Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W017: Health Services Research II: Health Economics (2888–2893)
Session Type: ACR/ARP Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Prednisone is commonly used to treat rheumatic diseases, yet few comparative effectiveness studies on different dosing regimens are available. Electronic health records (EHR) and prescriptions are potential data sources for such research. However, a barrier to this work is organizing non-standardized prednisone “sigs”, or free-text instructions within a prescription, into a standardized and analyzable format. Natural language processing (NLP) tools can potentially be used to extract accurate doses from complex sigs across large prescription data sets. In this study, we compared the daily prednisone dose derived from application of a commercially available NLP tool to manual review of prednisone sigs. Additionally, to understand if sigs accurately captured physicians’ recommendations, we compared the prednisone dose derived from analysis of the sig alone to a review of the clinical notes.
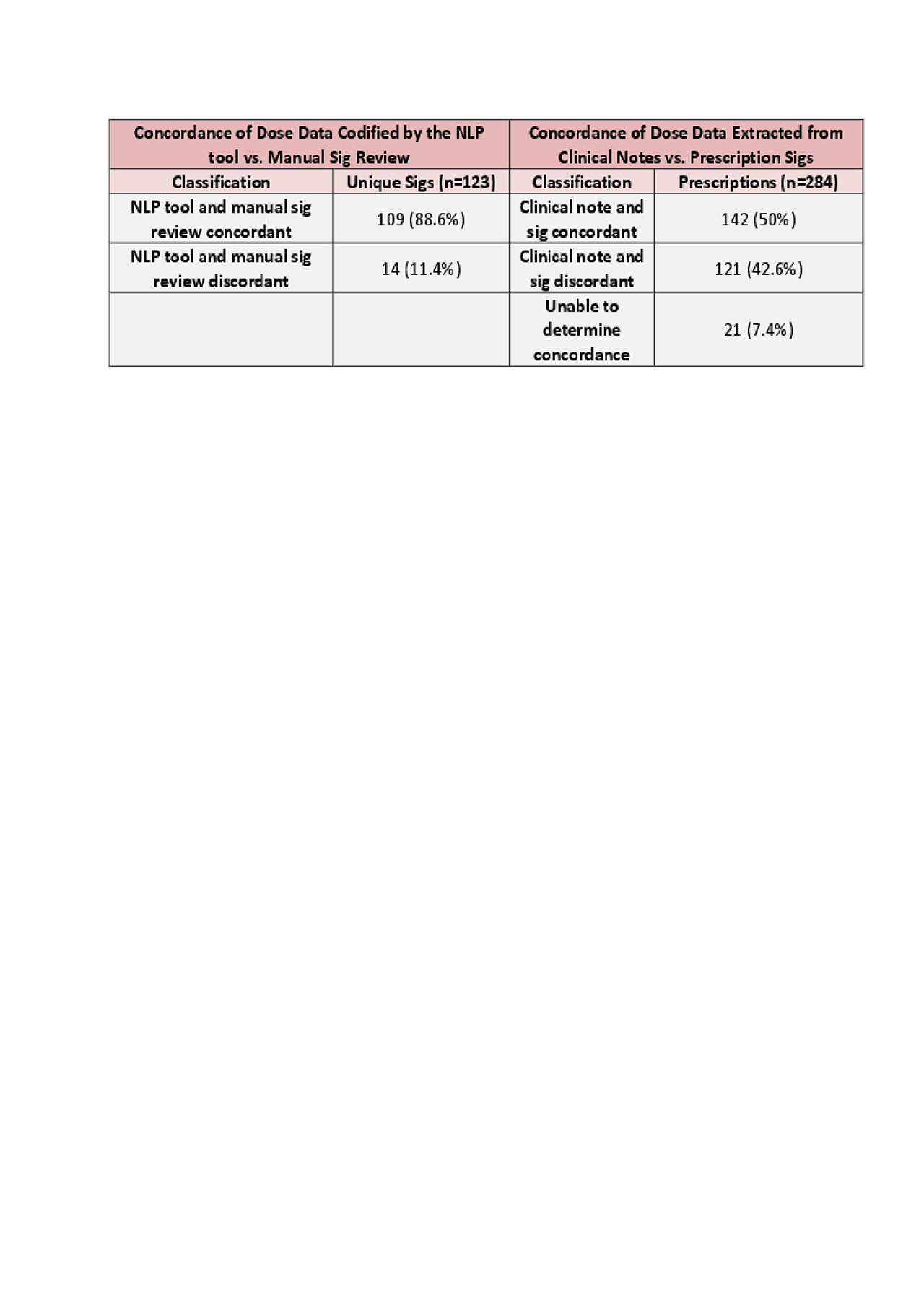
Methods: Data for this study were derived from the EHR of an academic health center. 284 prescriptions from 113 randomly selected patients receiving prednisone in clinical encounters between January 1, 2018 and June 22, 2018 were analyzed. Two reviewers independently codified each prescription’s sig into discrete structured data, which were used as the benchmark for comparison. An NLP tool, Sigmaster, was then used to automate this data extraction. Sigmaster uses a database of common sigs to map clinical text and translates this information into discrete data, such as dose, frequency, duration, and units. Its performance in determining patients’ prednisone doses was assessed by applying it to the sig data and evaluating its output to our manual review-adjudicated benchmark. The validity of sigs as a data source was also evaluated by comparing daily doses of prednisone derived from our manual review of sigs with physician-recommended prednisone doses as recorded in clinical notes. Doses were considered concordant if they were an exact match.
Results: The NLP tool achieved 88.6% concordance with the manual review-derived sig interpretations. The most common reasons for discordance were ambiguous sigs (“Take 1 tab daily, or as directed”) and sigs containing multiple phrases (“Take 1 tablet (5 mg total) by mouth daily. Take with one mg tablets to achieve prednisone taper”). However, only 50% of sigs were concordant with physician recommendations derived from clinical notes. The most common reasons for this latter discordance included failure to record tapers in sigs, inaccurate doses in sigs, and sigs with ranges larger than the dose recorded in the note. Given the discordance between manually reviewed sigs and clinical notes, application of the NLP tool to the sig alone would have captured the physician’s recommendation in the note only 44% of the time.
Conclusion: Although application of an NLP system to extract prednisone doses from complex prescription sigs had relatively high accuracy, significant discordance between sigs and physician notes suggests that sigs alone may be inadequate for research studies. Our study suggests that future NLP systems may need to create a hierarchy to capture physician-intent in glucocorticoid prescribing from EHRs, prioritizing data from clinical notes over prescription sigs alone.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Castillo F, Strait A, Evans M, Kay J, Gianfrancesco M, Izadi Z, Trupin L, Hoang M, Shalaby J, Schmajuk G, Yazdany J. Deriving Accurate Prednisone Dosing from Electronic Health Records: Analysis of a Natural Language Processing Tool for Complex Prescription Instructions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deriving-accurate-prednisone-dosing-from-electronic-health-records-analysis-of-a-natural-language-processing-tool-for-complex-prescription-instructions/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/deriving-accurate-prednisone-dosing-from-electronic-health-records-analysis-of-a-natural-language-processing-tool-for-complex-prescription-instructions/