Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: The aim was to examine the rates of putative pneumococcal infections up to 10 years before and after administration of heptavalent conjugated pneumococcal vaccine (PCV7) in patients with inflammatory arthritis compared to non-vaccinated arthritis patients.
Methods: Adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and spondylarthropathy (SpA) including psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients, at the Department of Rheumatology at Skåne University Hospital, Sweden were offered one single intramuscular dose of PCV7 between May 2008 and February 2012. 595 patients participated (RA=342; 80% women, and SpA=253; 45% women). Mean age was 62 and 51 years, mean disease duration was 16 and 14 years respectively. For each patient, 4 reference subjects were identified, matched for arthritis diagnosis, age, sex, and geographical area, and date of vaccination of the patient was also used as index date for its references. References were presumed to be non-vaccinated for pneumococci, following the current national guidelines.
At the time of vaccination, 420 patients were treated with bDMARDs including anti-TNF agents (n=330), tocilizumab (n=15), abatacept (n=18), anakinra (n=1) and rituximab (n=56). Methotrexate (MTX) was given as monotherapy (n=86), or in combination with bDMARD (n=220). Eighty-nine of the SpA patients were treated with NSAIDs without DMARD. Thirty percent (n=176) of the patients were treated with prednisolone, mean weekly dose 41 (1-140) mg.
The Skåne Healthcare Register was searched for ICD-10 diagnostic codes for serious putative pneumococcal infections between January 2000 and December 2018 for both patients and reference subjects. The outcome events included community acquired pneumonia, lower respiratory tract infection, septicemia, meningitis, and septic arthritis. We compared the frequency of outcome events after vs before date of vaccination by calculating relative risks (RRs). The ratio of relative risk (RRR) was calculated comparing the RR of vaccinated patients vs non-vaccinated references. A generalized estimated equation (GEE) was used to handle correlated data for several events in the same individual and included time of follow up as a covariate. We also did a survival analysis (Kaplan-Meier) and Cox regression to investigate time to first event after vaccination.
Results: The point estimate of RRR for pneumonia only was 0.47, 95% CI 0.28-0.77 and for all serious putative pneumococcal infections the RRR was 0.54, 95% CI 0.33-0.89 (Table). Time to first pneumonia or other serious infection after vaccination was significantly shorter among vaccinated patients compared to references (Figure), but after adjusting for number of the same type of infection before vaccination, there was no longer a statistically significant difference after vaccination (p=0.12) and (p=0.09), respectively.
Conclusion: A single dose of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine may decrease the risk of putative serious pneumococcal infection up to 10 years after vaccination in adult patients with inflammatory arthritis receiving immunomodulating treatment. However, the vaccine does not seem to prolong the time to first serious infection.
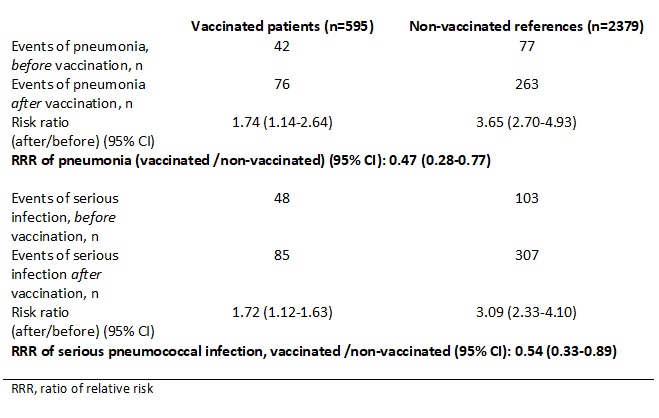 Table. Relative risk (RR) and ratio of relative risk (RRR) of pneumonia and all serious pneumococcal infections among vaccinated and non-vaccinated individuals before and after date of vaccination.
Table. Relative risk (RR) and ratio of relative risk (RRR) of pneumonia and all serious pneumococcal infections among vaccinated and non-vaccinated individuals before and after date of vaccination.
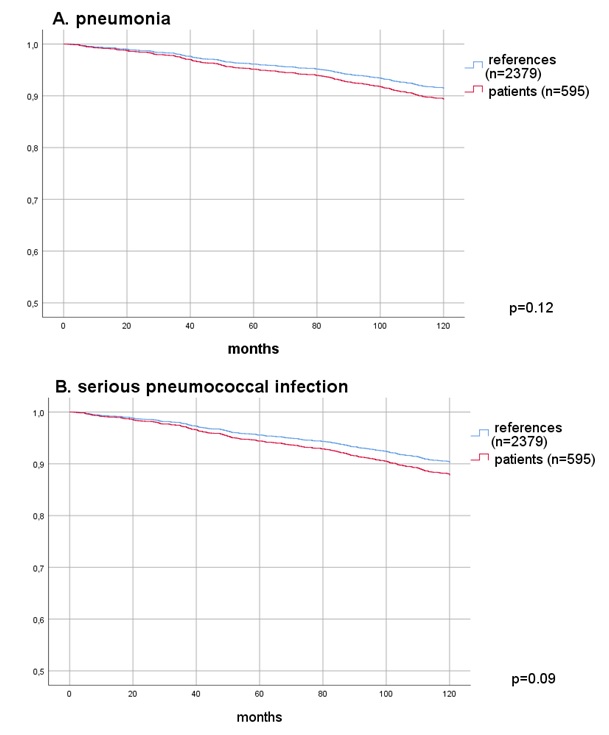 Figure. Cox regression; Time to first event, death or loss of follow-up after date of vaccination for pneumonia only (A), all serious pneumococcal infections (B), adjusted for number of events before date of vaccination.
Figure. Cox regression; Time to first event, death or loss of follow-up after date of vaccination for pneumonia only (A), all serious pneumococcal infections (B), adjusted for number of events before date of vaccination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nagel J, Jönsson G, Nilsson J, Manuswin C, Englund M, Saxne T, Geborek P, Kapetanovic M. Reduced Risk of Serious Pneumococcal Infection up to 10 Years After Immunization with 7-valent Conjugated Pneumococcal Vaccine in Patients with Inflammatory Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-risk-of-serious-pneumococcal-infection-up-to-10-years-after-immunization-with-7-valent-conjugated-pneumococcal-vaccine-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reduced-risk-of-serious-pneumococcal-infection-up-to-10-years-after-immunization-with-7-valent-conjugated-pneumococcal-vaccine-in-patients-with-inflammatory-arthritis/
