Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis is characterized by calcium deposition in skin and subcutaneous tissues and progresses over one year in the majority of systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients. Since vascular hypoxia may contribute to calcinosis pathophysiology, we evaluated the safety and efficacy of oral treprostinil in preventing progression of SSc-associated calcinosis.
Methods: We performed a prospective, open-label, single-institution study in 12 SSc patients meeting 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria with confirmed radiological and physical examination evidence of >1 subcutaneous calcium deposit in the hands (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02663895). Patients received oral treprostinil for 1 year with evaluations every 3 months. Primary endpoints were safety/tolerability and percentage of patients without radiographic progression of calcinosis at 1 year assessed by the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium radiographic score. Progression of calcinosis was defined as >25% increase in score, improvement as >25% decrease, and stabilization as values in-between. Radiographs were scored by a radiologist blinded to treatment history and sequence of images. Secondary endpoints included 1-year changes in the Scleroderma HAQ (SHAQ), Cochin Hand Functional Scale, SF-36, Raynaud Condition Score, and patient and physician assessment of calcinosis severity. Endpoints were assessed using Wilcoxan signed rank test.
Results: Twelve female patients were enrolled (half had diffuse cutaneous SSc disease), with mean age 55 years (range 35-68 years) (Table 1). Five patients completed the study, tolerating up to a median dosage of 1mg TID (range 0.25-7.625 mg TID). Seven patients withdrew from the trial at a median dosage of 1.3mg TID (range 0-5mg TID) at a median follow-up of 5 months (range 0.25-10 months) due to the following: intolerable side effects (n=3, diarrhea, headaches), withdrawn by investigator for intercurrent illness unrelated to drug (n=2, cirrhosis, cancer), progressive SSc (n=1), and personal reasons (n=1). Most patients developed headaches and gastrointestinal side effects, consistent with the known side effect profile of treprostinil (Table 2). No serious adverse events occurred. Four of the 12 (33%) patients experienced progression of calcinosis at 1 year. Of the 5 patients who completed 12 months of treatment, 4 had stability and 1 had progression of calcinosis (1-year median % score change: 22.2%, range: 5.3-85.5%, p=0.06). Of the 6 patients who withdrew but had 1-year follow-up radiographs, 3 had stability/improvement of calcinosis while 3 progressed (1-year median % score change: 38.4%, range: -38.9%-111%, p=0.16). Including all 12 enrolled patients, worsening of the SHAQ-VAS-GI score was observed (median change/month: 0.03, range 0-0.25, p=0.016); there were no significant changes in other secondary endpoints.
Conclusion: Oral treprostinil was poorly tolerated in SSc patients with calcinosis, with most patients developing headaches and gastrointestinal side effects. Of patients who were able to complete the treatment period, most (80%) had stability of calcinosis on hand radiographs at 1 year.
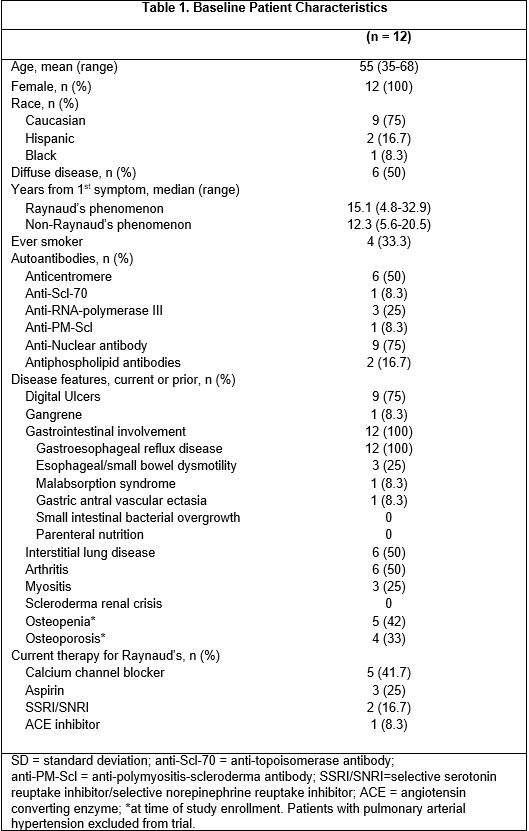 Table 1: Baseline Patient Demographics
Table 1: Baseline Patient Demographics
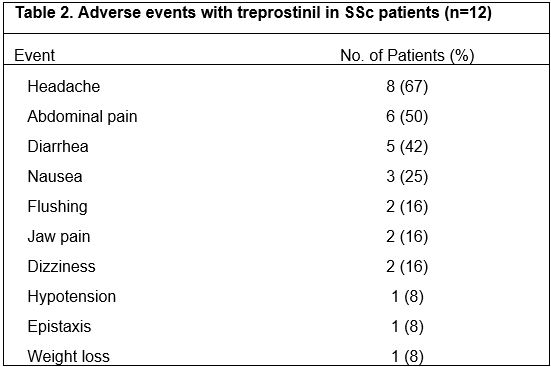 Table 2: Adverse events with treprostinil in SSc patients (n=12)
Table 2: Adverse events with treprostinil in SSc patients (n=12)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chung M, Valenzuela Vergara A, Catanese B, Li S, Stevens K, Chung L. A Pilot Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Treprostinil in the Treatment of Calcinosis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-pilot-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-treprostinil-in-the-treatment-of-calcinosis-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-pilot-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-treprostinil-in-the-treatment-of-calcinosis-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/
