Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There are several conventional synthetic, targeted synthetic and biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic medications (DMARDs) approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in Japan. Little is known regarding the characteristics of patients treated by these DMARD classes and their respective effectiveness in a real-world cohort of patients in Japan.
Methods: We identified RA patients in the Corrona RA Japan Registry who initiated a DMARD (methotrexate [MTX], TNFi, nonTNFi, tofacitinib) between March 1, 2016 to December 31, 2019 with enrollment capping for some drug classes. We characterized the four drug groups in terms of sociodemographics, comorbidities, disease characteristics, medications (current and prior), disease activity, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs). Drug effectiveness in each of the drug groups was assessed for all initiators with baseline and 6-month follow-up (FU) visits available by change in Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) and PROs (pain, fatigue, patient global assessment, and J-HAQ), as well as the achievement of minimal clinically important difference (MCID) in CDAI and modified ACR20/50/70s in the six months following medication initiation.
Results: There were 1293 patients in the registry with 275 MTX, 331 TNFi, 525 nonTNFi, and 162 tofacitinib initiators that had both baseline and 6-month FU visits available. Mean disease duration was 2.4, 7.2, 9.8, and 11.8 years, respectively, in the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib groups. Almost all MTX initiators (99.3%) were biological naïve. Among TNFi initiators, 76.7%, 16.9%, 3.6%, and 2.7% received their drug as their 1st, 2nd, 3rd, and 4th biological/Janus Kinase inhibitor (JAKi), respectively. For patients in the nonTNFi group, it was 62.7% 21.3%, 9.3%, and 6.7%, respectively. Among tofacitinib initiators, 26.5% of patients received the drug as their 1st, 35.2% as their 2nd, 21.0% as their 3rd, and 17.3% as their 4th biological/JAKi. At initiation, mean disease activity, as measured by CDAI, was 19.0, 22.6, 21.9, and 23.1 for the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib patients, respectively (Table 1).
At the 6-month FU visit following initiation, mean change in CDAI was -9.9, -11.6, -11.8 and -12.4 in the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib initiators, respectively. Additionally, the majority of the patients (61.0%, 62.6%, 67.1%, and 66.7% for the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib initiators, respectively) reached MCID in CDAI. Almost half of all initiators achieved ACR20 responses (46.9%, 42.6%, 48.2%, and 45.1% of the MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib initiators, respectively). Approximately 80% or more initiators remained on the drug until their 6-month FU visit (79.6%, 82.8%, 85.1%, and 85.2% for MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib, respectively) (Table 2).
Conclusion: There were distinct patient profiles for those initiating each of the four drug classes in Japan. Overall, the majority of patients receiving MTX, TNFi, nonTNFi, and tofacitinib all had good responses. This positive patient response to DMARDS in a Japanese population adds to the growing scientific literature for those seeking to understand real-world outcomes.
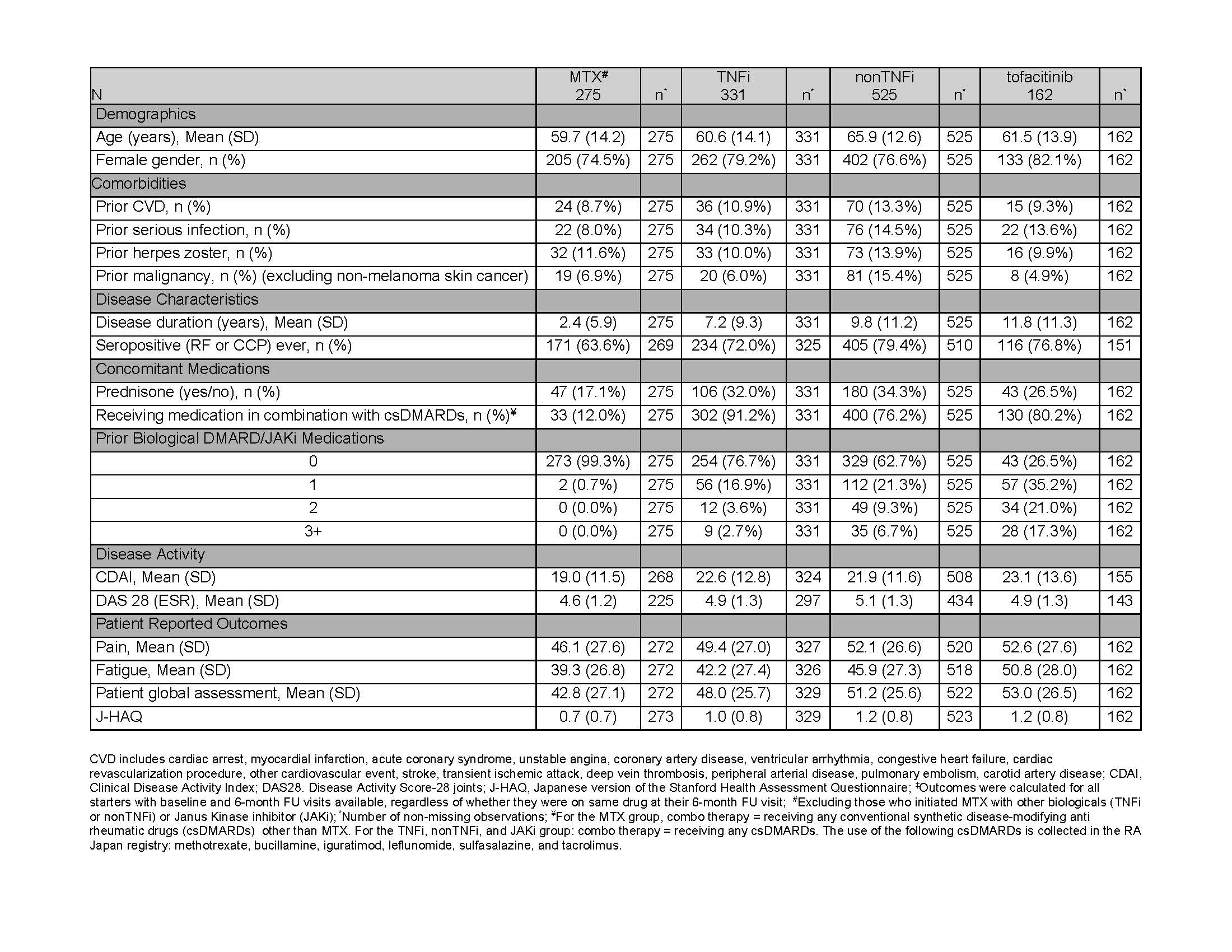 Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of the Effectiveness Cohort by Drug Group‡
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of the Effectiveness Cohort by Drug Group‡
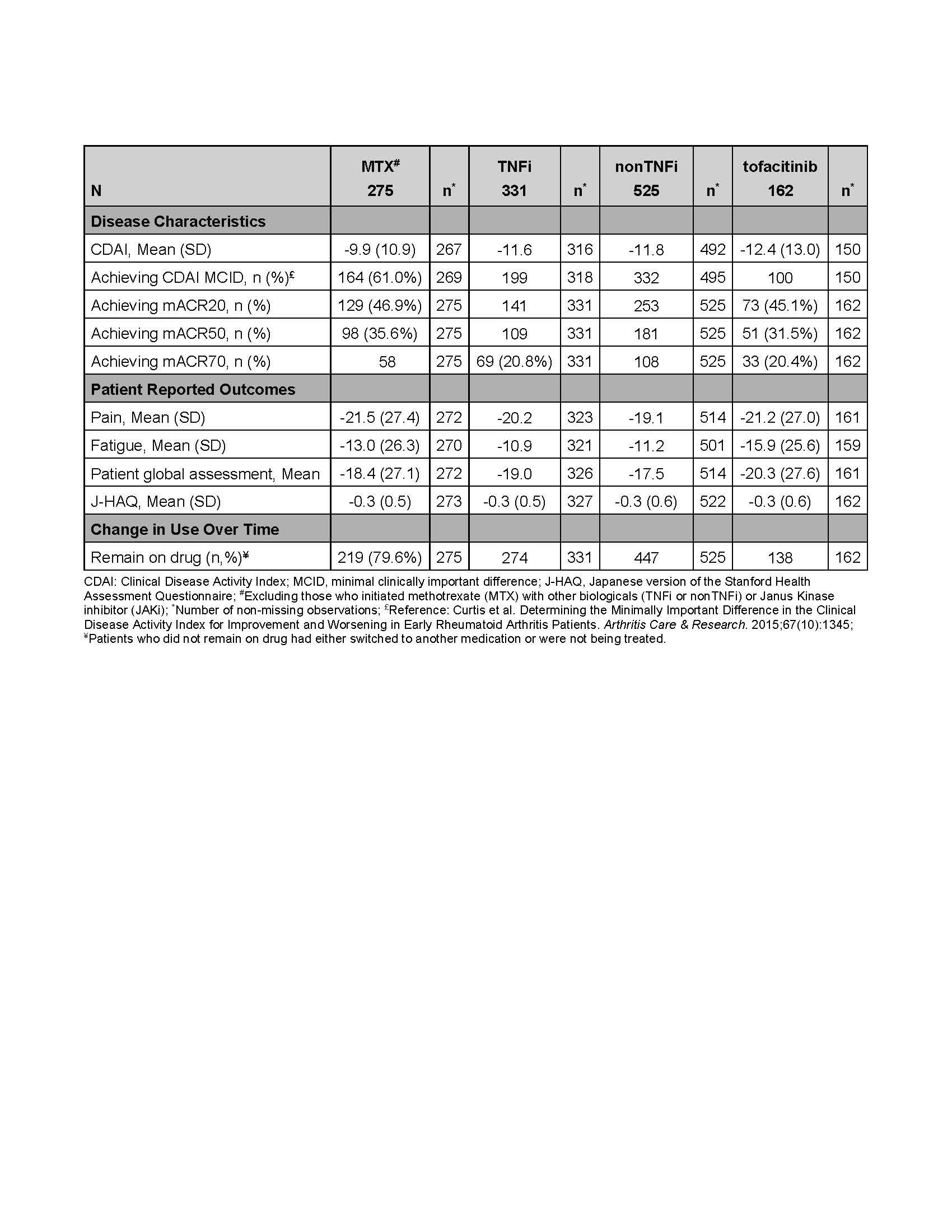 Table 2. Unadjusted Effectiveness Outcomes (Baseline to 6-month follow-up) by Drug Group
Table 2. Unadjusted Effectiveness Outcomes (Baseline to 6-month follow-up) by Drug Group
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tanaka Y, Yamanaka H, Harrold L, Lin T, Agarwal E, Rivas J, Sugiyama N, Greenberg J, Kishimoto M. Real-World DMARD Experience and Outcomes for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in Japan: Effectiveness [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-dmard-experience-and-outcomes-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-japan-effectiveness/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-dmard-experience-and-outcomes-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-in-japan-effectiveness/
