Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The importance of non-pharmacologic interventions in systemic sclerosis (SSc) is increasingly recognized. Physical therapy is among the most frequently used interventions, but knowledge on its actual provision in daily practice and patients’ perspectives on its delivery is absent. Therefore this study aimed to assess among patients with SSc the usage, contents, satisfaction, needs and preferences regarding the provision of physical therapy.
Methods: Four hundred and five SSc patients, fulfilling the ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria for SSc and participating in the multidisciplinary SSc care pathway of the Leiden University Medical Center were invited. They are seen by a physical therapist at the yearly assessment related to the care pathway, if treatment is needed they are referred to primary care. Between July-August 2019 they received a pen-and-paper questionnaire consisting of 39 questions regarding usage of physical therapy over the past two years (thirteen multiple-choice questions), contents (five multiple-choice questions), satisfaction (eight questions, 0-10 scale-based, multi-response, open field), and needs and preferences (thirteen questions, dichotomous, multi-response, open field).
Results: In total, 204 SSc patients (median age: 63 years, 80% female) were included (Table 1). Over the past two years, 62% (n=127) patients received physical therapy (PT-group; 94% in the primary care setting), whereas 38% (n=77) did not (No-PT-group). Regarding active treatment modalities, muscle strengthening (n=91, 71%), range of motion (n=88, 69%) and aerobic exercises (n=72, 56%) were most frequently mentioned (Table 2). Concerning passive modalities, 46% (n=59) of patients received massage and 16% (n=21) kinesiotaping. Twenty percent of patients reported SSc specific treatments including hand (n=20, 16%) and mouth (n=7, 6%) exercises. Thirty-one percent (n=40) of the patients were encouraged to spend time on physical activity at home. Seventy percent (n=142) of all included patients indicated physical therapy as a valuable part of the standardized Care Pathway at the Leiden University Medical Center. Of the total group, 47% (n=96) patients preferred to receive more information regarding physical therapy and 63% (n=128) to continue/(re)start physical therapy in the near future, favoring individual continuous therapy (n=50/128, 39%) by physical therapist close to home (n=61/128, 48%). Eighty percent (n=163) stated that specific knowledge on systemic sclerosis and/or rheumatic diseases is necessary for physical therapists to treat systemic sclerosis patients.
Conclusion: Sixty-two percent of systemic sclerosis patients received physical therapy in a period of two years mostly consisting of active treatment.The use of passive treatment modalities and hand and mouth exercises was highly variable. Although all patients are seen once-yearly by a physical therapist in a multidisciplinary care pathway, more than half expressed an unmet need regarding physical therapy. These results could help improve content and patient education regarding physical therapy for SSc.
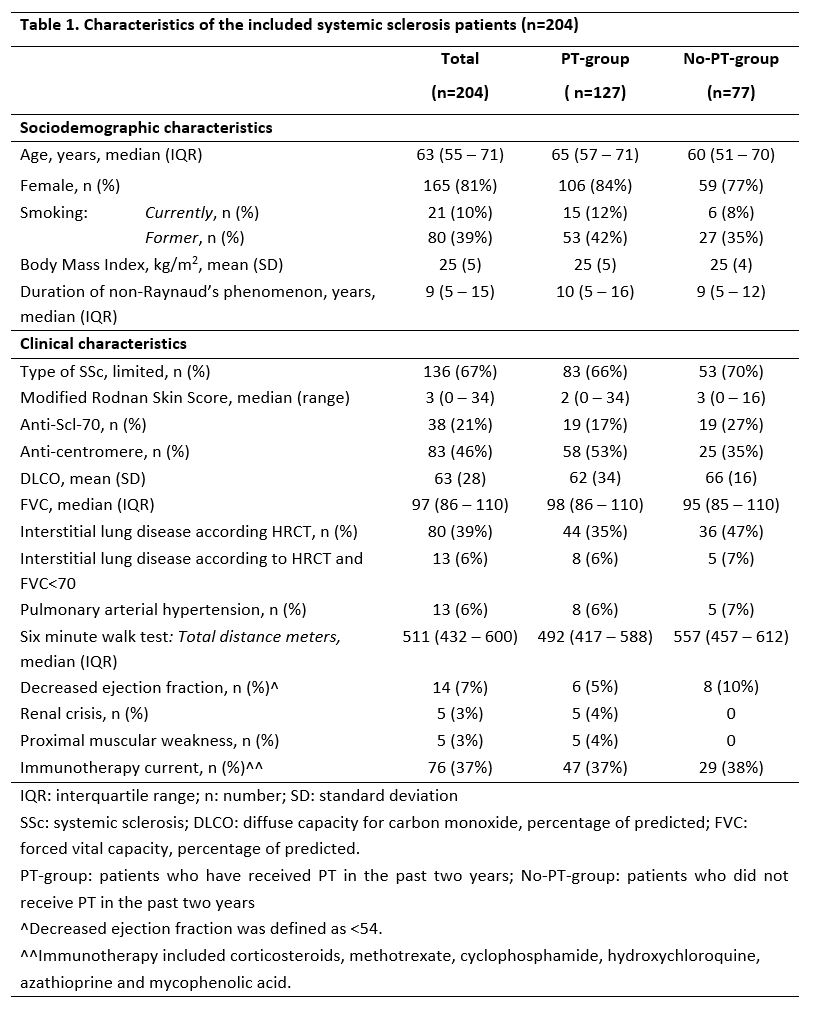 Table 1. Characteristics of the included systemic sclerosis patients (n=204)
Table 1. Characteristics of the included systemic sclerosis patients (n=204)
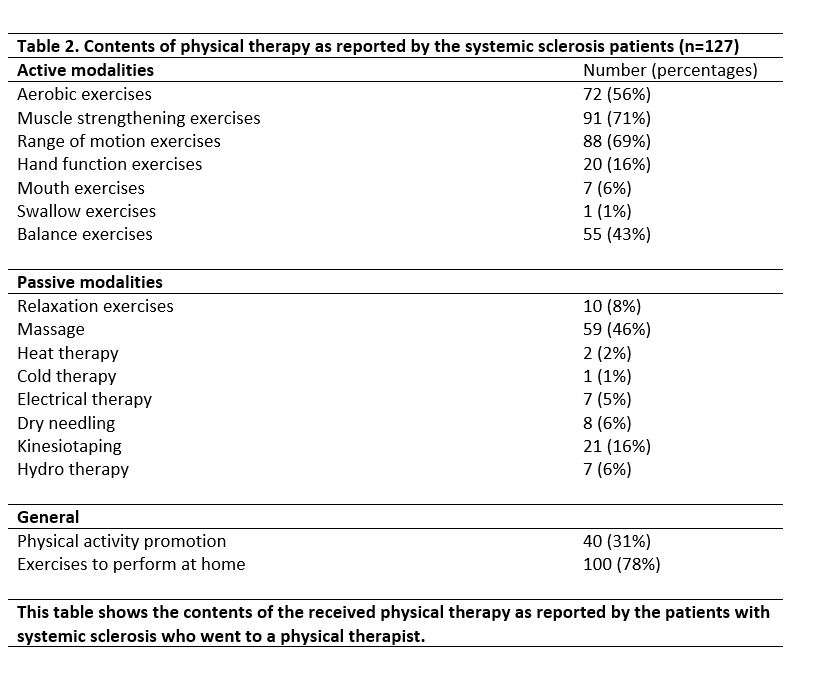 Table 2. Contents of physical therapy as reported by the systemic sclerosis patients (n=127)
Table 2. Contents of physical therapy as reported by the systemic sclerosis patients (n=127)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Liem S, van Leeuwen N, Vliet Vlieland T, de Pundert L, Schriemer R, Spierings J, Vonk M, de Vries-Bouwstra J. Usage, Needs and Preferences Regarding Physical Therapy in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/usage-needs-and-preferences-regarding-physical-therapy-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/usage-needs-and-preferences-regarding-physical-therapy-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/
