Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I: Diagnosis and Testing
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibro inflammatory condition of unclear etiology. This rare condition can affect any organ system and has protean manifestations mimicking many other diseases. As the knowledge regarding this condition has increased among providers, there has been a tendency to over diagnose IgG4-RD. Therefore, the primary aim of this retrospective study is to identify common mimickers of IgG4-RD in an United States cohort.
Methods: The study design is a retrospective chart review. All patients referred to the IgG4 clinic at Emory University with specific diagnosis of IgG4-RD from August 2013- February 2020 were reviewed and categorized into mimickers versus IgG4-RD. The diagnosis of IgG4-RD and mimickers were made with clinicopathological correlation. Emory University Institutional Review Board approved this study.
Results: From August 2013- February 2020, a total of 198 patients were referred to the Emory IgG4- RD clinic. As outlined in Table 1, 85 or 43% were noted be mimickers of IgG4-RD. We classified the mimickers into infection (2%), neoplastic disease (21%), autoimmune disease (31%), and other (46%). Based on the IgG-RD classification criteria, 93% of these cases met exclusion criteria and only 7% met inclusion criteria, which had mean scores of 3 and ranged from 0-10 (greater than 20 meets criteria).
The neoplastic category included lymphoma (28%), plasma cell dyscrasia (17%), and histiocytosis (Rosai Dorfman, Langerhans’s, Erdheim Chester Disease) (17%). Noteworthy, 75% of the neoplastic diagnoses were made when repeat biopsy was performed either due to clinical suspicion or lack of response to treatment.
Sjogren’s syndrome was the predominant condition mistaken by IgG4-RD in the autoimmune category. We included cases that could not be proven to be IgG4-RD or any other specific diagnosis in the other category. Interestingly, in that category 60% had a GI manifestation, with half of those cases being recurrent pancreatitis as shown in Table 4.
The average serum IgG4 level across all mimickers was normal, but the levels ranged from 5-4,060 mg/dL (normal range 1-123 mg/dL). We identified 20 cases with elevated serum IgG4. Based on the IgG-RD classification criteria, these patients met exclusion criteria with 9 cases meeting pathologic criteria, 7 radiologic, 2 serologic, and 2 disease specific exclusions. Of note, 8 of these 20 cases had neoplastic disease and 4 cases had recurrent pancreatitis.
Conclusion: This study highlights that almost half of the patients referred for diagnosis of IgG4-RD actually were found to have a mimic of the disease. GI manifestations, particularly recurrent pancreatitis, were among the most common referred diagnosis in our center. It should be emphasized that serum IgG4 levels are not diagnostic for the disease and can be elevated in other conditions. A tissue biopsy is indicated in majority of cases with atypical clinical presentation and repeating the biopsy is indicated if the patient’s course is not typical for IgG4-RD. Also, a lymph node biopsy is not considered diagnostic. By identifying these mimickers, we hope to emphasize the necessity of considering these conditions while evaluating patients with IgG4-RD.
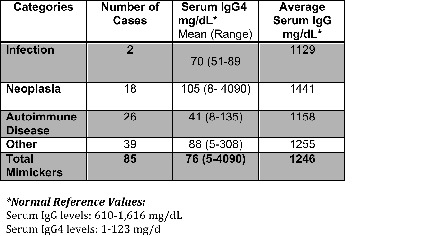 Table 1: Categories of Mimickers
Table 1: Categories of Mimickers
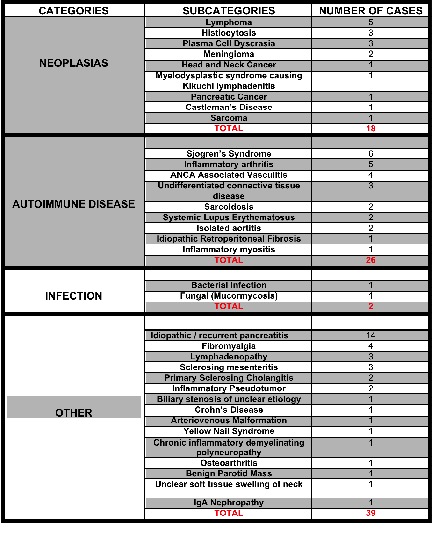 Table 2: Subcategories of Mimickers
Table 2: Subcategories of Mimickers
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmad M, Spandorfer R, Khosroshahi A. Mimickers of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mimickers-of-immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mimickers-of-immunoglobulin-g4-related-disease/
