Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster III: Inflammatory Rheumatic Disease
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Pain is a common symptom among ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients and can be debilitating, making pain management an integral part of caring for these patients. The purpose of this analysis was to describe pain medication utilization of patients with AS and PsA over 12-months before and after initiation of a biologic.
Methods: This is a retrospective observational cohort study using administrative claims from the HealthCore Integrated Research Database (HIRD®). Patients newly diagnosed with AS or PsA who initiated a biologic from 1/1/2014 to 7/31/2017 were included. Medications that could be used for pain were assessed 12-months prior and 12-months after biologic initiation. Demographics, baseline clinical characteristics, and pain medication use were described using descriptive statistics. Frequencies and percentages were provided for categorical variables and means, standard deviations, and medians were presented for continuous measures. The differences in pain medication use were assessed using McNemar’s Test for categorical variables or Wilcoxon signed-rank test for continuous variables as appropriate for comparing before and after biologic initiation.
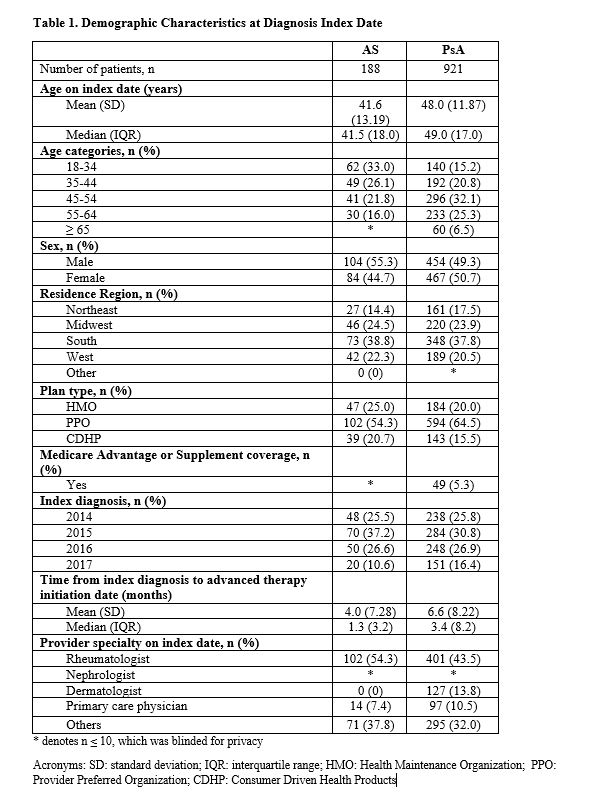
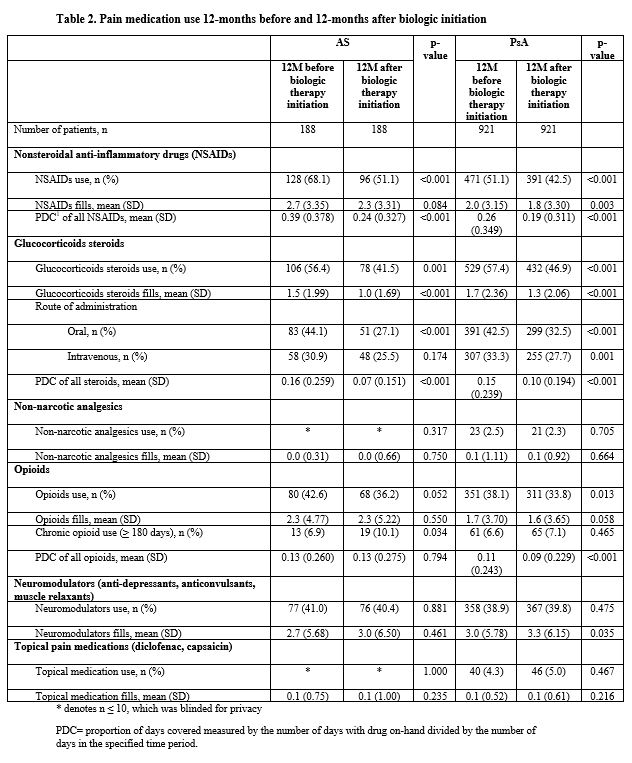
Results: 188 AS patients and 921 PsA patients were included in this analysis. AS patients had a mean age of 41.6 years, 55.3% were male, and the mean time from diagnosis to biologic initiation was 4.0 months. PsA patients had a mean age of 48.0 years, 49.3% were male, and the mean time from diagnosis to biologic initiation was 6.6 months. Prior to biologic initiation, 68.1% of AS patients were prescribed NSAIDs, 56.4% glucocorticoids, 42.6% opioids, and 41.0% neuromodulators. Similarly, prior to biologic initiation, 51.1% of PsA patients were receiving NSAIDs, 57.4% glucocorticoids, 38.1% opioids, 38.9% neuromodulators, and 4.3% topical pain medication. Twelve months after biologic initiation, use of NSAIDs (AS: 68.1% vs. 51.1%; PsA: 51.1% vs. 42.5%) and glucocorticoids (AS: 56.4% vs. 41.5%; PsA: 57.4% vs. 46.9%) and opioids (AS: 42.6% vs. 36.2%; PsA: 38.1% vs. 33.8%) significantly decreased among AS and PsA patients. Use of neuromodulators did not significantly change from the 12-months prior to the 12-months after biologic initiation among AS (41.0% vs. 40.4%) and PsA (38.9% vs. 39.8%) patients.
Conclusion: Use of pain medications such as NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, opioids, and neuromodulators are common among AS and PsA patients. Though rates of NSAIDs and glucocorticoids decreased after the initiation of biologics, over 40% of AS and PsA patients were still receiving these medications 12-months after initiation of a biologic. In addition, over 30% of AS and PsA patients were still receiving opioids 12-months after initiation of a biologic. The results suggest that AS and PsA patients still require pain medication even after initiating biologics.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hunter T, Nguyen C, Birt J, Smith J, Shan M, Tan H, Lisse J, Isenberg K. Pain Medication Use Among Ankylosing Spondylitis and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients Before and After Initiation of Biologic Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-medication-use-among-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-before-and-after-initiation-of-biologic-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pain-medication-use-among-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-before-and-after-initiation-of-biologic-therapy/