Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: IIn rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a patient’s biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD) history and the duration of time they remain on each drug may provide an alternative approach to studying treatment efficacy. Due to the complexity of these data, how to determine if patients are similar based on their past bDMARD use is challenging. Bioinformatics methods designed to study genetic sequences are now available that cluster sequences by similarity. In this proof of concept study, we applied and modified this bioinformatics approach to cluster RA patients by similar sequences of bDMARD prescriptions.
Methods: We studied patients from a validated electronic health record cohort of RA patients from two tertiary care centers and extracted data on all subjects who initiated a bDMARD 1/1/2008 through 07/31/2019. Inclusion criteria included subjects with ≥6 months of data prior to 1/1/2008 and no bDMARD prescription. The sequence of bDMARD for each subject was initiated with the 1st bDMARD prescription. Sequences were defined by 5 bDMARD drug classes: tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi), CTLA4-Ig/abatacept, IL6R blockade/tocilizumab, JAK inhibitor/tofacitinib (small molecule grouped as bDMARD for this study), and anti-CD20/rituximab. A change in bDMARD was defined as a change in bDMARD therapy ≥3 months from the prior bDMARD prescription. A sequence by drug class was constructed for each subject. The sequences were then analyzed using mixture Markov chain analysis. We consider the transitions of drug classes of a patient over the time as Markov chains where each of the drug classes was considered a state. We clustered the patients based on the sequence of drug classes. We calculated descriptive statistics for demographics, and obtained the Charlson comorbidity index at the time of the 1st bDMARD prescription to compare across clusters.
Results: We studied 8684 RA subjects who initiated a bDMARD after 1/1/2008. The mean age was 48.9 years, 73% female, 82% white, 68% seropositive, with mean follow-up time of 6.2 years; each subject had a unique sequence, thus there were 8684 sequences. The sequences clustered in 4 main groups (Figure). Descriptively, group 1 included patients who persisted on abatacept and tocilizumab therapy. Group 2 contained patients on TNFi for the majority of their follow-up. Group 3 contained a mixture of patients persisting on rituximab and TNFi. Group 4 included patients who tried multiple bDMARDs for variable lengths of time. The lowest % of females was observed in Group 2 (70%) compared to Group 4 (83%) which had the highest (p< 0.0001) (Table). The highest % seropositive was observed in group 1 (80.5%) compared with group 2 (65%) which had the lowest (p< 0.0001).
Conclusion: Transforming bDMARD prescription histories into a sequence allowed us to cluster RA patients into 4 main groups which demonstrated differing clinical characteristics at the time of the 1st bDMARD prescription. Future studies will examine whether the clinical profiles of patients in these clusters can be used to inform optimal bDMARD choices among RA patients prospectively.
 Visualization of the 4 groups identified from clustering bDMARD sequences. Data from 75 random patients from each group shown with x-axis denoting the first 20 states (V1-V20) for each patient.
Visualization of the 4 groups identified from clustering bDMARD sequences. Data from 75 random patients from each group shown with x-axis denoting the first 20 states (V1-V20) for each patient.
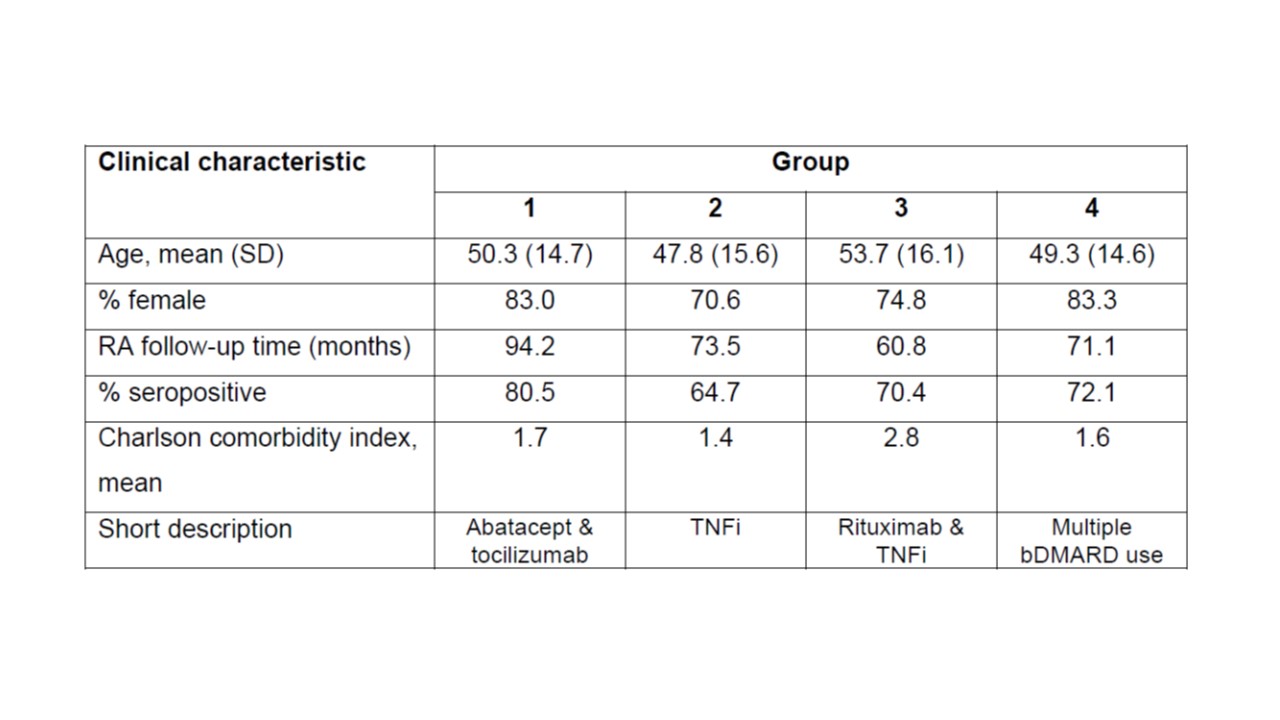 Comparison of clinical characteristics at the time of first bDMARD prescription across the 4 groups.
Comparison of clinical characteristics at the time of first bDMARD prescription across the 4 groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Das P, Huang S, Dahal K, Zheng H, Coblyn J, Weinblatt M, Cai T, Liao K. Characterizing Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients by Their Biologic DMARD Prescription History [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-by-their-biologic-dmard-prescription-history/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/characterizing-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-by-their-biologic-dmard-prescription-history/
