Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjogren’s syndrome (pSS) is a multi-organ autoimmune disease primarily affecting excretory glands and characterized by B-cell hyperactivity. No approved systemic treatments are available. Ianalumab (VAY736) is an anti-B-cell activating factor (BAFF) receptor fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody, engineered for direct ADCC-mediated B-cell depletion, thus providing a dual mode of action and targeted approach to treat pSS. The current phase 2b study aimed at establishing a dose-response relationship over a wide range of VAY736 doses, using change from baseline (BL) in the EULAR Sjogren’s Syndrome Disease Activity index (ESSDAI) over 24 Weeks (Wks) as the primary endpoint. Here we report Wk24 efficacy and safety. The study is ongoing with a second blinded treatment period up to Wk52.
Methods: 190 patients with pSS were randomized 1:1:1:1 to monthly s.c. administrations of placebo (PBO) or one of three VAY736 doses; 5mg, 50mg and 300mg. First-dose premedication was 250mg IV methylprednisolone. To be eligible, patients had to fulfill the American European Consensus Group (AECG) criteria for pSS, be anti-Ro/SSA positive, have an ESSDAI ≥6 (on 7/12 domains: glandular, articular, lymphadenopathy, constitutional, cutaneous, hematologic, biologic), and EULAR Sjogren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI) ≥5. Statistical methods included MCP-Mod to assess the dose-response on change of ESSDAI (12 domains) from BL and responder analysis to calculate the proportion of patients with ≥3 points improvement on ESSDAI as secondary analysis. Secondary endpoints included ESSPRI, Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue (FACIT-F), Physician’s (PhGA) and Patient’s Global Assessments (PGA), SF-36, stimulated salivary flow (sSF) and Schirmer’s test.
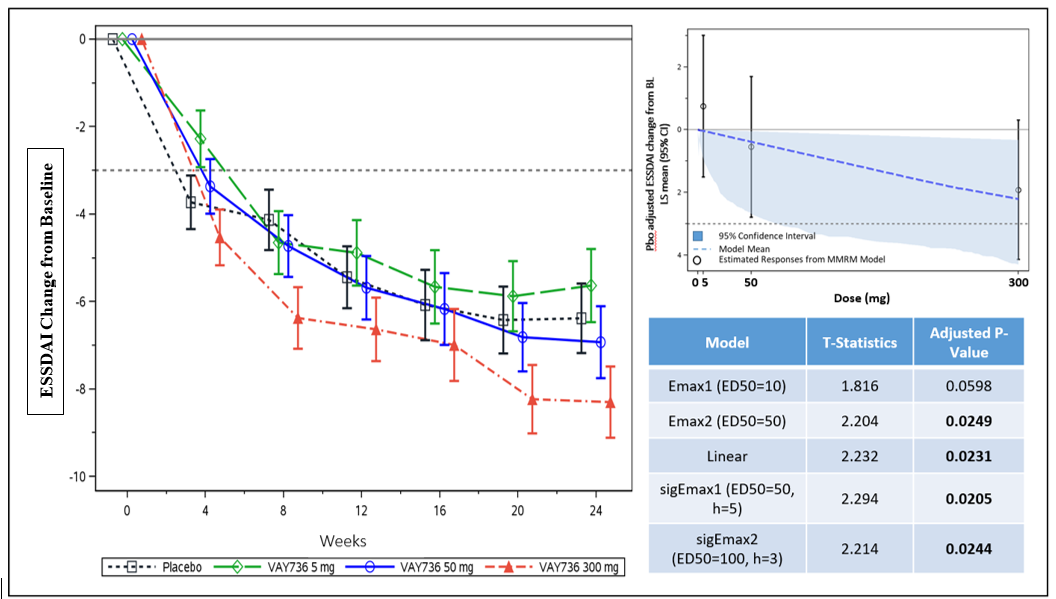
Results: The primary endpoint of the study was met with a statistically significant dose-response for ESSDAI (Figure 1). The largest reduction in ESSDAI was 1.92 points over PBO for VAY736 300mg at Wk24. Secondary analysis on ESSDAI revealed for 300mg vs PBO responder rates of 42/47 (89.4%) vs 30/49 (61.2%), a difference of 28.1% (p=0.0019), while no differences were seen for 5mg and 50mg vs PBO. Consistent with this result, PhGA change from BL was significantly different between VAY736 300mg and PBO (p=0.022). A numerical trend for improvement of sSF for VAY736 300mg compared to PBO was notable at Wk24 (p=0.092). However, the secondary efficacy endpoints ESSPRI and FACIT-F showed no benefits over PBO for improvements in the burden of illness. PBO responses were generally high. Incidence of treatment emergent adverse events were comparable across PBO and active groups, whereby local injection reactions were most frequent, mostly mild and showed a dose-response.
Conclusion: The defined primary endpoint assessing ESSDAI was met, showing statistically significant dose-response for ianalumab with clinically important improvement over placebo at the highest tested dose. The preliminary safety profile was good. Future analysis will focus on PK and immunogenicity, salivary and tear flow parameters and the exploration of ESSDAI domains, and the ongoing-blinded treatment period up to Week 52.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Nash P, Tahir H, Schulze-Koops H, Li L, Hojnik M, Gellett A, Liu-Leage S, Pillai S, Mease P. Ianalumab (VAY736), a Dual Mode of Action Biologic Combining BAFF Receptor Inhibition with B Cell Depletion, for Treatment of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Results of an International Randomized, Placebo Controlled Dose Range Finding Study in 190 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-vay736-a-dual-mode-of-action-biologic-combining-baff-receptor-inhibition-with-b-cell-depletion-for-treatment-of-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-results-of-an-international-randomized/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ianalumab-vay736-a-dual-mode-of-action-biologic-combining-baff-receptor-inhibition-with-b-cell-depletion-for-treatment-of-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-results-of-an-international-randomized/