Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is limited information on the real-world safety of disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Japan. Using a Japanese RA registry, rates of serious adverse events among initiators of methotrexate (MTX), TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib were calculated.
Methods: We identified RA patients (pts) in the Corrona RA Japan Registry who initiated a DMARD between 03/01/2016 to 12/31/2019 and had at least one follow-up (FU) visit or had an adverse event before the first FU visit. If pts switched to another drug in the same drug class, they remained in the original drug group. Each initiation was considered so pts could be in ≥ 1 drug group. Adverse events of interest were cardiovascular disease (CVD), serious infections, Herpes Zoster [(HZ) serious and non-serious], and malignancy, excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC). The incidence of adverse events was calculated. For all events except malignancy, person-time at risk was estimated from time of drug initiation until the occurrence of the first event or 90 days after discontinuation. For risk of malignancies, the risk window for any therapy included all person-time in the designated period (time since starting therapy) and extended until the end of data collection. Incidence rates (IR), expressed as number of first events per 100 person-years (PY), were calculated with 95% confidence intervals (CI) assuming a Poisson distribution.
Results: There were 1,546 pts with first-time use of MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, or tofacitinib who had at least one FU visit or had an adverse event before the first FU visit. Drug groups included 296 MTX, 491 TNFi, 560 nonTNFi, and 199 tofacitinib initiators. History of prior CVD, serious infection, HZ, and malignancy ranged from 8-14%, 9-15%, 10-14%, and 6-16%, respectively (Table 1).
The average PY of FU time was 2.0, 1.6, 1.5, and 1.4 PY for MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib initiators, respectively (Table 2). The IR for serious infections was (IR=6.47, 95% CI, 4.70-8.68) for nonTNFi, (3.86, 1.77-7.33) for tofacitinib, (3.46, 2.17-5.24) for TNFi, and (2.16, 1.04-3.97) for the MTX groups. The tofacitinib group had the highest IR for HZ (9.31, 5.76-14.23) and nonTNFi (2.02, 1.11-3.40), TNFi (0.93, 0.34-2.03), and the MTX (0.86, 0.23-2.20) groups were lower. All the HZ events were non-serious (e.g., did not require hospitalization or intravenous antivirals). Total CVD was (0.43, 0.05-1.54), (0.77, 0.25-1.80), (1.57, 0.79-2.82), and (1.27, 0.26-3.72 in the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and the tofacitinib groups, respectively. For malignancy excluding NMSC, the IRs were (1.65, 0.88-2.82) in TNFi, (1.52,0.70-2.89) in MTX, (1.20, 0.58-2.21) in nonTNFi, and (0.35, 0.01-1.96) in the tofacitinib groups (Table 3).
Conclusion: There were similar rates of serious infection, CVD, and malignancy adverse events among pts initiating MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib. Yet, the rate of HZ, due to non-serious events, was greater in those initiating tofacitinib, which is consistent with what is known from Japanese tofacitinib clinical trial data.
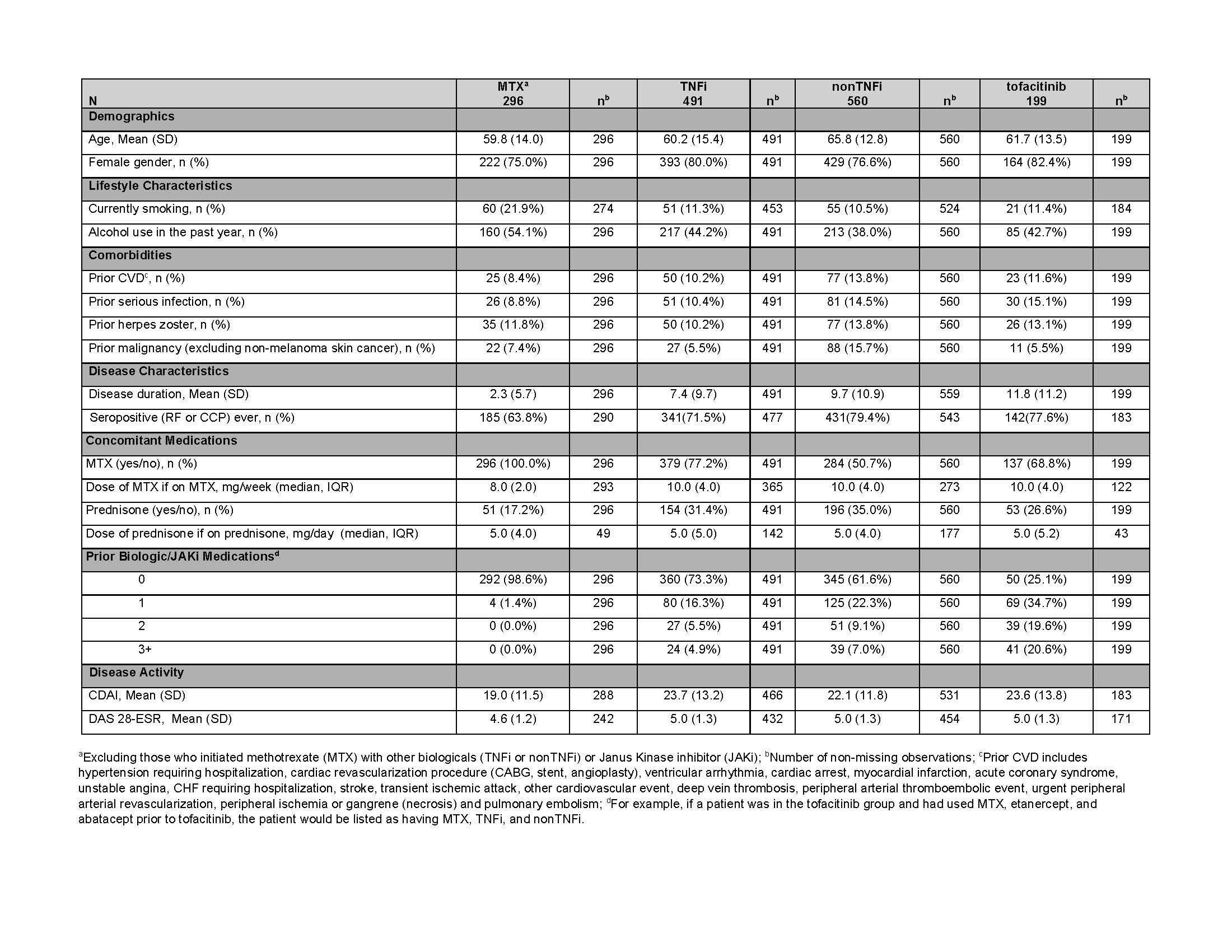 Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of the Safety Cohort
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of the Safety Cohort
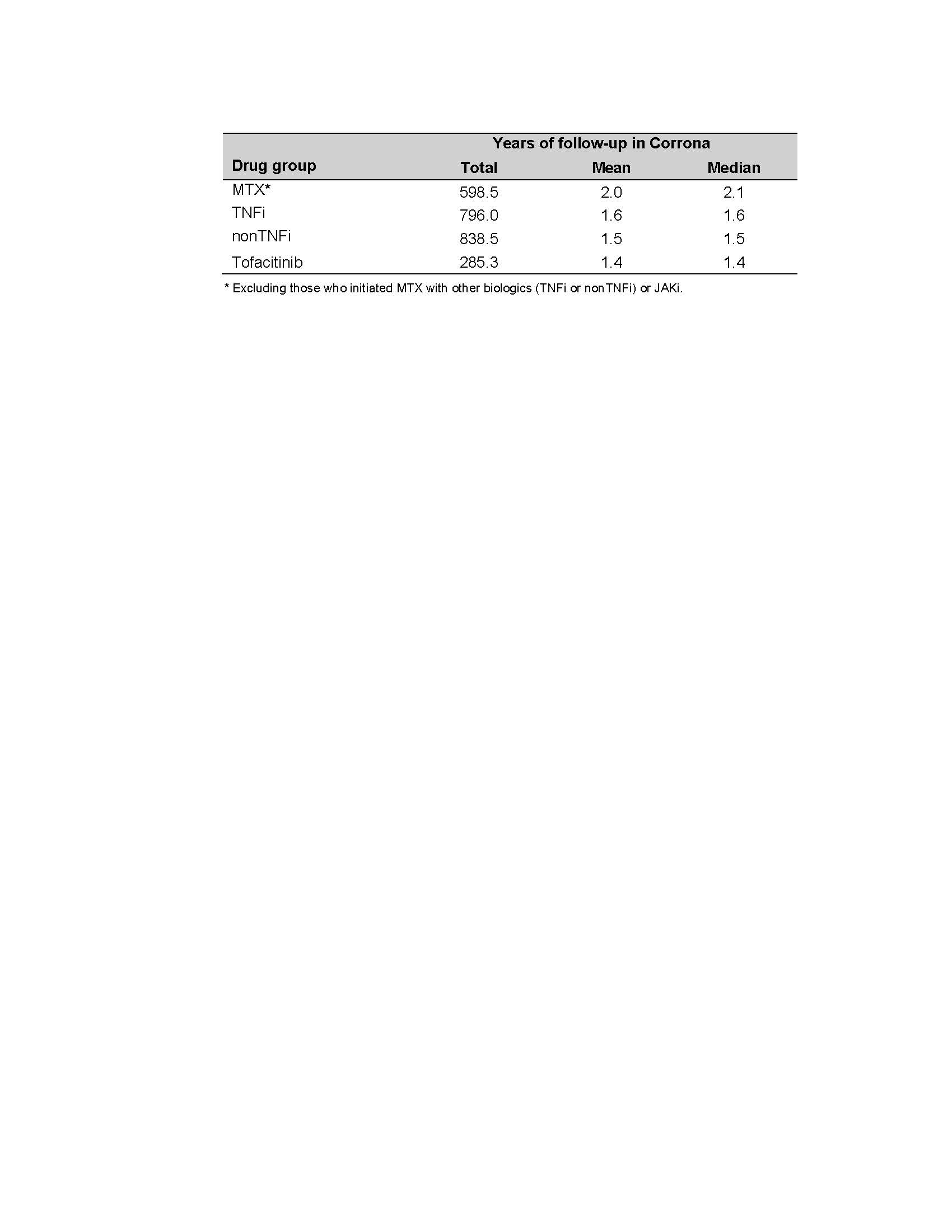 Table 2. Follow-up Time for Each Drug Group
Table 2. Follow-up Time for Each Drug Group
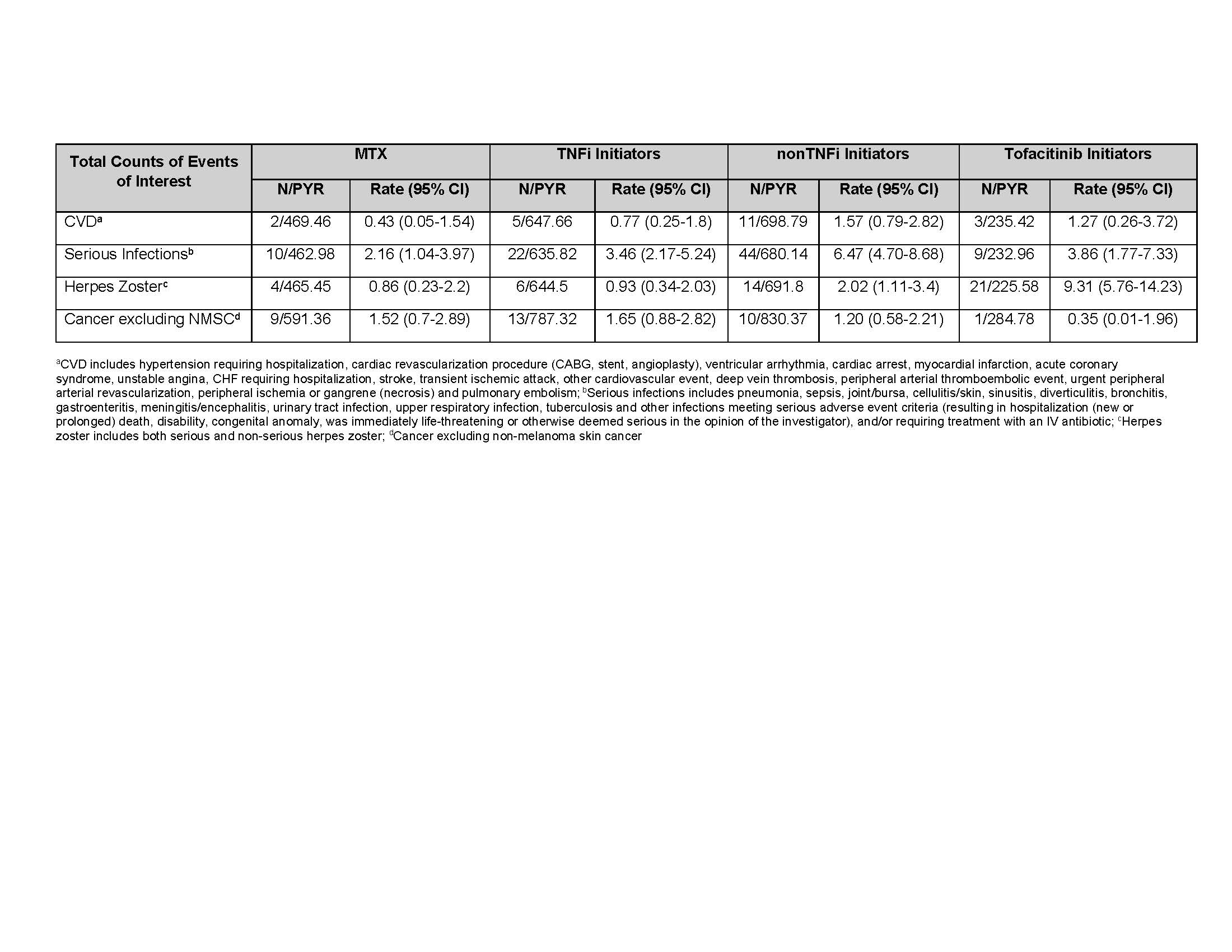 Table 3. Crude Incidence Rates (number of first events/100 PY) for MTX group, TNFi Initiators, nonTNFi Initiators, and Tofacitinib Initiators
Table 3. Crude Incidence Rates (number of first events/100 PY) for MTX group, TNFi Initiators, nonTNFi Initiators, and Tofacitinib Initiators
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kishimoto M, Tanaka Y, Harrold L, Onofrei A, Barr C, Agarwal E, Rivas J, Sugiyama N, Greenberg J, Yamanaka H. Real-World DMARD Experience and Outcomes for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Japan: Safety [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-dmard-experience-and-outcomes-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-japan-safety/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-dmard-experience-and-outcomes-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-japan-safety/
