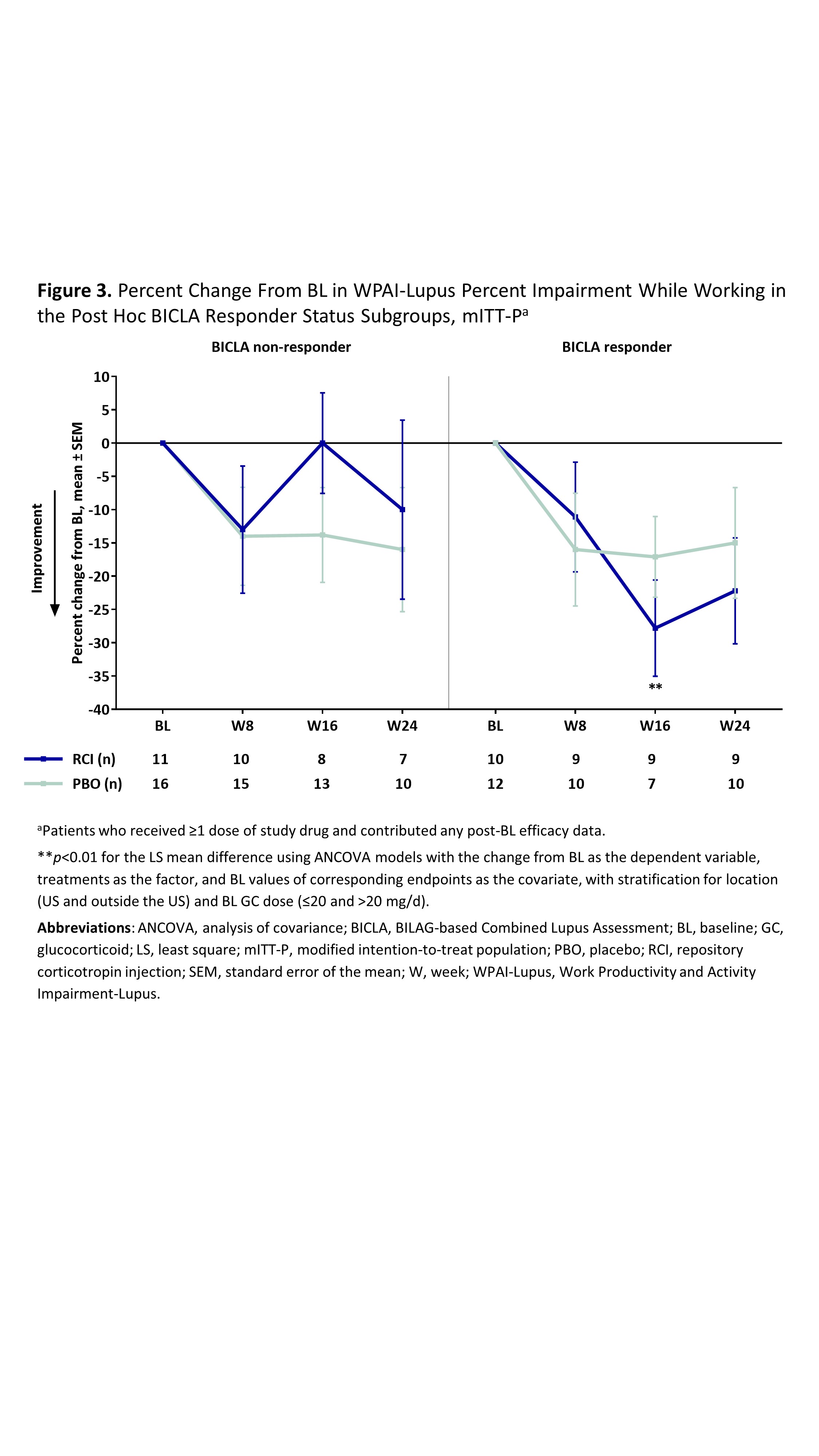
Results: The mITT-P (RCI, n=84; PBO, n=85) was predominantly female (91.7%) with a mean age of 39.7 years, mean BL GC dose of 11.1 mg, and mean BL SLEDAI-2K score of 9.9. RCI treatment resulted in significantly greater improvement in the LupusQOL pain domain at W16 and planning domain at W24 compared with PBO (Figure 1) and exceeded the minimal clinically important difference at all time points. Post hoc analyses demonstrated significant improvements in the pain, planning, and fatigue domains at multiple time points in RCI-treated patients with higher disease activity by BL SLEDAI-2K, CLASI-A, and BILAG and in BICLA responders (Figure 2). No significant differences between treatment groups were observed for any WPAI-Lupus parameter through W24 in the primary analysis or with higher disease activity in post hoc SLEDAI-2K, BILAG, or CLASI-A subgroups. However, RCI treatment resulted in significant improvements in percent work time missed at W24 in patients with BL CLASI-A < 11 (RCI mean change –8.4 [standard deviation (SD) 25.1]; PBO mean change 7.8 [SD 21.9]; p=0.0182 for least square mean difference) and in percent impairment while working at W16 in BICLA responders compared with PBO (Figure 3).
Conclusion: RCI treatment resulted in greater improvements in several PROs compared with PBO. These results suggest that treatment with RCI may improve QOL and work productivity in patients who have persistently active SLE despite treatment with standard SLE therapy, particularly in those with higher disease activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, Wan G, Panaccio M, Zhao E, Zhu J, Bilyk R, Furie R. Repository Corticotropin Injection (Acthar® Gel) for Persistently Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Post Hoc Analyses of Patient-Reported Outcomes from a Phase 4, Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/repository-corticotropin-injection-acthar-gel-for-persistently-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-post-hoc-analyses-of-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-phase-4-multicenter-randomized-doub/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/repository-corticotropin-injection-acthar-gel-for-persistently-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-post-hoc-analyses-of-patient-reported-outcomes-from-a-phase-4-multicenter-randomized-doub/