Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W011: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes V: Treatment (2870–2875)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose:
Severe infections, frequently resulting in hospitalization, are a well-known adverse effects of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi). However, studies regarding outpatient treated infections are needed.
Our objective was to investigate the use of antimicrobials (antibiotics, antifungals and antivirals; excluding antimycobacterials) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and the effect of initiation of TNFi in biologic-naïve patients.
Methods:
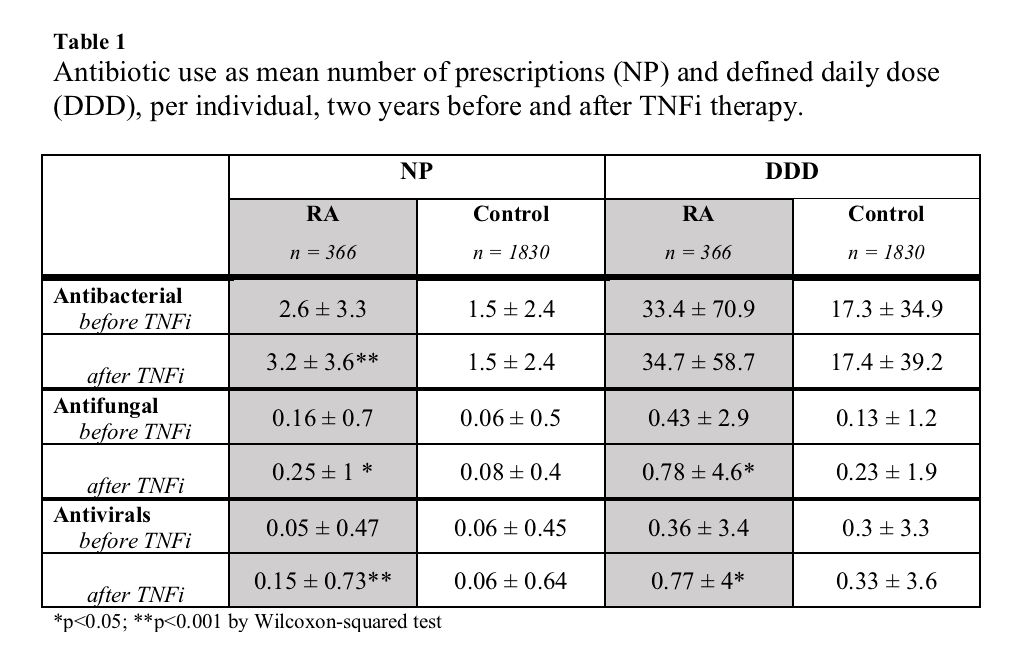
Over 98% of patients with inflammatory arthritides who are treated with biologic DMARDs in Iceland are registered in ICEBIO, a nationwide registry. On February 1st 2016, ICEBIO contained information on 1058 individuals. Information about all biologic-naïve patients with RA was extracted and each patient matched on age, sex and calendar time to five randomly selected individuals. All filled antimicrobial prescriptions in the two years before and after initiation of first TNFi were extracted from the Icelandic Medicine Database (IMD), a registry that includes over 95% of all filled prescriptions in Iceland. Antimicrobial use was quantified using the number of filled prescriptions (NP) and defined daily dose (DDD). NP and DDD are shown as individual means per two years before and after TNFi therapy.
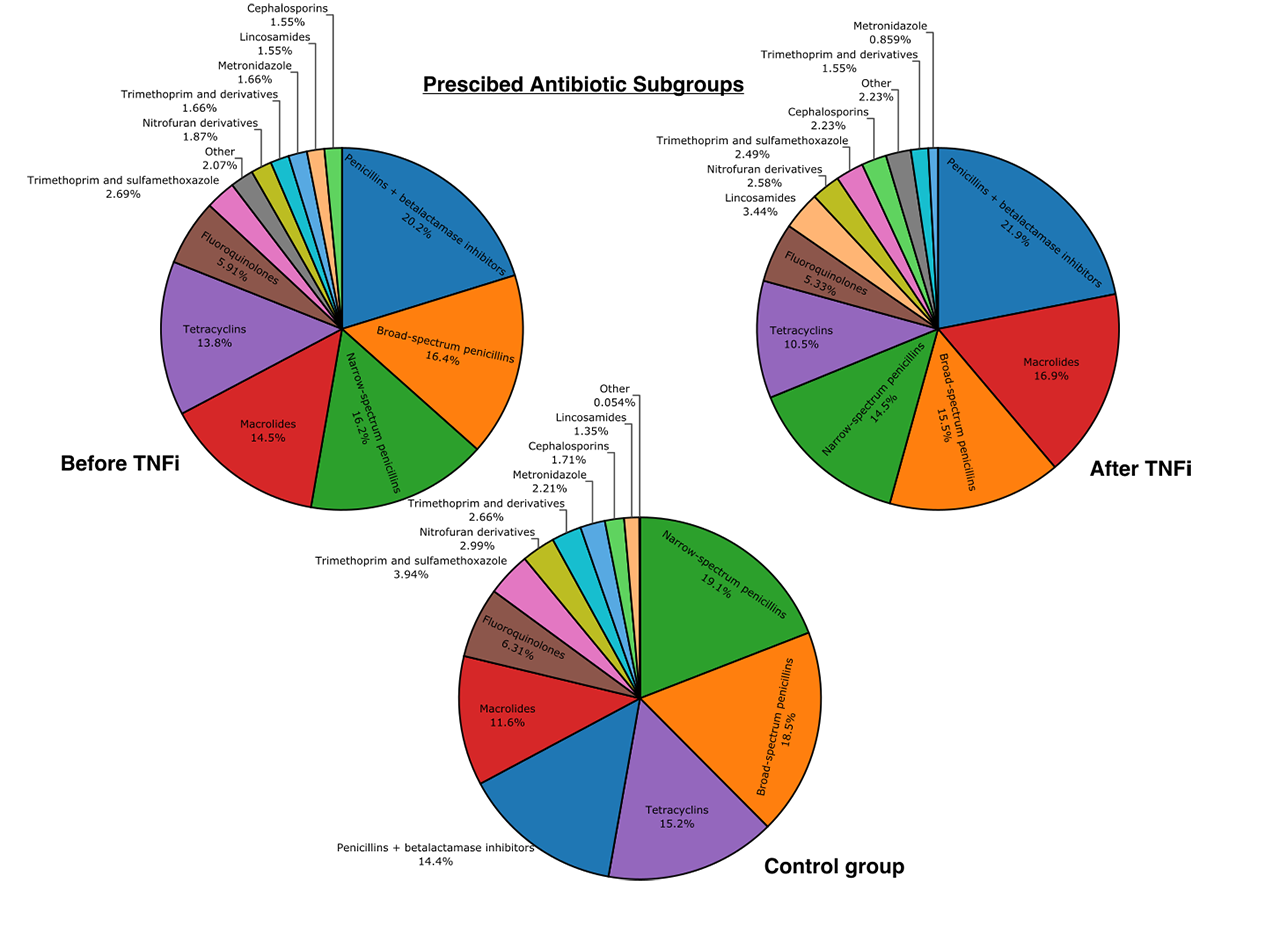
Results: We extracted information on 366 patients with RA and 1833 controls. Patients with RA received nearly twice the number of antimicrobial prescriptions compared to controls before TNFi therapy (2.9 vs 1.6 NP; p< 0.001, figure 1). After initiation of TNFi the mean NP for RA patients increased (2.9 to 3.6; p< 0.001) and further increased over a two-year period (figure 1); antibiotics 2.6 to 3.2 (p< 0.001), antivirals 0.06 to 0.15 (p< 0.001) and antifungals 0.16 to 0.25 (p< 0.05) (table 1). Conversely, DDD of antibiotics was stable (33.4 to 34.7; p >0.1). However, DDD for both antivirals and antifungals increased (p< 0.05). After TNFi initiation, antifungal usage increased predominantly in women (0.4 to 0.84 DDD; p< 0.05) and antivirals in men (0.00 to 0.82 DDD; p< 0.05). No correlation was found between NP and age, BMI or baseline DAS28-CRP. However, a minor positive correlation (r 0.2) was between NP and HAQ score at beginning of TNFi therapy. Patients with HAQ score higher than 2.0 received significantly higher NP after TNFi therapy (3.1 vs 5.7 NP; p< 0.001). No difference was found between smokers and non-smokers (3.1 vs 3.8; p=0.38). Interestingly, mean DDD per prescription decreased after initiation of TNFi (14.5 to 10.2 DDD, p< 0.001). Physicians selection of antibiotics did not appear to change after TNFi treatment (figure 2).
Conclusion: Patients with RA use significantly more antimicrobials two years antedating TNFi treatment compared to controls. TNFi treatment further increases antimicrobial use in patients with RA and usage increased throughout the two-year period. This contrasts the literature regarding hospital admissions due to infections, where admissions frequency peaks the first year after TNFi treatment, but then decreases with TNFi treatment duration1. High HAQ score at the start of TNFi treatment was related to increased antimicrobial usage following TNFi therapy.
Reference:
1) Askling J., et al., Ann Rheum Dis, 2007;66;1339–44.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bjornsson A, Palsson O, Kristjansson M, Gunnarsson P, Grondal G, Gudbjornsson B, Love T. Antimicrobial Use Is High in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Further Increases with First-Line TNFi Therapy – Nationwide Results from Iceland [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antimicrobial-use-is-high-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-further-increases-with-first-line-tnfi-therapy-nationwide-results-from-iceland/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antimicrobial-use-is-high-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-further-increases-with-first-line-tnfi-therapy-nationwide-results-from-iceland/