Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W017: Health Services Research II: Health Economics (2888–2893)
Session Type: ACR/ARP Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
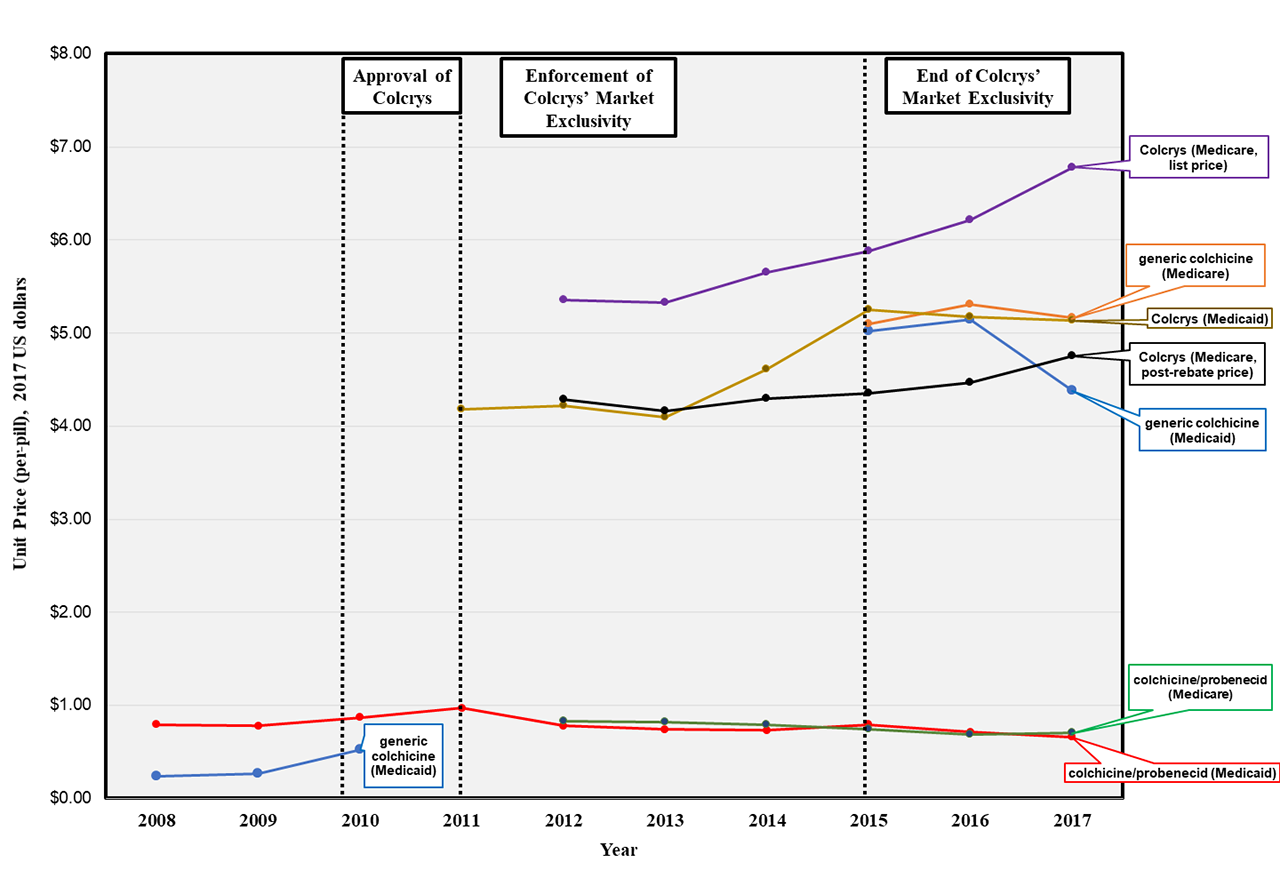
Background/Purpose: Gout affects >4 million US adults aged ≥ 65 years, but little is known about the scale and drivers of public spending on gout medications, including colchicine. Used for decades, its price rose drastically after one brand-name form (Colcrys) was granted market exclusivity from 2011-2014, as part of the FDA Unapproved Drugs Initiative.
We quantified changes in total spending and unit prices for gout drugs in Medicare and Medicaid, and key drivers. We also assessed colchicine prices and spending before, during, and after Colcrys’ market exclusivity.
Methods: We used Medicare Parts B & D and Medicaid drug spending data for years 2012-2017, and Medicaid Drug Utilization Data for 2008-2017. These contain aggregated prescription claims for the > 42 million beneficiaries enrolled in Medicare Part B (fee-for-service) or Part D (stand-alone or Medicare Advantage plans) or Medicaid. We included 5 drugs in our main analysis (colchicine, probenecid, allopurinol, febuxostat and pegloticase) along with rasburicase (a urate kinase, like pegloticase, but not indicated for gout).
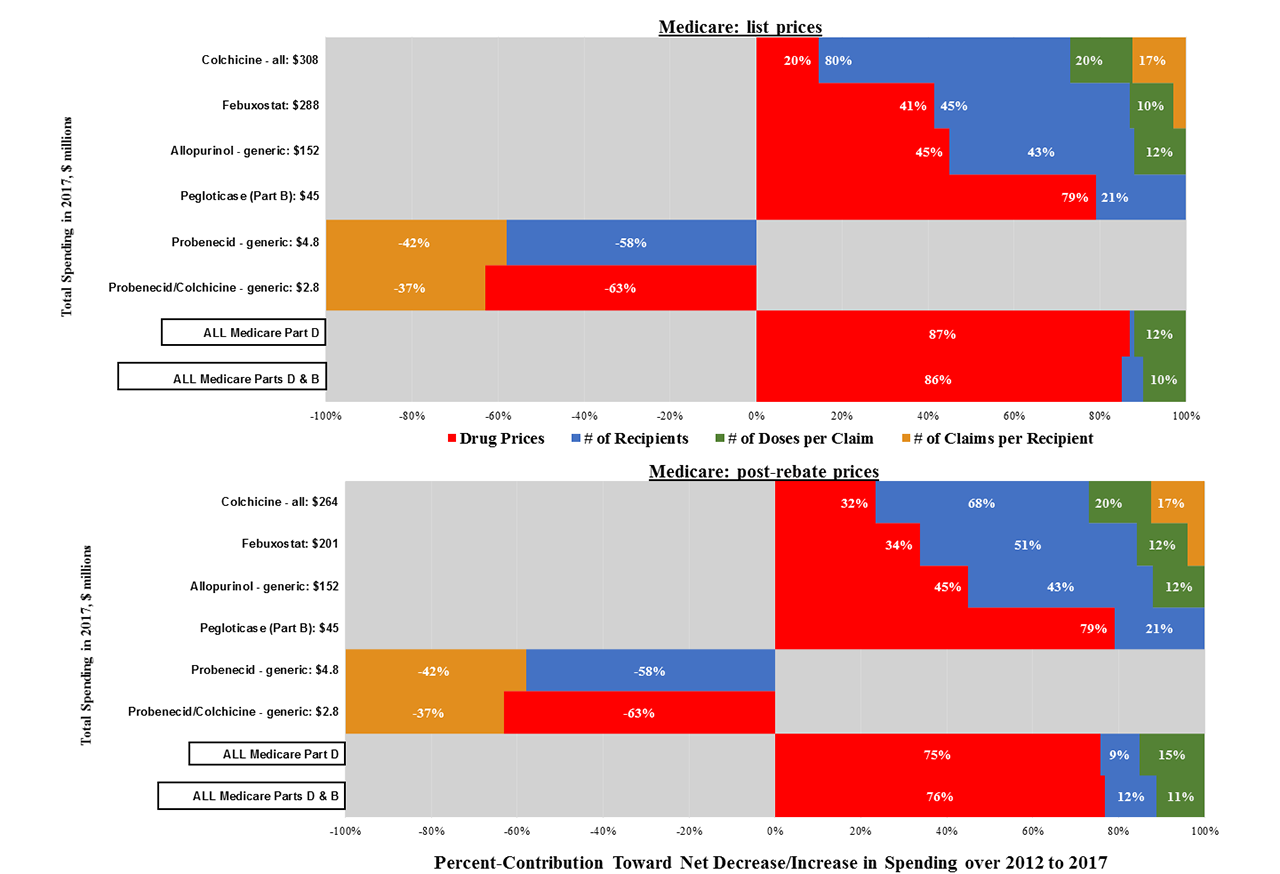
Analysis: We calculated six-year changes in total spending and unit prices (mean cost/dose) for each drug and in aggregate, standardised to 2017 dollars, and assessed colchicine over 2012-2014 (Colcrys-only) and 2015-2017. We performed standard decomposition analyses to isolate four sources of spending growth: drug prices, uptake [# recipients], treatment intensity [mean # doses/claim], and annual # of claims/recipient.
We conducted our analysis including statutory Medicaid rebates (as these decrease public spending) and excluding and including estimated time-varying Medicare rebates for brand-name drugs (which are paid to Pharmacy Benefit Managers and Part D plans).
Results: From 2012-2017, public-payer and beneficiary spending on the five main gout drugs nearly doubled, from $439 to $872 million (Table). Colchicine accounted for 39% of 2017 spending, followed by febuxostat (35%), allopurinol (19%), pegloticase (6%) and probenecid (1%).
Spending on allopurinol and febuxostat increased ~200% over six years, driven nearly equally by growth in recipient numbers and unit prices (Figure 1). Pegloticase spending rose by 600%, mainly due to a > 5-fold unit-price hike (from $327 to $1,828 per-mg), while price hikes drove just 25% of spending growth for rasburicase.
Medicare spending on colchicine rose by 19% over the six years, from $258 to $308 million. Annual spending rose by 25% from 2012-2014 (Colcrys only) but changed little from 2015-2017 (Colcrys + generics) (Table).
Still, unit prices for the generics ($5.13/pill in 2017) were only marginally lower than Colcrys’ ($6.78/pill), and considerably higher than colchicine before Colcrys’ approval (~$0.50/pill) and the probenecid-colchicine combination pill in any year (~$0.70/pill) (Figure 2).
Trends were similar with and without Medicare price rebates (Table, Figures).
Conclusion: Main drivers of increased public spending were the substantial, > 5-fold price hikes for colchicine and pegloticase, and greater uptake of urate-lowering drugs (which may be positive). The re-entry of generic forms did little to mitigate the large financial burden colchicine now imposes on taxpayers and patients.
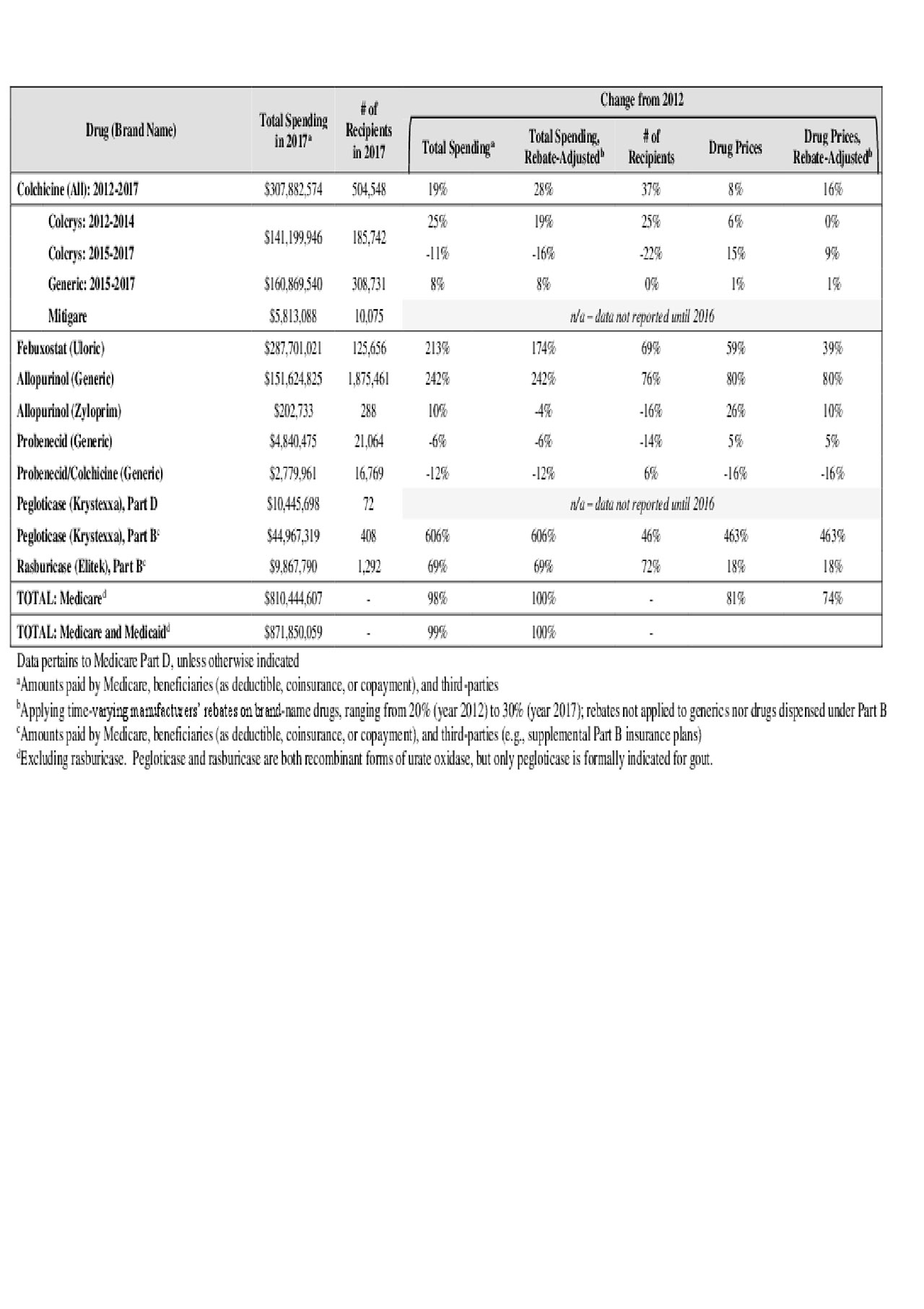
acr gout meds abstract table june3
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McCormick N, Wallace Z, Yokose C, Jorge A, Sacks C, Hsu J, Choi H. From a Potential Solution to Part of the Problem: Analysis of Spending and Price Trends for Brand-Name and Generic Colchicine and Other Gout Medications [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/from-a-potential-solution-to-part-of-the-problem-analysis-of-spending-and-price-trends-for-brand-name-and-generic-colchicine-and-other-gout-medications/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/from-a-potential-solution-to-part-of-the-problem-analysis-of-spending-and-price-trends-for-brand-name-and-generic-colchicine-and-other-gout-medications/