Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis. Aberrant T cell regulation has been implicated in the process of inflammation in PsA. One of the regulatory receptors expressed on T cells is lymphocyte-activation gene (LAG)-3. We aimed to assess the surface expression levels of LAG-3 on CD4+ T cells derived from PsA patients with low and high disease activity in comparison with healthy controls and to determine the in vitro effect of biologics on the LAG-3+ T cell population.
Methods: Consecutive patients with PsA were recruited to this study, clinically assessed and classified as having minimal disease activity (MDA) or non-MDA. healthy donors were included as controls. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were co-cultured with medium alone or with TNF or IL-17A inhibitors and their effect on CD4+LAG-3+ T cells proportion was determined.
Results: The basal levels of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells in fresh PBMCs was undetectable, we then used in vitro conditions to detect CD4+LAG-3+ T cells. In PBMCs derived from healthy controls (n=15) as well as from MDA PsA patients (n=14) the percentages of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells after 5 days of in vitro incubation with medium alone was (7.7±0.6 and 7.5±0.9, respectively). Supplementation of either TNF or IL-17A inhibitors to the culture had no effect on the percentages of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells (8.5±0.6, 7.0±0.6 and 7.6±0.9, 7.7±0.9, respectively) (Figure 1).
In contrast, significantly lower percentages of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells were found in non-MDA (n=13) (3.1±03, p< 0.0001) as compared to MDA PsA patients and healthy controls (7.7±0.6 and 7.5±0.9). In non-MDA PsA patients, incubation with TNF inhibitor restored the percentages of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells compared to medium control (7.9±0.9, p< 0.0001), to an equivalent levels as determined after incubation with medium alone in healthy and MDA PsA patients. On the other hand, after supplementation of IL-17A inhibitor the CD4+LAG-3+ T cells proportion remain low (3.2±0.4).
Moreover, there was a significant inverse correlation between percentages of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells after in vitro culture with medium alone and the clinical disease activity of the PsA patients in the cohort (CPDAI, r=-0.47, p < 0.02 and PASDAS, r=-0.51, p < 0.008).
Conclusion: Lower surface LAG-3 expression levels on CD4+ T cells may reflect active PsA disease state. TNF inhibitors have potency to up-regulate this population. Larger studies are needed to verify this observation.
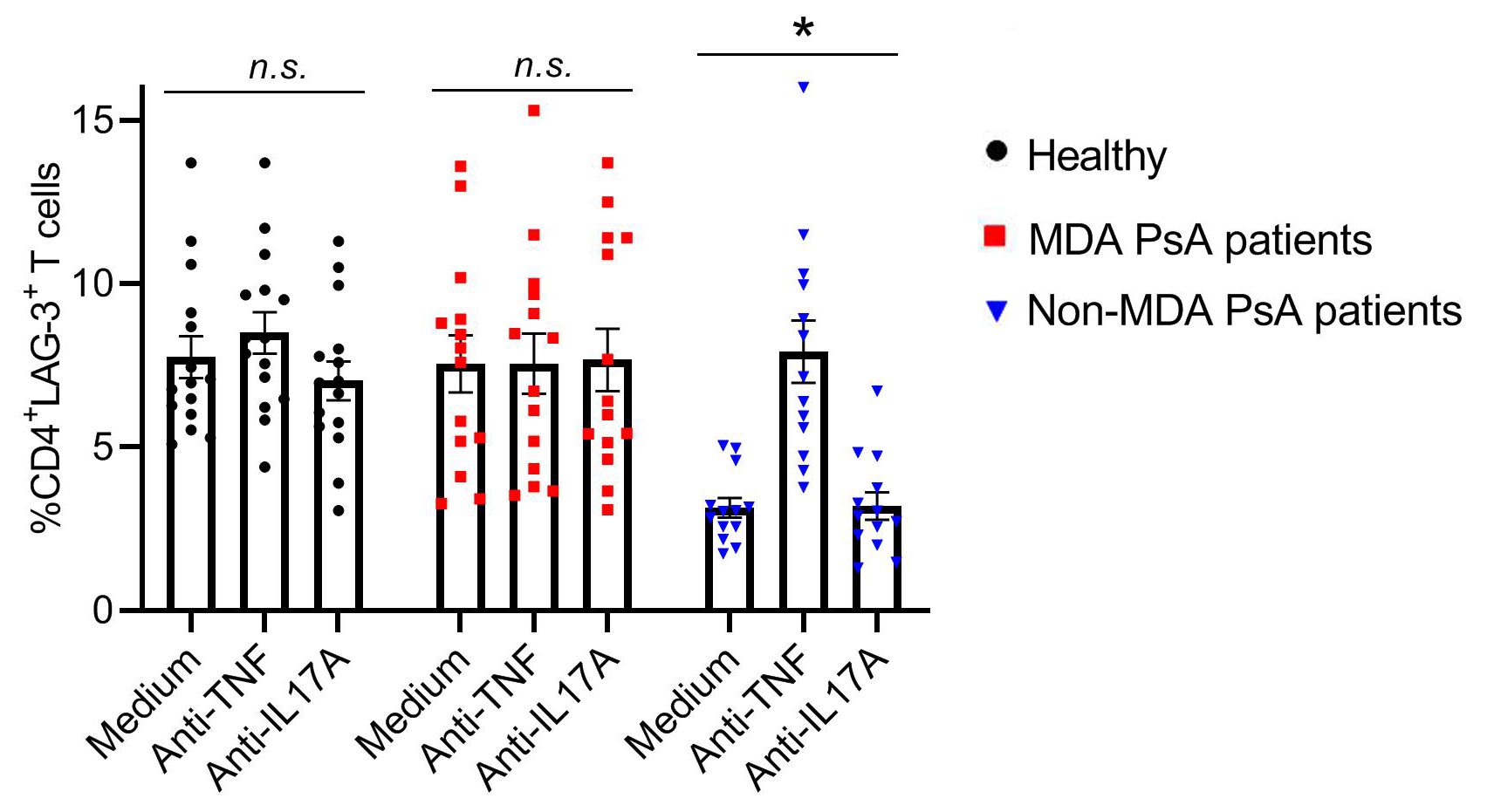 Figure 1. Levels of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells in PBMCs derived from healthy, MDA and non-MDA PsA patients and the ability of TNF and IL-17 inhibitors to modulate the CD4+LAG-3+ T cells in vitro. Freshly isolated PBMCs from healthy donors (n=15), MDA (n=14) and non-MDA (n=13) PsA patients were co-cultured for 5 days in RPMI medium alone or supplemented with TNF inhibitor (Adalimumab) or IL-17A inhibitor (Ixekizumab). Cells were subsequently stained with CD4 and LAG-3 Abs. Surface CD4 and LAG-3 expression was determined by flow cytometry. Graphs represent the mean percentages ±SEM of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells. Significance between groups was determined by Mann-Whitney U test, * p < 0.0001.
Figure 1. Levels of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells in PBMCs derived from healthy, MDA and non-MDA PsA patients and the ability of TNF and IL-17 inhibitors to modulate the CD4+LAG-3+ T cells in vitro. Freshly isolated PBMCs from healthy donors (n=15), MDA (n=14) and non-MDA (n=13) PsA patients were co-cultured for 5 days in RPMI medium alone or supplemented with TNF inhibitor (Adalimumab) or IL-17A inhibitor (Ixekizumab). Cells were subsequently stained with CD4 and LAG-3 Abs. Surface CD4 and LAG-3 expression was determined by flow cytometry. Graphs represent the mean percentages ±SEM of CD4+LAG-3+ T cells. Significance between groups was determined by Mann-Whitney U test, * p < 0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gertel S, Polachek A, Furer V, Levartovsky D, Elkayam O. LAG-3+ T Cells Are Diminished in Active Psoriatic Arthritis Patients and Their Restoration in Vitro Is Mediated by TNF Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lag-3-t-cells-are-diminished-in-active-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-and-their-restoration-in-vitro-is-mediated-by-tnf-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/lag-3-t-cells-are-diminished-in-active-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-and-their-restoration-in-vitro-is-mediated-by-tnf-inhibitors/
