Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor engineered to have greater selectivity for JAK1 vs JAK2, JAK3, and tyrosine kinase 2, and is approved for the treatment of RA. Across 2 double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled Phase 3 studies of UPA in patients with RA, after an initial increase through Week 8, lipid levels remained stable up to Week 24.1,2 Previous studies of JAK or IL-6 receptor inhibitors have reported a negative correlation between changes in lipid levels and RA disease activity.3,4 The aim of this analysis was to determine the relationship between changes in lipid levels and disease activity outcomes in patients with RA treated with UPA.
Methods: Patients with RA and an inadequate response to conventional synthetic/biologic DMARDs (cs/bDMARD-IR) from SELECT-NEXT/SELECT-BEYOND, respectively, were randomized to receive UPA 15 mg once daily (QD), UPA 30 mg QD, or PBO for 12 weeks followed by an extension of up to 5 years; patients randomized to PBO switched to UPA 15 or 30 mg after 12 weeks. Spearman correlations of maximum changes from baseline (BL) through Week 12 in fasting-state lipid levels (low- and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL-C; HDL-C], and total cholesterol [TC]) with clinical disease activity outcomes measured by change from BL in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), DAS of 28 joints using CRP (DAS28[CRP]), tender/swollen joint count in 28 joints (TJC28/SJC28), and pain by visual analog scale (VAS) at Weeks 12 and 24, were determined. Spearman correlations of maximum changes from BL in lipid levels and CRP through Week 12 were also determined.
Results: Available fasting samples from 1,160 pooled patients (UPA 15 mg, n=386; UPA 30 mg, n=384; PBO, n=390) were included. Modest, but statistically significant, negative correlations were observed between maximum changes from BL in TC through Week 12 and change from BL in CDAI, DAS28(CRP), SJC28, and pain (VAS) at Week 12 with UPA 15 or 30 mg (Table 1); similar trends were observed at Week 24. Significant correlations between changes in LDL-C and HDL-C and disease activity outcomes were also observed, but were not consistent across UPA doses and time points. No significant correlations were noted between changes in lipid levels and disease activity outcomes in the PBO group. Statistically significant weak negative relationships were observed between maximum changes from BL in lipid levels and CRP levels through Week 12 with UPA 15 mg (HDL-C and TC) or UPA 30 mg (LDL-C and TC) (Table 2).
Conclusion: In this large pooled data set of patients receiving UPA, increases in lipid levels showed modest, but statistically significant, correlations with improvement in clinical disease activity outcomes in patients with cs/bDMARD-IR RA. These results add to evidence suggesting a relationship between systemic inflammation and lipid metabolism in patients with RA, which is modifiable with effective interventions, and reinforce the importance of monitoring for hyperlipidemia in these patients.
- Burmester GR, et al. Lancet 2018;391:2503–12.
- Genovese MC, et al. Lancet 2018;391:2513–24.
- Kremer JM, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2017;69:943–52.
- Cacciapaglia F, et al. Mediators Inflamm 2018;2018:2453265.
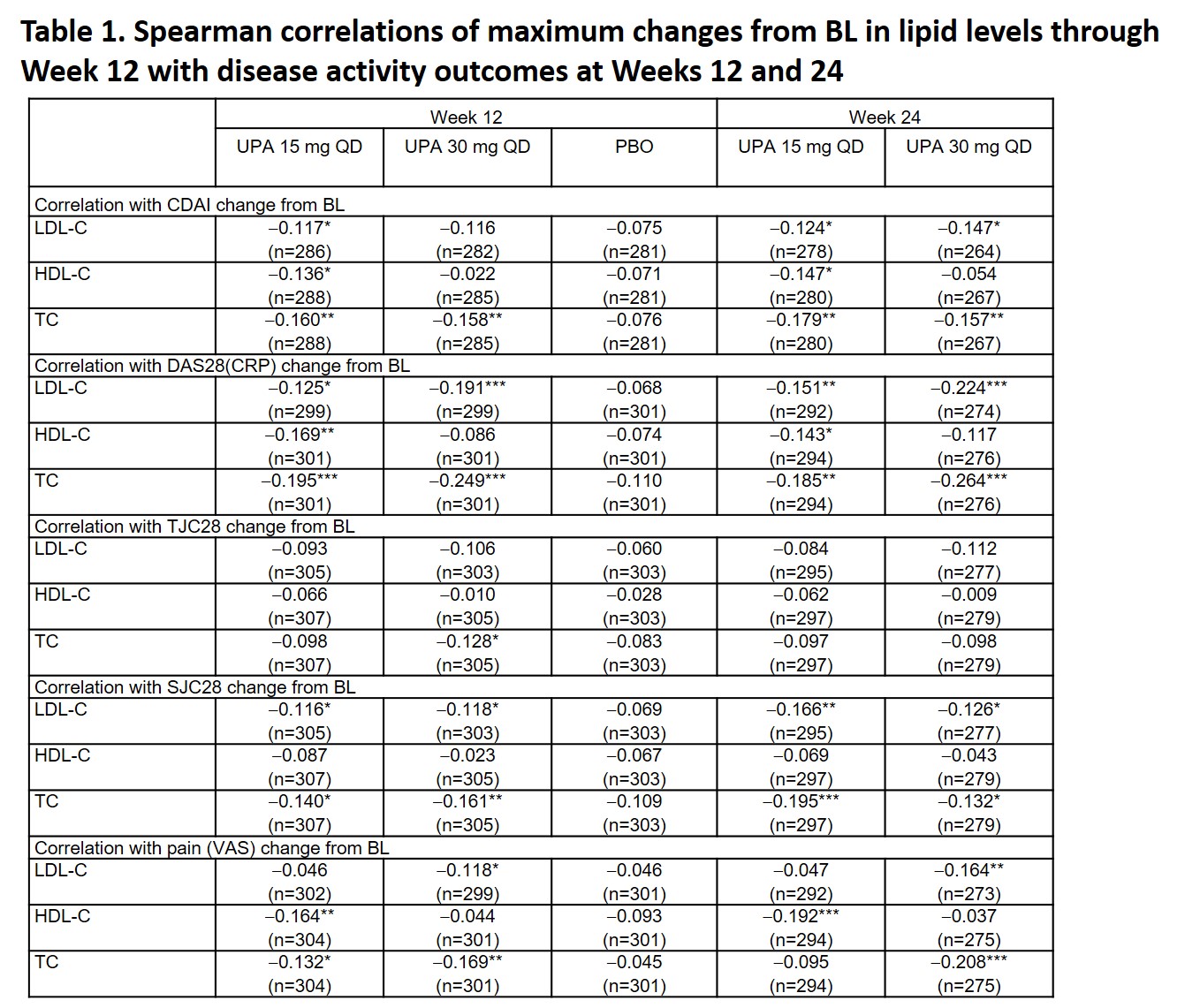 *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. BL, baseline; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; DAS28(CRP), DAS of 28 joints using CRP; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PBO, placebo; QD, once daily; SJC28, swollen joint count in 28 joints; TC, total cholesterol; TJC28, total joint count in 28 joints; UPA, upadacitinib; VAS, visual analog scale
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. BL, baseline; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; DAS28(CRP), DAS of 28 joints using CRP; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PBO, placebo; QD, once daily; SJC28, swollen joint count in 28 joints; TC, total cholesterol; TJC28, total joint count in 28 joints; UPA, upadacitinib; VAS, visual analog scale
 **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PBO, placebo; QD, once daily; TC, total cholesterol; UPA, upadacitinib
**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; PBO, placebo; QD, once daily; TC, total cholesterol; UPA, upadacitinib
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Charles-Schoeman C, Giles J, Lane N, Choy E, Camp H, Song Y, Anyanwu S, McInnes I. Relationship Between Changes in Lipid Levels and Improvement in Disease Activity Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Upadacitinib Treatment: Pooled Analysis of Data from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-changes-in-lipid-levels-and-improvement-in-disease-activity-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-upadacitinib-treatment-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-two-phase/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-changes-in-lipid-levels-and-improvement-in-disease-activity-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-upadacitinib-treatment-pooled-analysis-of-data-from-two-phase/
